
Cell Communication and Cell Signaling
Why is cell signaling important?
Why is cell signaling important? • Allows cells to communicate and coordinate functions/activities of the organism • Usually involves the cell membrane
Cell Communication • Communication involves transduction of stimulatory or inhibitory signals from other cells, organisms or the environment • Correct and appropriate signal transduction pathways are generally under strong selective pressure
Single-Celled Organisms • Signal transduction pathways influence how the cell responds to its environment • Example: quorum sensing in bacteria
Multicellular Organisms • Signal transduction pathways coordinate the activities within individual cells that support the function of the organism as a whole • Example: Epinephrine stimulation of glycogen breakdown in mammals
Cell Communication Long Distance Local Signaling Signaling Cell Junctions Hormones Cell to Cell Contact Neural Circuits Local Regulators
Local Signaling: Cell Junctions • Plasmodesmata in plant cells and gap junctions in animals • Allows signaling molecules to pass readily between adjacent cells
Local Signaling: Cell-to-Cell Contact • Communication through direct interaction between molecules extending from the surface of the cells (glycolipids and glycoproteins) • Example: tissue development and immune responses
Local Signaling: Local Regulators • Local regulators are signaling molecules that only target cells in the vicinity of the emitting cell • Examples: paracrine signaling and synaptic signaling
Evolution: Paracrine Signaling • Paracrine factors involved in differential development are similar between different species • Evidence of common ancestry, highly conserved in animals from fruit flies to humans Receptor and Pathway Groups: - Fibroblast Growth Factor Family (blood vessel, wound healing, limb development, embryonic development) - Hedgehog Family (embryonic development, bilateralism) - Wnt Family (bone, heart, muscle, regeneration of tissue) - TGF – β Family (immunity, cell proliferation)
Long Distance Signaling: Hormones • Endocrine signals (hormones) produced by endocrine cells travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body • Example: Insulin produced in pancreas, targets liver cells
Plants Have Hormones! • Ethylene – gaseous hormone that ripens fruit • Auxin – chemical messenger that influences fruit development and cell growth
Long Distance Signaling: Neural Circuits • Neurons may transmit messages (nerve impulses) over a long distance
Local or Long Distance - Cell Signaling Pathway is Similar Reception Transduction Response
Cell Signaling Pathway
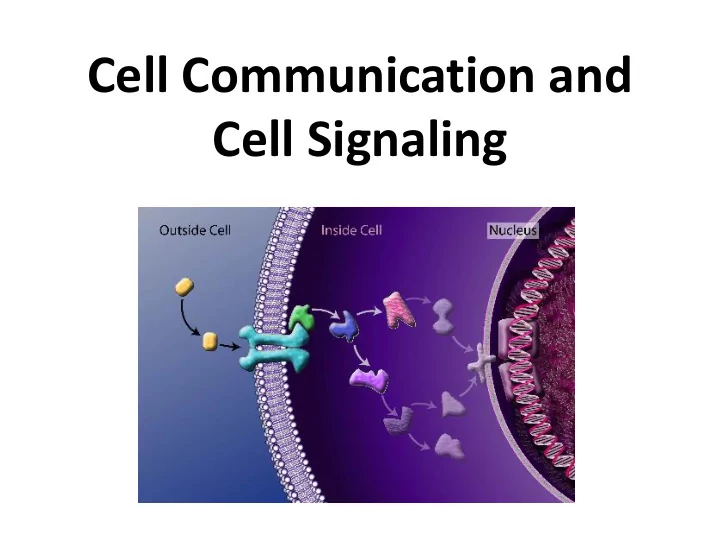
Stage 1: Signal Reception • Signaling begins with the recognition of a chemical messenger ( ligand ) by a receptor protein • Complementary shapes
Types of Receptor Proteins • Transmembrane Proteins (within the cell membrane) – also known as extracellular receptors - G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) - Ligand-Gated Ion Channels • Intracellular Receptors (within cytoplasm or nucleus) - Targeted by lipid soluble ligands (pass through the plasma membrane)
Transmembrane Protein Receptors: GPCRs
Transmembrane Protein Receptors: Ligand-Gated Ion Channels
Intracellular Receptors
Receptor Proteins • Different receptors recognize different chemical messengers, which can be peptides, small chemicals, or proteins, in a specific one- to-one relationship • A receptor protein recognizes signal molecules, causing the receptor protein’s shape to change, which then initiates transduction of the signal
Review of Signal Reception • What occurs during Stage 1: Signal Reception? • What is a ligand? • What is the difference between transmembrane protein receptors and intracellular receptors?
Stage 2: Signal Transduction • Signal transduction is the process by which a signal is converted to a cellular response • One step or a series of many steps
Signal Transduction • Signaling cascades relay signals from receptors to cell targets, often amplifying the incoming signals • Second messengers are often essential to the function of the cascade cyclic AMP (cAMP) or calcium ions (Ca 2+ )
Signaling Cascade • Protein kinases – turn “on” or activate proteins by adding phosphates to the proteins ( phosphorylation cascade ) • Protein phosphatases – turn “off” or deactivate proteins and kinases by removing phosphates from the proteins ( dephosphorylation )
Second Messengers
Review of Signal Transduction • What occurs during Stage 2: Signal Transduction? • What is the function of a protein kinase? • What is the function of a protein phosphatase? • Identify a second messenger.
Stage 3: Cellular Response • The signal transduction pathway initiates a change in cellular activity • Response occurs in the cytoplasm or nucleus
Response: Regulation of Protein Synthesis • Most signaling pathways activate transcription factors • Transcription factors regulate cellular responses by: - Turning a gene “on” Protein OR - Turning a gene “off” No protein OR - Regulating the activity of a particular protein
Testosterone Cellular response increases gene activity for proteins involved in: • Muscle mass • Bone growth • Body hair • Reproductive tissue
Blood Glucose Regulation
Cell Signaling Summary
Recommend
More recommend