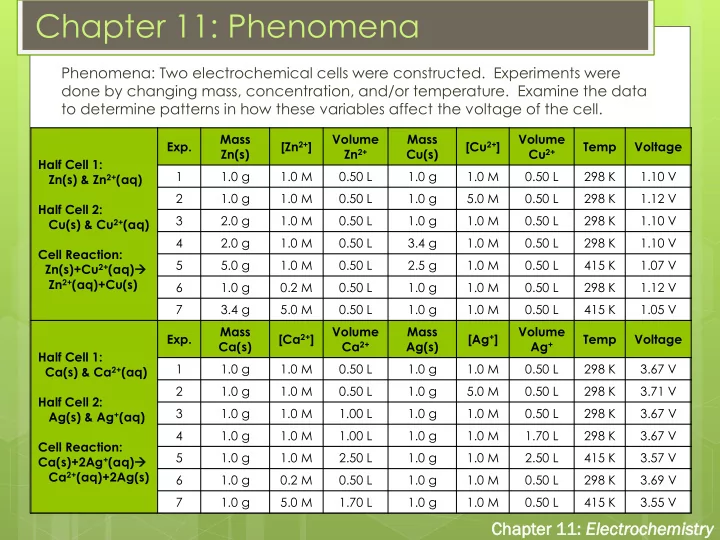

Chapter 11: Phenomena Phenomena: Two electrochemical cells were constructed. Experiments were done by changing mass, concentration, and/or temperature. Examine the data to determine patterns in how these variables affect the voltage of the cell. Mass Volume Mass Volume Exp. [Zn 2+ ] [Cu 2+ ] Temp Voltage Zn(s) Zn 2+ Cu(s) Cu 2+ Half Cell 1: 1 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 298 K 1.10 V Zn(s) & Zn 2+ (aq) 2 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 1.0 g 5.0 M 0.50 L 298 K 1.12 V Half Cell 2: 3 2.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 298 K 1.10 V Cu(s) & Cu 2+ (aq) 4 2.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 3.4 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 298 K 1.10 V Cell Reaction: 5 5.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 2.5 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 415 K 1.07 V Zn(s)+Cu 2+ (aq) Zn 2+ (aq)+Cu(s) 6 1.0 g 0.2 M 0.50 L 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 298 K 1.12 V 7 3.4 g 5.0 M 0.50 L 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 415 K 1.05 V Mass Volume Mass Volume Exp. [Ca 2+ ] [Ag + ] Temp Voltage Ca(s) Ca 2+ Ag(s) Ag + Half Cell 1: 1 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 298 K 3.67 V Ca(s) & Ca 2+ (aq) 2 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 1.0 g 5.0 M 0.50 L 298 K 3.71 V Half Cell 2: 3 1.0 g 1.0 M 1.00 L 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 298 K 3.67 V Ag(s) & Ag + (aq) 4 1.0 g 1.0 M 1.00 L 1.0 g 1.0 M 1.70 L 298 K 3.67 V Cell Reaction: 5 1.0 g 1.0 M 2.50 L 1.0 g 1.0 M 2.50 L 415 K 3.57 V Ca(s)+2Ag + (aq) Ca 2+ (aq)+2Ag(s) 6 1.0 g 0.2 M 0.50 L 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 298 K 3.69 V 7 1.0 g 5.0 M 1.70 L 1.0 g 1.0 M 0.50 L 415 K 3.55 V Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try
Chapter 11 Electrochemistry o Redox Reaction Review Big Idea: Electron transfer in a o Galvanic Cells chemical reaction is o Thermo of both material and Electrochemistry concentration o Nernst Equation specific. If the process o Batteries / Fuel Cells is spontaneous the o Electrolytic Cells transfer of electrons can be used to produce a current and drive electrical devices. 2
Redox Reaction Review Assigning Oxidation Numbers The oxidation number (ON) of an element uncombined with another element is zero: Na(s) ON = 0, and H 2 (g) ON = 0. For monatomic ions, the charge is the ON: Na + ON = +1. The ONs of elements in group 1 equal 1 (ex. Lithium ON = +1) ONs of elements in group 2 equal 2 (ex. Magnesium ON = +2), when the atoms are in a compound. The ON of fluorine is always -1 in compounds. The ON of the other elements in group 7 usually equal -1 when the atoms are in a compound. The ON of oxygen is usually -2 in compounds. Exceptions are fluorine compounds and peroxide (a compound that contains an O-O single bond). Hydrogen's ON is +1 when combined with non metals and -1 when combined with metals. The sum of the ON’s of all the atoms in a species is equal to its total charge. Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 3
