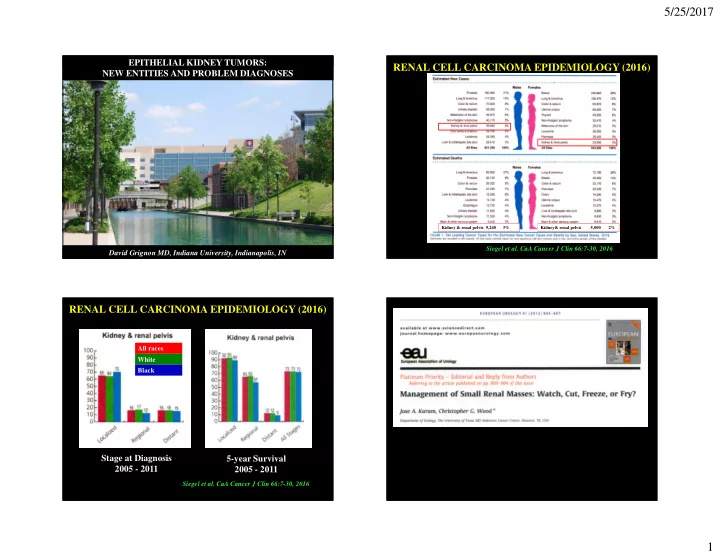

5/25/2017 EPITHELIAL KIDNEY TUMORS: RENAL CELL CARCINOMA EPIDEMIOLOGY (2016) NEW ENTITIES AND PROBLEM DIAGNOSES Kidney & renal pelvis 9,240 3% Kidney& renal pelvis 5,000 2% Siegel et al. CaA Cancer J Clin 66:7-30, 2016 David Grignon MD, Indiana University, Indianapolis, IN RENAL CELL CARCINOMA EPIDEMIOLOGY (2016) All races White Black Stage at Diagnosis 5-year Survival 2005 - 2011 2005 - 2011 Siegel et al. CaA Cancer J Clin 66:7-30, 2016 1
5/25/2017 RENAL CELL CARCINOMA NEEDLE BIOPSY DIAGNOSIS ACTIVE SURVEILLANCE Clear cell RCC Favorable • Clear, NG 1 • Papillary, type 1, NG 1 • Chromophobe Intermediate • Clear, NG 2 • Papillary, type 1, NG 2 • Papillary, NOS Papillary RCC • Oncocytic neoplasm, NOS Unfavorable • Clear, NG 3 & 4 • Papillary, type 1, NG 3 & 4 • Papillary type 2 • Sarcomatoid Halverson, et al. J Urol 189:441-446, 2013 NEEDLE BIOPSY DIAGNOSIS NEEDLE BIOPSY DIAGNOSIS Mucinous tubular and spindle cell RCC Metanephric adenoma Trabecular angiomyolipoma Medullary RCC 2
5/25/2017 WHO 2016 CLASSIFICATION WHO 2016 CLASSIFICATION EPITHELIAL TUMORS EPITHELIAL TUMORS MALIGNANT BENIGN Clear cell RCC Papillary adenoma Multilocular cystic renal neoplasm of low Metanephric malignant potential adenoma Papillary RCC Metanephric Chromophobe RCC adenofibroma Collecting duct Oncocytoma carcinoma Medullary carcinoma Adenoma Chromophobe RCC WHO 2016 CLASSIFICATION WHO 2016 CLASSIFICATION EPITHELIAL TUMORS EPITHELIAL TUMORS MALIGNANT MALIGNANT MiT family translocation Clear cell papillary carcinomas RCC Xp11 and t(6;11) HLRCC syndrome Carcinoma associated with associated RCC neuroblastoma SDH deficiency Mucinous tubular and associated RCC spindle cell ca Unclassified RCC Tubulocystic RCC Acquired cystic disease associated RCC Acquired cystic disease associated RCC Clear cell papillary RCC 3
5/25/2017 Kidney tumors with pink cells WHO 2016 CLASSIFICATION Tumors Not Ready to be Added • Specific hereditary types of RCC – Birtt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome • Oncocytic papillary RCC* • So-called “hybrid” oncocytoma/chromophobe RCC** • ALK-translocation associated • Thyroid-like follicular carcinoma • Others * left in Type 2 papillary RCC ** include in unclassified RCC category RENAL ONCOCYTOMA DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS ONCOCYTOMA CHROMOPHOBE RCC CLEAR CELL RCC UNCLASSIFIED RCC PAPILLARY RCC COLLECTING DUCT CA TRANSLOCATION CARCINOMAS 5% of kidney tumors in adults; wide age range; more common in females (2-3:1); majority are SDH ASSOCIATED RCC asymptomatic; variable cytogenetics: -1 and –Y most often reported EPITHELIOID ANGIOMYOLIPOMA 4
5/25/2017 RENAL ONCOCYTOMA RENAL ONCOCYTOMA CYSTIC CHANGE PAPILLARY ARCHITECTURE 5
