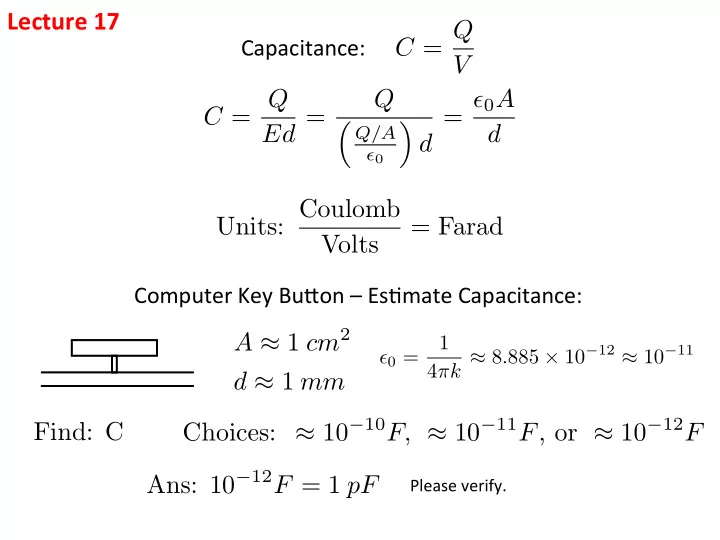

Lecture ¡17 ¡ C = Q Capacitance: ¡ V C = Q Q = ✏ 0 A Ed = ⇣ ⌘ d Q/A d ✏ 0 Units: Coulomb = Farad Volts Computer ¡Key ¡Bu2on ¡– ¡Es6mate ¡Capacitance: ¡ A ≈ 1 cm 2 1 4 ⇡ k ≈ 8 . 885 × 10 − 12 ≈ 10 − 11 ✏ 0 = d ≈ 1 mm Choices: ≈ 10 − 10 F, ≈ 10 − 11 F , or ≈ 10 − 12 F Find: C Ans: 10 − 12 F = 1 pF Please ¡verify. ¡
Energy ¡stored ¡in ¡a ¡capacitor, ¡Q, ¡A, ¡D ¡ Revisit: ¡ U = F ext d = QE 1 plate d Q ✓ Q/A ◆ = Q d 2 ✏ 0 = Q 2 1 2 · ✏ 0 A d U = Q 2 2 C
Fig(clicker) ¡17-‑1 ¡ Lec16-2 Attraction between two plates fig16.2a Given: a parallel plate system with plate charge Q and area A . Within the gap, E gap = ( Q / A ) / ✏ 0 What is the electric force that the bottom plate exerts on the top plate? Choice F 1 QE gap 2 0 . 5 QE gap Hint: In general, the force on exerted on q by a field E is given by “ F = qE ”. Here, “ E ” is the field due to all source charges except q , since self-force (i.e. q on q) is 0.
Fig(clicker) ¡17-‑1 ¡cont. ¡ E = Q/A , Q = ✏ 0 EA ✏ 0 1 ∴ U = Q 2 2 C = ( ✏ 0 EA ) 2 d ⇣ ✏ 0 2 E 2 ⌘ ✏ 0 A = ✏ 0 A = ( Ad ) · 2 d Ad = ✏ 0 E 2 u = U 2 When ¡there ¡is ¡E ¡there ¡is ¡electric ¡energy ¡
Dielectric ¡Mediums ¡ For ¡fixed ¡plate ¡charge ¡Q ¡ Q Q E 0 = E E E' κ Microscopic ¡Picture: ¡ Examples ¡of ¡κ ¡ Q κ ¡ Vacuum ¡ 1 ¡ Air ¡ 1.0006 ¡ E pol Plas6c ¡ 5 ¡ Water ¡ 80 ¡ Semi-‑conductor ¡ 300 ¡ Conductor ¡ infinity ¡ E 0 = E − E pol = E κ
Dielectric ¡Mediums ¡con0nued... ¡ E 0 = E − E pol = E κ Q/A − Q pol /A = Q/A Q − Q pol = Q , ✏ 0 ✏ 0 ✏ 0 � 1 − 1 1 Q pol = Q κ � 1 − 1 2 ¡limits: ¡ vacuum k = 1 ⇒ Q pol = Q = 0 1 � 1 − 1 metal k = ∞ ⇒ Q pol = Q = Q ∞ E 0 = E κ , V 0 = V General ¡κ ¡and ¡Q ¡fixed: ¡ 1 < κ < ∞ κ U = Q 2 2 C , U 0 = Q 2 C = Q V , C 0 = Q 2 C 0 U 0 = U V 0 = κ C, κ
Fig(clicker) ¡17.2 ¡ Lec16-5 Capacitance in the presence of a dielectric medium The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor in free space is given by C = Q / V = ( Q ) / ( ( Q / A ) d ) = ✏ 0 A d , where V is the potential di ff erence ✏ 0 across the gap. When the gap is filled with a dielectric medium of dielectric constant , the electric field is reduced from the free space field E to E 0 = E / . Determine V 0 and C 0 — the potential di ff erence and capacitance in the presence of the dielectric. Choice V’ C’ 1 V / C 2 V C 3 V / C / 4 C / V
Fig(clicker) ¡17.3 ¡ Lec16-6 Energy stored in a capacitor filled with a dielectric medium Given: a parallel plate capacitor with plate area A and gap width d . Determine the energy stored in the capacitor for a plate charge Q when there is a dielectric within the gap with dielectric constant κ . Hint: From Lecture 16-2, the energy stored in the capacitor in the absence of a dielectric is: 2 V = Q 2 d = Q ⇥ 1 ⇤ 2 C , U = Fd = 2 QE gap where V = Ed and V = Q / C were used. Also C 0 = κ C . Choice U’ 1 κ U U 2 U / κ 3
Hint ¡on ¡HW17-‑3 ¡: ¡005 ¡ #1 #2 Find: V 1 f q 1 = Q q 2 = 0 V 1 i V 1 i κ Hint: ¡ Q 0 /A − Q 0 Q 0 V 1 f ✏ 0 = = Q 0 + Q 00 Q/A V 1 i Q 0 Q 00 ✏ 0 V 0 V 1 f 1 2 f = 1 + Q 00 Q 0
Find: V at 0 V 0 = V shell 1 + V shell 2 + V shell 3 0 0 0 Where ¡charges ¡are ¡all ¡at ¡the ¡ surface ¡of ¡the ¡three ¡shells ¡ q 0 q 00 with charges: q 1 , 2 , 2 radii: R 1 , R 2 , R 3
Preview ¡of ¡Ch. ¡18: ¡Magne6c ¡Field ¡due ¡to ¡a ¡long ¡wire ¡ ~ B I ∆ ~ B = µ 0 l × ˆ r ∆ ~ r 2 4 ⇡ I ∆ l
Recommend
More recommend