Redox Reaction Review Assigning Oxidation Numbers NaCl Element Oxidation Number Reason Na Cl Fe 2 (SO 4 ) 3 Element Oxidation Number Reason SO 4 O S Fe Br 2 Element Oxidation Number Reason Br Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 4
Redox Reaction Review Determining Which Element is Oxidized and Which is Reduced Step 1: Assign oxidation numbers. Step 2: Use oxidation numbers and ‘OIL RIG’ to identify which element is oxidized and which is reduced. Not ote: If the question asks which “ substance is oxidized;” instead of giving the element that is oxidized give the entire compound. Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 5
Redox Reaction Review Oxidizing Agent: A species that removes electrons from a species being oxidized in a redox reaction. Not ote: Oxidizing agent is the species being reduced. Reducing Agent: The species that supplies electrons to a substance being reduced in a redox reaction. Note: Reducing agent is the species being oxidized. Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 6
Redox Reaction Review Balancing Redox Reactions in Acidic Conditions Step 1: Write unbalanced half reactions. Step 2: Balance half reactions except for O and H. Step 3: Balance O by using H 2 O. Step 4: Balance H by using H + . Step 5: Balance electrons in each half reaction. Step 6: Multiply half reactions by an integer so that number of electrons match, then add the reactions together. Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 7
Redox Reaction Review Balancing Redox Reactions in Basic Conditions Step 1: Balance the reaction as if it were in acidic conditions. Step 2: Determine the number of H + in the balanced equation. Step 3: Add the same number OH - as there are H + to BOTH sided of the equation. Step 4: The H + and OH - on one side of the reaction will combine and form H 2 O. Step 5: Simplify your reaction (combine waters) if necessary. Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 8
Galvanic Cell Electrochemical Cell: Device in which an electric current is produced by either a spontaneous reaction or is used to bring about a non spontaneous reaction. Galvanic Cell: An electrochemical cell in which a spontaneous chemical reaction is used to generate an electrical current. Electrode : Metal contacts. Electrolyte : Ionically conducting medium. Salt Bridge : Allows for the flow of ions but prohibits reactions from taking place. Anode: Is where oxidation occurs. Cathode: Is where reduction occurs. Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 9
Galvanic Cell Short Hand Cell Notation The anode is written on the left and cathode on the right. 1) Phase interfaces are separated with a ‘|’ 2) Same phase species are separated by a ‘,’ 3) For same phases, the species that is capable of being the 4) oxidizing agent is written 1 st followed by the species that is capable of being the reducing agent. Example: Fe 3+ (aq) + e - Fe 2+ (aq) Fe 3+ is the oxidizing agent (anode) Fe 3+ (aq), Fe 2+ (aq)|| (cathode) ||Fe 3+ (aq), Fe 2+ (aq) The salt bridge is represented by || 5) Never include water 6) Anode order of phase: solid | gas | liquid | aqueous 7) Cathode order of phase: aqueous | liquid | gas | solid 8) An inert electrode always goes on the outside (usually made 9) up of Pt(s) or C(gr)) Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 10
