
RNA and Gene Expression
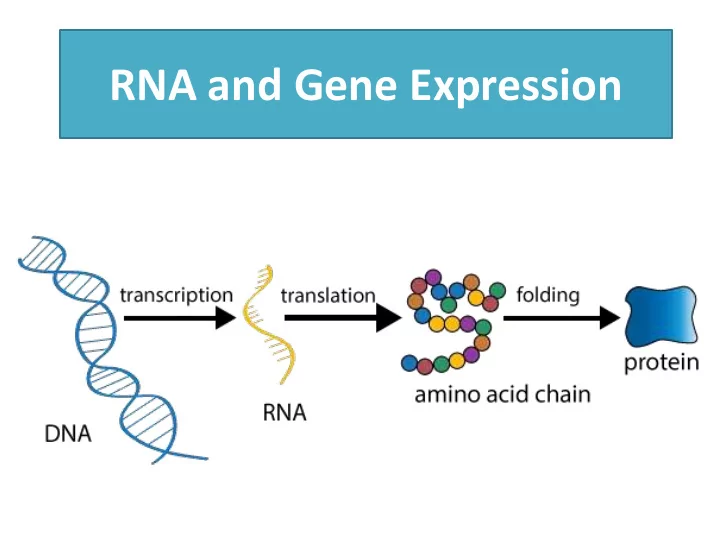
How does DNA determine our traits? • By directing the synthesis of proteins • Proteins represent functional genes • Molecular flow of information is: DNA RNA Protein
Gene Expression 1. Transcription – Genetic information is transferred from DNA to mRNA 2. RNA Processing – enzyme-regulated modifications to the mRNA transcript (eukaryotes only) 3. Translation – mRNA information is decoded to synthesize proteins
• Histone acetylation ( unpack DNA )
RNA (Ribonucleic acid) • A nucleic acid composed of ribose sugars, phosphates, and nitrogenous bases • How does RNA differ from DNA?
DNA RNA • Double stranded • Single stranded • Deoxyribose sugar • Ribose sugar • Adenine, Cytosine, • Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine, and Thymine Guanine and Uracil • Nucleus only • Nucleus, cytoplasm, and ribosomes
What molecules are required for gene expression?
Gene Expression Molecules 1. mRNA 2. tRNA 3. rRNA 4. amino acids 5. ribosomes
mRNA (messenger) • linear RNA that transfers genetic information from DNA to ribosomes
tRNA (transfer) • RNA (~80 nucleotides in length) twisted in hairpin shape • supplies the amino acids to ribosomes for translation
rRNA (ribosomal) • globular RNA that composes ribosomes, forms the peptide bond between amino acids during protein synthesis
Amino Acids • monomers of proteins • linked together to form proteins during translation
Ribosomes • site of translation (third step of gene expression)
Gene Expression Animation Overview of Gene Expression
Eukaryotic Gene Structure • Promoter • Exon • Intron • Terminator
Gene Expression 1. Transcription 2. RNA Processing (eukaryotes only) 3. Translation
Transcription and RNA Processing
Transcription
Transcription Animations Transcription – Virtual Cell HHMI Transcription
RNA Processing • Enzyme-mediated modifications to the mRNA transcript 1. Addition of a GTP cap to 5’ end (protection, bind to ribosome) 2. Addition of a poly- A tail to 3’ end (protection) 3. Excision (removal) of introns: non-coding segments of DNA ( RNA splicing ) • mRNA then exits the nucleus
RNA Processing
Translation (Gene to Protein) • Genetic information from a sequence of nucleotides in a gene is used to produce a sequence of amino acids in a protein • Occurs on ribosomes in the cytoplasm
Translation • Initiation • Elongation • Termination
Translation Terminology • Codon • Start codon • Ribosome • Stop codon • Anti-codon • mRNA • tRNA • rRNA
Translation- Virtual Cell (Animation)
Genetic Code
Translation Animation HHMI Translation Animation
RNA interference (RNAi) • Regulates gene expression at the level of mRNA transcription • Example of an RNAi molecule is microRNA ( miRNA ) – Degrades the target mRNA OR – Blocks translation of the mRNA
Phenotypes Are Determined Through Protein Activities • Post translation protein modifications determine the function of proteins: – Transport proteins – Catalytic proteins – Structural proteins
Recommend
More recommend