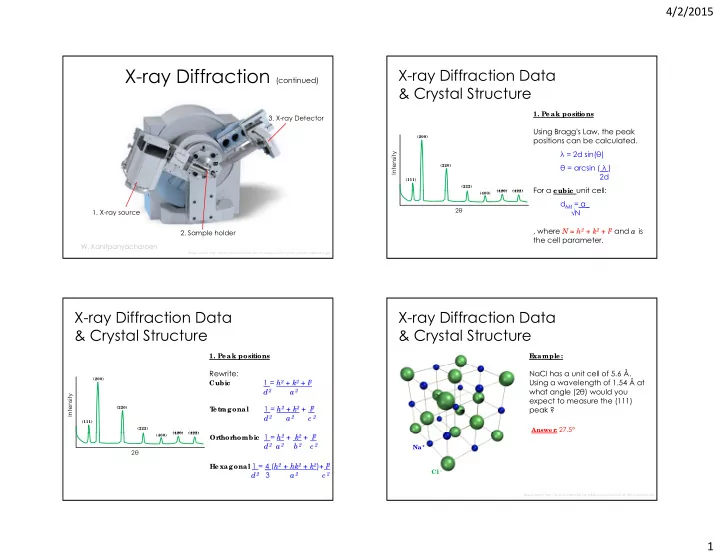

4/2/2015 X-ray Diffraction (continued) X-ray Diffraction Data & Crystal Structure 1. Peak positions 3. X-ray Detector Using Bragg's Law, the peak (200) positions can be calculated. λ = 2d sin( θ ) Intensity θ = arcsin ( λ ) (220) 2d (111) (222) For a c ubic unit cell: For a c ubic unit cell: (420) (420) (422) (422) (400) d hkl = a_ 2 θ 1. X-ray source √ N 2 and a is , where N = h 2 + k 2 + l 2. Sample holder the cell parameter. W. Kanitpanyacharoen I mage so urc e http:/ / www.h-and-m-analytic al.c o m/ image s/ se rvic e s/ x-ray-po wde r-diffrac tio n.jpg X-ray Diffraction Data X-ray Diffraction Data & Crystal Structure & Crystal Structure 1. Peak positions E xample: Rewrite: NaCl has a unit cell of 5.6 Å. (200) 1 = h 2 + k 2 + l Using a wavelength of 1.54 Å at 2 Cubic what angle (2 θ ) would you d 2 a 2 Intensity expect to measure the (111) 1 = h 2 + k 2 + l peak ? (220) 2 T etr agonal d 2 a 2 c 2 (111) : 27.5° (222) Answer (420) (420) (422) (422) hombic 1 = h 2 + k 2 + l (400) 2 Or thor d 2 a 2 b 2 c 2 Na + 2 θ Hexagonal 1 = 4 ( h 2 + hk 2 + k 2 ) + l 2 Cl - 3 a 2 d 2 c 2 I mage so urc e http:/ / uplo ad.wikime dia.o rg/ wikipe dia/ c o mmo ns/ d/ de / Nac l-struc ture .jpg 1
4/2/2015 X-ray Diffraction Data X-ray Diffraction Data & Crystal Structure & Crystal Structure E xample: 2. Peak intensities Zircon has a unit cell of a = 3.2 Å The intensity of a peak I hkl is and c = 7.8 Å. Using a given by: Intensity wavelength of 1.54 Å at what I hkl α l F hkl l 2 angle (2 θ ) would you expect to measure the (002) peak ? , where structure factor ( F hkl ) describes how an atom scatters : 22.6° Answer incident X-ray. It is dependent on incident X-ray It is dependent on the type of atoms and their 2 θ Na + positions (x, y, z) in the unit cell. It also tells us which {hkl} peak to Cl - appear in the XRD data. When 2 = 0, there is no peak. F hkl I mage so urc e http:/ / uplo ad.wikime dia.o rg/ wikipe dia/ c o mmo ns/ d/ de / Nac l-struc ture .jpg I mage so urc e http:/ / ipo .lbl.go v/ wp-c o nte nt/ uplo ads/ site s/ 8/ 2014/ 08/ 2080fig2.jpg X-ray Diffraction Data X-ray Diffraction Data & Crystal Structure & Crystal Structure 3. Peak widths F hkl = ∑ f i exp 2 π i (hx i + ky i + lz i ) The peak width ( β ) in radians (measured at full width at half Intensity Intensity f i is the scattering factor for atom maximum, FWHM) is inversely i and is related to its atomic proportional to the crystallite size Peak width number ( L hkl ) perpendicular to hkl plane. at FWHM Differences in X-ray intensity L hkl = ____ λ ____ relate to changes in chemistry relate to changes in chemistry β β FWHM cos θ cos θ (scattering factor). 2 θ 2 θ Small crystals are the most For multiphase samples, changes common cause of line in X-ray intensities are related to broadening but other defects the amount of each mineral can also cause peak widths to present in the sample. increase. I mage so urc e http:/ / ipo .lbl.go v/ wp-c o nte nt/ uplo ads/ site s/ 8/ 2014/ 08/ 2080fig2.jpg I mage so urc e http:/ / ipo .lbl.go v/ wp-c o nte nt/ uplo ads/ site s/ 8/ 2014/ 08/ 2080fig2.jpg 2
4/2/2015 ‐ Synchrotron X ‐ ray is the electromagnetic radiation emitted APS Sync hr otr on Argonne, IL, USA when electrons, moving at velocities close to the speed of light , are forced to change direction by a magnetic field. ‐ Synchrotron light has a number of unique properties such as: High brightness: synchrotron light is extremely intense High brightness: synchrotron light is extremely intense (hundreds of thousands of times more intense than that from conventional x ‐ ray tubes) and highly collimated. Wide energy spectrum: synchrotron light is emitted with energies ranging from infrared light to hard x ‐ rays. Tunable: it is possible to obtain an intense beam of any selected wavelength wavelength. Highly polarised: the synchrotron emits highly polarised Your c ar ! radiation, which can be linear, circular or elliptical. Emitted in very short pulses: pulses emitted are typically less than a nano ‐ second (a billionth of a second), enabling time ‐ resolved (real time!) studies. Source: http://www.lynceantech.com/images/aps.jpg I mage so urc e http:/ / ipo .lbl.go v/ wp-c o nte nt/ uplo ads/ site s/ 8/ 2014/ 08/ 2080fig2.jpg Inside the APS Synchrotron X-ray diffraction High pressure, temperature experiment in the “ Diamond Anvil Cell (DAC) ” Source: http://topicstock.pantip.com/wahkor/topicstock/2009/12/X8704611/X8704611-52.jpg; http://umet.univ-lille1.fr/Mineraux/Ressources/diamants_h.jpg 3
4/2/2015 Lab This Week Synchrotron X-ray diffraction: Study Earth’s interiors - Presentation < 10 mins - Report < 3 pages Olivine -2 samples analysis Wadsleyite - Single phase: calculate d-spacing, post post- -perovskite perovskite + + ferropericlase ferropericlase {hkl}, etc. Discovered by Discovered by - Multiple phases: search peaks Murakami et al. c ie nc e (2004) Ringwoodite S from database Useful website: Perovskite Post-perovskite http://webmineral.com/help/XRayDiffraction.shtml#.VRtm_vmUd8E Source: http://www.quranandscience.com/images/stories/earth_layers.jpg I mage so urc e http:/ / ipo .lbl.go v/ wp-c o nte nt/ uplo ads/ site s/ 8/ 2014/ 08/ 2080fig2.jpg 4
Recommend
More recommend