5/25/2017 CLEAR CELL CHANGE NUCLEAR PLEOMORPHISM PERINEPHRIC FAT INVASION RENAL VEIN INVASION 6
5/25/2017 ENTRAPPED TUBULES HALE’S COLLOIDAL IRON CK7 ONCOCYTOMA – SPECIAL STUDIES ONCOCYTOMA – SPECIAL STUDIES CK7 Vimentin CK7 Vimentin CD117 Hale colloidal iron CD117 Hale colloidal iron 7
5/25/2017 ONCOCYTOMA - IHC RENAL ONCOCYTOMA CK7 VIM Cytokeratin 7 ONCOCYTOMA – NEEDLE BIOPSY: OUR CRITERIA ONCOCYTOMA - LIKE Typical morphology Vimentin CD10 Cytokeratin 7 Vimentin Hale’s colloidal iron 8
5/25/2017 ONCOCYTOMA - LIKE CLEAR CELL RENAL CELL CARCINOMA CA IX CD10 CK7 CK7 CD117 CD10 PAPILLARY RENAL CELL CARCINOMA CHROMOPHOBE CARCINOMA 5% of kidney tumors, adults, M=F, excellent prognosis (>90% survival); distinctive cytogenetic profile with -1, -2, -6, -13, -17, -21 CK7 AMACR/p504s 9
5/25/2017 CHROMOPHOBE CARCINOMA CHROMOPHOBE CARCINOMA CHROMOPHOBE CARCINOMA CHROMOPHOBE CARCINOMA 10
5/25/2017 HALE’S COLLOIDAL IRON CHROMOPHOBE CARCINOMA CHROMOPHOBE CARCINOMA CHROMOPHOBE CARCINOMA IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY CK7 Vimentin CD10 Hale’s CK7 VIMENTIN CD10 11
5/25/2017 RENAL ONCOCYTOSIS “HYBRID” TUMORS • RENAL ONCOCYTOSIS – Bilateral, multiple tumors – Oncocytoma, chromophobe RCC and hybrid tumors • BIRT HOGG DUBE SYNDROME – Skin tumors (trichofolliculomas, achrocordons), multiple renal tumors and pneumothoraces – Oncocytoma, chromophobe and clear cell RCC, and hybrid tumors – Autosomal dominant, 17p11.2 (folliculin) • DE NOVO – 4/425 cases in recent series RENAL TUMOR OF ONCOCYTOSIS RENAL ONCOCYTOSIS Hale’s colloidal iron 12
5/25/2017 BIRT HOGG DUBE SYNDROME BIRT HOGG DUBE SYNDROME 27 year old female with multiple, bilateral kidney tumors Left - tumor #1 Left – tumor #2 Right - tumor #3 ACQUIRED CYSTIC DISEASE ASSOCIATED ACQUIRED CYSTIC KIDNEY DISEASE RENAL CELL CARCINOMA • Examined 66 kidneys from 52 patients • To date have occurred exclusively in patients with acquired cystic disease • Identified a variety of tumor types: • Increase in frequency with increased – ACD associated carcinoma 33% length of time on dialysis – Clear cell papillary carcinoma 21% • Occur at any age – Papillary carcinoma 16% – Chromophobe carcinoma 16% • No specific genetic mutations recognized – Clear cell carcinoma 14% • Limited prognostic information but • Considered the first two potentially metastases reported in 8% to 22^ of unique tumor types patients Tickoo et al, Am J Surg Pathol 30:141, 2006 13
5/25/2017 AcqCKD ASSOCIATED CARCINOMA AcqCKD ASSOCIATED CARCINOMA AcqCKD ASSOCIATED CARCINOMA AcqCKD ASSOCIATED CARCINOMA Calcium oxalate crystals Calcium oxalate crystals 14
5/25/2017 AcqCKD ASSOCIATED CARCINOMA CLEAR CELL PAPILLARY RCC • 3 – 4% of resected kidney tumors • Wide age range; slight male predominance • 95% T1a (< 4 cm) • Not genetically related to clear cell or papillary RCC • Distinctive IHC profile • Excellent prognosis CLEAR CELL PAPILLARY RCC CLEAR CELL PAPILLARY RCC 15
