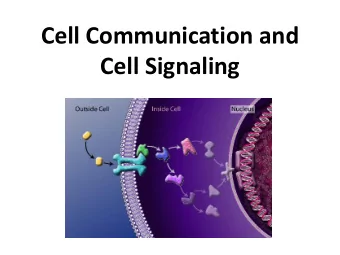
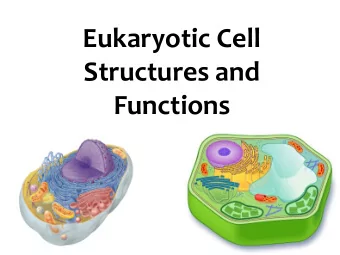
Cell Structure Lecture 04 1 Objectives At the end of this series - PDF document
09 Feb 20 Cell Structure Lecture 04 1 Objectives At the end of this series of lectures you should be able to: Define terms. Explain cell theory. Describe the relative sizes of objects in biology. Explain why most cells
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Cell Structure Lecture 04 1 Objectives At the end of this series of lectures you should be able to: Define terms. Explain cell theory. Describe the relative sizes of objects in biology. Explain why most cells are small. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Describe the structure and function of the parts of typical plant and animal cells. Discuss the theory of endosymbiosis. 2 1
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Relative Sizes 1 meter (m) 1 centimeter = 0.01 m 1 millimeter = 0.001 m or 10 ‐ 3 m 1 micrometer = 0.000001 m or 10 ‐ 6 m 1 nanometer = 0.000000001 m 10 ‐ 9 m 3 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 4 2
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 http://htwins.net/scale2/ 5 Cell Theory All organisms are made up of cells. Cells are the smallest units of life Cells come only from preexisting cells. Cells do things. 6 3
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Most Cells are Small Have to be large enough to contain all of the materials that they need to do their job. Need to be relatively small to have a large surface to volume ratio. Efficient transfer of materials into and out of the cell. 7 Figure 4.7 Jeffrey Mahr, CC BY 3.0, http://cnx.org/contents/263caa9c ‐ 31e1 ‐ 4c8a ‐ 80ea ‐ afdc47b43228@2 8 4
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Nucleoid – no membrane Membrane bound nucleus Small Large No internal Internal compartments compartments DNA linear DNA circular Membranous organelles Protozoa, Fungi, Plants and Bacteria and Archea Animals. 9 Eukaryotic The structures and organelles perform four basic functions. Genetic control of the cell Nucleus and ribosomes Manufacture, distribution, and breakdown of molecules Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and peroxisomes Energy processing Mitochondria and chloroplasts Structural support, movement, and communication Cytoskeleton, plasma membrane, and cell wall 10 5
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Plant vs. Animal Cells Plant Cells Animal Cells Cell wall Lysosomes Chloroplasts Centrioles Vacuole 11 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 12 6
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 13 Plasma Membrane Function Keeps the cell intact. Regulates what enters and exits the cell. Is semipermeable – some things can enter the cell others are blocked. Made of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins (Fluid mosaic model) 14 7
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 15 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 16 8
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Cytoplasm The portion of the cell between the nucleus and the plasma membrane A semifluid medium made mostly of water and dissolved or suspended molecules. 17 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 18 9
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Nucleus Contains the DNA Controls the cell activities by directing protein synthesis. A dark structure in the nucleus – nucleolus Synthesizes ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Enclosed in a double membrane – nuclear envelope. Perforated – nuclear pores 19 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 20 10
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 21 Ribosome Site of protein synthesis Made of rRNA and protein Free in the cytoplasm or attached (bound) to the endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER). 22 11
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 23 Jeffrey Mahr, CC BY 3.0, http://cnx.org/contents/b848f154 ‐ 6e98 ‐ 4237 ‐ 9c03 ‐ 7cb75a0d1905@1 24 12
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Endoplasmic Reticulum Membranous tubules and sacs Two types Smooth ER – No attached/bound ribosomes Synthesis of many types of lipids Rough ER – Attached/bound ribosomes The ribosomes produce proteins that are embedded in the membrane, transported to other organelles, or secreted by the cell. 25 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 26 13
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 27 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 28 14
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Golgi Apparatus Slightly curved stack of large flattened vesicles. (Stack of pancakes) The Golgi apparatus serves as storage and finishing facility for products from the ER. Products travel in vesicles from the ER to the Golgi. Contains enzymes that modify proteins and lipids. 29 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 30 15
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 31 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 32 16
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Lyososomes Lysosomes help digest food particles engulfed by a cell. A food vacuole binds with a lysosome. The enzymes in the lysosome digest the food. The nutrients are then released into the cell. Lysosomes also help remove or recycle damaged parts of a cell. 33 Vacuoles Large vesicles that have a variety of functions. Protists/Protozoa Contractile vacuoles that eliminate excess water. Plants Digestive functions Contain pigments Contain toxins for protection or storage 34 17
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Peroxisomes Break down fatty acids to use as fuels Detoxifiy materials 35 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 36 18
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Mitochondria Site of most ATP synthesis ‐‐ Converts energy from glucose to ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Aerobic cellular respiration Small peanut ‐ shaped organelles Double membrane Outer membrane is smooth Inner membrane is heavily folded – folds are called cristae. The inner most portion is the matrix. Endosymbiosis DNA, ribosomes (type), double membrane, antibiotics 37 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 38 19
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 39 Chloroplast Occurs in plants and some protists. Where photosynthesis occurs ‐‐ convert solar energy to chemical energy . Double membrane Thylakoid – flattened sacs with chlorophyll Granum – a stack of thylakoids Stroma ‐‐ thickened fluid that surrounds the granum 40 20
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Biology by OpenStax College is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 41 Cytoskeleton A network of filaments and microtubules Similar to an animal’s skeleton Provides structure and movement. Can change shape and configuration. 42 21
09 ‐ Feb ‐ 20 Movement Flagellum Cilia (Cilium) Psuedopodium 43 22
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.