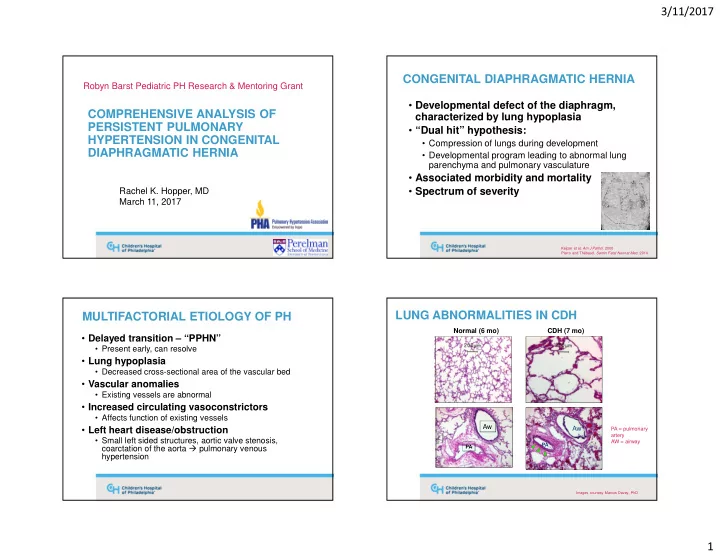

3/11/2017 CONGENITAL DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA Robyn Barst Pediatric PH Research & Mentoring Grant • Developmental defect of the diaphragm, COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF characterized by lung hypoplasia PERSISTENT PULMONARY • “Dual hit” hypothesis: HYPERTENSION IN CONGENITAL • Compression of lungs during development DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA • Developmental program leading to abnormal lung parenchyma and pulmonary vasculature • Associated morbidity and mortality Rachel K. Hopper, MD • Spectrum of severity March 11, 2017 Keijzer et al, Am J Pathol . 2000 Pierro and Thébaud. Semin Fetal Neonat Med . 2014 LUNG ABNORMALITIES IN CDH MULTIFACTORIAL ETIOLOGY OF PH Normal (6 mo) CDH (7 mo) • Delayed transition – “PPHN” • Present early, can resolve • Lung hypoplasia • Decreased cross-sectional area of the vascular bed • Vascular anomalies • Existing vessels are abnormal • Increased circulating vasoconstrictors • Affects function of existing vessels Aw • Left heart disease/obstruction Aw PA = pulmonary artery • Small left sided structures, aortic valve stenosis, AW = airway PA coarctation of the aorta � pulmonary venous PA hypertension Images courtesy Marcus Davey, PhD 1
3/11/2017 SEVERE PERSISTENT PH STUDY AIMS CDH (7 mo) CDH (3 mo) 1) Determine the prevalence and clinical risk factors for persistent PH in CDH • Retrospective cohort study of 322 patients with CDH at CHOP from 2005-2015 • Assess PH over time by blinded review of serial echocardiograms in first year of life • Determine clinical risk factors for persistent PH using existing clinical research database 2) Determine whether rare genetic variants increase the risk of PH in CDH • A subset of patients with severe PH • Increased muscularization, intimal hyperplasia, • Whole exome sequencing (WES) to assess for genetic variants associated with PH at 6 months of age similar to PAH • Mechanisms and risk factors unclear Images courtesy Marcus Davey, PhD, Kudakwashe Chikwava, MBBCh. HYPOTHESIS PRELIMINARY DATA • N=265 CDH infants (322 total) from 2005-2015 • PH persists in a significant subset of infants • High incidence of PH early, resolves in most with CDH • Nearly 30% continue to have at least moderate PH, defined by echo or PH treatment, at 6 months of age • Persistent PH in CDH is multifactorial in Probability of PH by age Probability of PH by age etiology Probability of PH severity by Age at ECHO 1 • Clinical factors (prenatal indices, postnatal insults) Probability of PH severity .8 • Genetic variants (PAH genes?) .6 • Understanding these risk factors is necessary to .4 improve clinical prediction and treatment .2 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 Age at Echo (days) 7 2
3/11/2017 PRELIMINARY DATA GENETIC ANALYSIS • Intrathoracic liver position associated with • Collaboration with CHOP Center for Applied persistent PH Genomics • Defect side, fetal lung volumes, LHR not associated • Whole exome sequencing (WES) of 24 patients • Plan to assess additional clinical factors with CDH and persistent PH • Preliminary analysis identified 23 potential pathogenic variants enriched in our population • Plan for additional sequencing for validation and compare to CDH without PH PRELIMINARY WES DATA THANK YOU • Pulmonary Hypertension Association • Dr. Robyn Barst • Mentors and collaborators: • Brian Hanna, MDCM, PhD • Steven Kawut, MD, MS • Hakon Hakonarson, MD, PhD • Holly Hedrick, MD 3
Recommend
More recommend