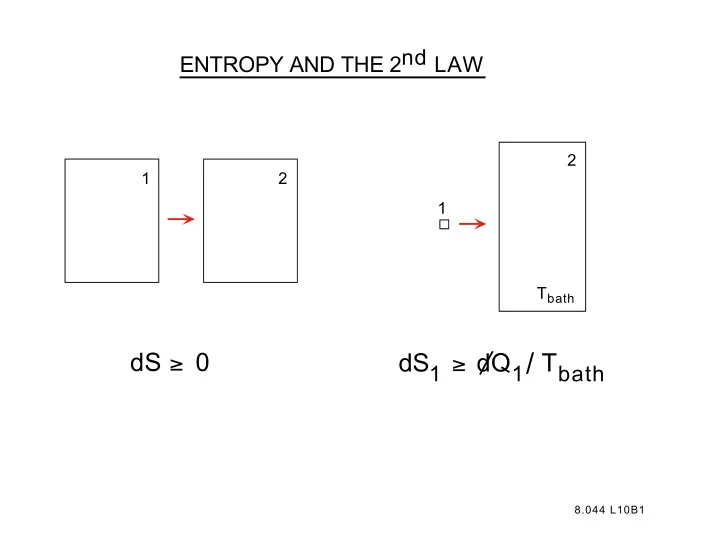

ENTROPY AND THE 2nd LAW 2 1 2 1 T bath dS 1 ≥ dQ 1 / T bath dS ≥ 0 8.044 L10B1
S as a State Function Note: adiabatic ( ≡ d /Q = 0) ⇒ constant S if the change is quasistatic. This is the origin of the sub- script S on the adiabatic compressibility. 1 ∂V 1 ∂V κ T ≡ − κ S ≡ − V ∂P V ∂P T S 8.044 L1 0 B2
Example A Hydrostatic System ∂S ∂S dS = dT + by expansion dV ∂T ∂V V T 1 P = dU + dV from dU = TdS − PdV T T 1 ∂U 1 ∂U = dT + + P dV T ∂T T ∂V V T by expansion of U But the cross derivatives of S must be equal. 8.044 L1 0 B3
1 ∂ 2 U ∂ 1 ∂U = ∂V T ∂T T ∂V ∂T V T 1 ∂ 2 U 1 1 1 ∂P ∂ ∂U ∂U + P = − + P + + T 2 ∂T T ∂V ∂V T ∂V ∂T T ∂T T T V V Equating these two expressions gives ∂U ∂P + P = T ∂V ∂T T V ∂U ∂P = T − P ∂V ∂T T V New Information! Does not contain S ! 8.044 L1 0 B4
CONSEQUENCES a) γ ∂U ∂U /Q = dU + d PdV = dT + + P dV ∂T ∂V V T ' V. ' V. C V ∂P T ∂T V d /Q ∂P ∂V ≡ C P = C V + T dT ∂T ∂T V P P ' V. αV 1 ∂V 1 ∂V Use α ≡ and κ T ≡ − . V ∂T V ∂P P T 8.044 L1 0 B5
∂V ( − 1) ∂P − 1 α ∂T P = = = ∂T ∂V ∂V ∂T κ T V ∂V ∂P ∂P P T T Tα 2 V Tα 2 V α C P − C V = T αV = → γ − 1 = κ T κ T κ T C V For an ideal gas PV = NkT ⇒ α = 1 /T and κ T = 1 /P . Thus V/T C P − C V = = Nk 1 /P This holds for polyatomic as well as monatomic gases. 8.044 L1 0 B6
CONSEQUENCES b) Ideal Gas: C V NkT ∂U Nk P = = T − P = P − P = 0 V ∂V V T ∂U ∂U dU = dT + dV = C V dT ∂T ∂V V T ' V. ' V. 0 C V T � C V ( T � , V ) dT � + constant U = 0 ( ∂U/∂V ) T = 0 for all T � C V is not f ( V ); C V = C V ( T ). 8.044 L1 0 B7
CONSEQUENCES c) Ideal Gas: S ∂S ∂S dS = dT + dV ∂T ∂V V T d /Q ∂S /Q = TdS d ≡ C V = T dT ∂T V V dU P dU = TdS − PdV ⇒ dS = + dV T T ∂S 1 ∂U P = + . ∂V T ∂V T T T -1L - 1L Nk/V 0 8.044 L1 0 B8
C V ( T ) Nk dS = dT + dV T V T C V ( T � ) V dT � + S ( T, V ) = Nk ln( ) + S ( T 0 , V 0 ) T 0 T � V 0 For a monatomic gas C V = (3 / 2) Nk . T V S ( T, V ) − S ( T 0 , V 0 ) = (3 / 2) Nk ln( ) + Nk ln( ) T 0 V 0 3 / 2 V T = Nk ln V 0 T 0 8.044 L1 0 B9
V T 3 / 2 V 2 / 3 T isentropic (adiabatic) ⇒ are constant V 5 / 3 P 8.044 L1 0 B10
Maxwell Relations ∂E ∂E dE ( S, V ) = dS + dV expansion ∂S ∂V V S 1 st and 2 nd laws = TdS − PdV ∂T ∂P = − ⇒ ∂V ∂S S V 8.044 L1 0 B1 1
∂T ∂ F dE ( S, L ) = TdS + = F dL ⇒ ∂L S ∂S L ∂T ∂H dE ( S, M ) = TdS + = HdM ⇒ ∂M ∂S S M Observe: d ( TS ) = TdS + SdT d ( PV ) = PdV + V dP 8.044 L1 0 B 1 2
F ≡ E − TS Helmholtz Free Energy ∂S ∂P dF = − SdT − PdV = ⇒ ∂V ∂T T V H ≡ E + PV Enthalpy ∂T ∂V dH = TdS + V dP = ⇒ ∂P ∂S S P 8.044 L1 0 B 1 3
G ≡ E + PV − TS Gibbs Free Energy ∂S ∂V dG = − SdT + V dP ⇒ = − ∂P ∂T T P E , F , H and G are called ”thermodynamic potentials”. 8.044 L1 0 B 1 4
The Magic Square Mnemonic x -V E F dE = TdS + Xdx S -T ∂S ∂V ( − 1) = ( − 1)( − 1) ∂P ∂T ' V. T P H P G (+1) X 8.044 L1 0 B 1 5
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 8.044 Statistical Physics I Spring 2013 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
Recommend
More recommend