5/25/2017 CLEAR CELL PAPILLARY RCC Clear cell Papillary RCC CLEAR CELL PAPILLARY RCC Clear cell Papillary RCC 16
5/25/2017 CLEAR CELL PAPILLARY RCC CLEAR CELL PAPILLARY RCC CLEAR CELL PAPILLARY RCC CA IX CK7 CD10 AMACR CAIX CD 10 CK 7 17
5/25/2017 CLEAR CELL PAPILLARY RCC EPITHELIAL KIDNEY TUMORS CLASSIFICATION Cancer Genet Cytogen CA IX CK7 21:165, 1986 EPITHELIAL KIDNEY TUMORS X:1 TRANSLOCATION ASSOCIATED CARCINOMA: CLASSIFICATION FREQUENCY BY AGE 80.0 70.0 60.0 50.0 40.0 30.0 20.0 10.0 0.0 0 - 10 11 - 20 21 - 30 31 - 40 > 40 Klatte et al. Am J Clin Pathol 137:761, 2012 18
5/25/2017 TRANSLOCATION ASSOCIATED CARCINOMA X:1 TRANSLOCATION CARCINOMA TRANSLOCATION ASSOCIATED CARCINOMA X:1 TRANSLOCATION ASSOCIATED CARCINOMAS TFE3 19
5/25/2017 X:1 TRANSLOCATION CARCINOMA TFE3 X:1 TRANSLOCATION CARCINOMA X:1 TRANSLOCATION RCC Type IV collagen Cathepsin K TFE3 20
5/25/2017 X:1 TRANSLOCATION CARCINOMA X:1 TRANSLOCATION RCC CK AE1/AE3 TFE3 TFE3 CK AE1/AE3 Xp11TRANSLOCATION 6:11 TRANSLOCATION CARCINOMA ASSOCIATED CARCINOMAS • Because of limited number of published cases prognostic features are unclear Prolonged survival in young patients with recurrence/metastases (4/8 with Xp11 translocation RCC) Komai et al, Urology 77:842, 2011 54 cases median age 36 50 TFE3 4 TFEB Type IV collagen Malouf et al, J Urol 185:24, 2011 21
5/25/2017 6:11 TRANSLOCATION CARCINOMA Cathepsin K Melan A HMB45 PAX 8 SDH ASSOCIATED RCC • Patients with mutation of SDHB >> SDHC (rarely SDHA or SDHD) Translocation associated renal • Paraganglioma and GIST • Wide age range (14 – 76 yrs; median 35) cell carcinoma is in the • Multifocal and/or bilateral in 30% differential diagnosis of ALL • Eosinophilic cells in nests and tubules; unclassifiable renal cell cytoplasmic inclusions; entrapped tubules; mast cells carcinomas • Most low grade but metastases develop in about 10% of patients Gill et al. Am J Surg Pathol 38:1588, 2014 Williamson et al. Mod Pathol 28:80, 2015 22
5/25/2017 SDH ASSOCIATED RENAL CELL CARCINOMA SDH ASSOCIATED RENAL CELL CARCINOMA CK AE1/AE3 SDHB HLRCC SYNDROME ASSOCIATED RCC HLRCC SYNDROME • Patients with mutation of fumarate hydratase gene (1q42.3-q43) • Cutaneous and uterine leiomyomas • Wide age range (17 – 87 years) • More common in females • Complex solid and papillary histology with macro orangophilic nucleoli and perinucleolar halo • Aggressive tumors with up to 50% with metastasis at diagnosis Merino et al. Am J Surg Pathol 31:1578, 2007 Grubb et al. J Urol 177:2074, 2007 23
5/25/2017 HLRCC SYNDROME ASSOCIATED RCC THYROID-LIKE FOLLICULAR CARCINOMA OF THE KIDNEY UNCLASSIFIED RENAL CELL CARCINOMA ONCOCYTIC PAPILLARY RCC 24
5/25/2017 Indianapolis, IN 25
Recommend
More recommend