Galvanic Cell Student Question Write the balanced reaction for the given cell Pt(s)|H 2 (g)|H + (aq)||Co 3+ (aq),Co 2+ (aq)|Pt(s) H 2 (g)+Co 3+ (aq) 2H + (aq)+Co 2+ (aq) a) Pt(s)+H 2 (g)+2Co 3+ (aq) 2H + (aq)+2Co 2+ (aq)+Pt(s) b) 2H + (aq)+Co 2+ (aq) H 2 (g)+Co 3+ (aq) c) H + (aq)+Co 2+ +e - (aq) H 2 (g)+Co 3+ (aq) d) None of the above e) Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 11
Thermo of Electrochemistry Standard Reaction Potentials at 298 K Standard Reaction Potentials at 298 K Half -Reaction E°(V) Half – Reaction E°(V) F 2 + 2e - 2F - Hg 2 Cl 2 + 2e - 2Hg + 2Cl - 2.87 0.27 Ce 4+ + e - Ce 3+ 1.70 AgCl + e- Ag + Cl - 0.22 - + 4H + + 3e - MnO 2 + 2H 2 O 2- + 4H + + 2e - H 2 SO 3 + H 2 O MnO 4 1.68 SO 4 0.20 - + 2H + + 2e - IO 3 - + H 2 O Cu 2+ +e - Cu + IO 4 1.60 0.16 - + 8H + + 5e - Mn 2+ + 4H 2 O 2H + + 2e - H 2 MnO 4 1.51 0.00 Au 3+ + 3e - Au Fe 3+ + 3e - Fe 1.50 -0.04 Pb 2+ + 2e - Pb Cl 2 + 2e - 2Cl - 1.36 -0.13 2- + 14H + + 6e - 2Cr 3+ + 7H 2 O Sn 2+ + 2e Sn Cr 2 O 7 1.33 -0.14 O 2 + 4H + + 4e - 2H 2 O Ni 2+ + 2e - Ni 1.23 -0.23 MnO 2 + 4H + + 2e - Mn 2+ + 2H 2 O PbSO 4 + 2e - Pb + SO 4 1.21 -0.35 2- - + 6H + + 5e - ½I 2 +3H 2 O Cd 2+ +2e - Cd IO 3 1.20 -0.40 Fe 2+ + 2e - Fe Br 2 + 2e - 2Br - 1.09 -0.44 + + 2H + + e - VO 2+ + H 2 O Cr 3+ + e - Cr 2+ VO 2 1.00 -0.50 - + 3e - Au + 4Cl - Cr 3+ + 3e - Cr AuCl 4 0.99 -0.73 - + 4H + + 3e - NO + 2H 2 O Zn 2+ + 2e - Zn NO 3 0.96 -0.76 ClO 2 + e - ClO 2 2H 2 O + 2e - H 2 + 2OH - - 0.95 -0.83 2Hg 2+ + 2e - Hg 2 Mn 2+ + 2e - Mn 0.91 -1.18 2+ Ag + + e - Ag Al 3+ + 3e - Al 0.80 -1.66 2+ + 2e - 2Hg H 2 + 2e - 2H - Hg 2 0.80 -2.23 Fe 3+ + e - Fe 2+ Mg 2+ + 2e - Mg 0.77 -2.37 - + e - MnO 4 La 3+ + 3e - La MnO 4 2- 0.56 -2.37 Na + + e - Na I 2 + 2e - 2I - 0.54 -2.71 Cu + + e - Cu K + +e - K 0.52 -2.92 Cu 2+ + 2e - Cu Li + + e- Li 0.34 -3.05 Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 12
Thermo of Electrochemistry All reaction of referenced to: H + (aq) + 2e - H 2 (g) E˚ = 0 V Things to remember: If you flip a reaction you change the sign of E˚ Exa xampl ple: e: F 2 + 2e - 2F - E˚= 2.87 2F - F 2 + 2e - E˚= -2.87 If you multiply a reaction by a constant DO NOT DO ANYTHING TO E˚ Example: F 2 + 2e - 2F - E˚= 2.87 2F 2 + 4e - 4F - E˚= 2.87 Not ote: The book gives you the following equation: = 𝐹 ° 𝑑𝑏𝑢ℎ𝑝𝑒𝑓 − 𝐹 ° 𝑏𝑜𝑝𝑒𝑓 ° 𝐹 𝑑𝑓𝑚𝑚 DO NOT USE THIS EQUATION IF YOU ARE USING THE FLIPPING METHOD Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 13
Thermo of Electrochemistry Student Question Calculate E° of the following cell Cr(s)|Cr 3+ (aq)||Br - (aq)|Br 2 (l)|Pt(s) Helpful Information: Cr 3+ + 3e - Cr E° = -0.73 V Br 2 + 2e - 2Br - E° = 1.09 V a) 2.55 V b) 1.82 V c) -1.82 V d) -2.55 V e) None of the above Bonus: Determine the balanced reaction for this cell. Chapt pter er 11: Electr troc ochem emis istr try 14
Recommend
More recommend