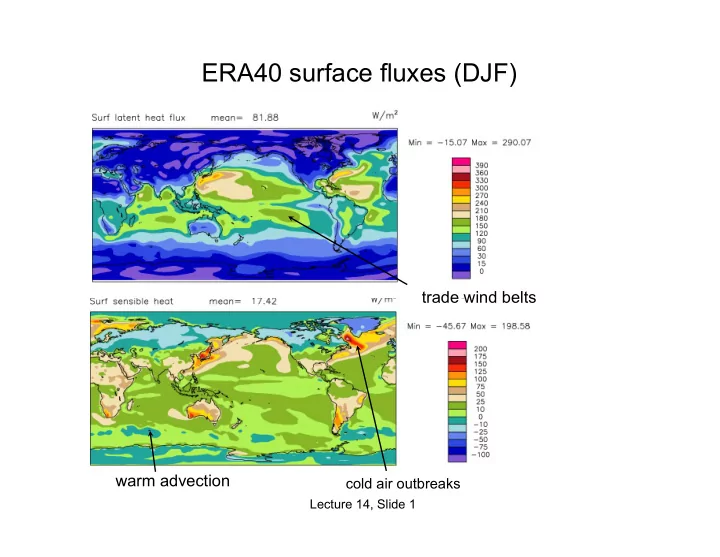
ERA40 surface fluxes (DJF) trade wind belts warm advection cold - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
ERA40 surface fluxes (DJF) trade wind belts warm advection cold air outbreaks Lecture 14, Slide 1 Cloud-topped BL processes Siems et al. 1993 Lecture 14, Slide 2 Some marine boundary-layer cloud types WMO cloud classification:
ERA40 surface fluxes (DJF) trade wind belts warm advection cold air outbreaks Lecture 14, Slide 1
Cloud-topped BL processes Siems et al. 1993 Lecture 14, Slide 2
Some marine boundary-layer cloud types WMO cloud classification: http://www.srh.noaa.gov/jetstream/synoptic/clouds_max.htm#max Stratus (St) Fractostratus Stratocumulus (Sc) Cu under Sc Cumulus (Cu) Cumulonimbus Lecture 14, Slide 3 ARM Image Library
Marine boundary layer clouds from space June 9, 1994 GOES-West Stratus Stratocumulus Shallow cumulus Deep convection Lecture 14, Slide 4
Observations over the oceans • Transition from Sc - shallow Cu - deep Cu as temperature of sea-surface rises compared to that of mid-troposphere. JJA St Sc Cu Cb MBL Lecture 1, Slide 5
‘stratus’ = stratus + stratocumulus + fog Lecture 14, Slide 6
Boundary-layer cloud amount and cloud radiative effect Low cloud CRE = change in net amount (shortwave+longwave) (%) radiation into TOA due to clouds. correlated with … BL clouds reflect sunlight but are too warm to much affect Net CRE outgoing longwave radiation, [W m -2 ] producing a negative SWCRE and little LWCRE, for negative net CRE. • Marine boundary-layer cloud is the most radiatively important cloud type for the current climate. MBL Lecture 1, Slide 7
Warren surface cloud climatology • http://www.atmos.washington.edu/CloudMap advection from • 45 years of routine ship observations warm to much colder SST advection from warm land to cold SST N of Gulf Stream, Kuroshio Coasts Cold tongue MBL Lecture 1, Slide 8 Norris et al. (1998, J Climate )
Cold-ocean MBL cloud types Weak air-sea Deep storm systems temperature differences Norris et al. (1998, J Climate ) MBL Lecture 1, Slide 9
Cool-ocean MBL cloud types Cold advection, cool SST Cold advection, medium SST Cold air outbreaks MBL Lecture 1, Slide 10
Lecture 14, Slide 11
Cumulus-topped MBLs Norris et al. (1998, J Climate ) Over warm oceans, Cu-topped MBLs > 70% of time. MBL Lecture 1, Slide 12
Subtropical PBL soundings LTS Bretherton 1997, after Albrecht et al. 1995 • Sc and St clouds favored by strong, low inversions, which go with large lower tropospheric stability. Lecture 14, Slide 13
Measures of lower-tropospheric stratification Lower tropospheric stability (Klein&Hartmann 1993) LTS = θ 700 - θ 1000 Estimated Inversion Strength (Wood&Breth 2006) EIS = LTS – Γ ma,850 ( z 700 – z LCL ) WB06 WB06 Lecture 14, Slide 14
EIS correlated to low cloud everywhere, LTS correlated to low cloud in low latitudes Lower tropospheric stability correlated with low-latitude marine low cloud (Klein and Hartmann 1993) EIS also captures midlat BL cloud underlying a cooler free troposphere: EIS is a more ‘ temperature- invariant ’ predictor of low cloud response to stratification change.
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.