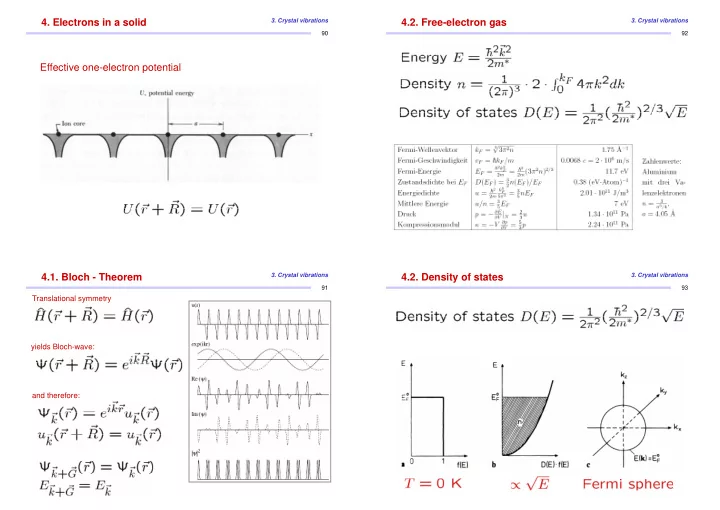

4. Electrons in a solid 3. Crystal vibrations 4.2. Free-electron gas 3. Crystal vibrations 90 92 Effective one-electron potential 4.1. Bloch - Theorem 3. Crystal vibrations 4.2. Density of states 3. Crystal vibrations 91 93 Translational symmetry yields Bloch-wave: and therefore:
4.2. Dispersion relation - bandstructure 3. Crystal vibrations 4.4. Specific heat 4. Electrons in solids 94 96 D(E) E 4.3. Fermi distribution-function 4. Electrons in solids 4.4. Specific heat 4. Electrons in solids 95 97 f(E,T) 4 E/k (10 K) 15.4 2 k T B B 1.0 E kin e 0.8 E vac ν h T= 0.6 750 K E F f(E,T) 500 K 290 K 0.4 100 K 0.2 0.0 -0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 E - E F (eV)
4.5. Electrostatic Screening 4. Electrons in solids 4.5. Thermionic emission 4. Electrons in solids 98 100 for slowly varying potential δ U: Poisson equation: Solution: Work function whereby Thomas-Fermi screening length: 4.5. Mott insulator 4. Electrons in solids 4.6. Nearly free electrons 4. Electrons in solids 99 101 E deloc E vac In a shallow potential the number energy of bound states decreases E loc r/rTF e /r 1/r r n.n. dist. conductivity increase of n ⇒ decrease of r TF ⇒ free electrons insulator metal Mott transition: insulator ⇒ metal n
4.6. Nearly free electrons 4. Electrons in solids 4.6. Nearly free electrons 4. Electrons in solids 102 104 Extended zone scheme Reduced zone scheme Repeated zone scheme K=2 π /a 4.6. Nearly free electrons 4. Electrons in solids 4.6. Solution at Brillouin zone-boundary 4. Electrons in solids 103 105 Standing waves:
4.6 Standing wave at Brillouin zone-boundary 4. Electrons in solids 4.7 s- and p z - waves 4. Electrons in solids 106 108 Energie Bandlücke: 2V |V| |V| G/2 0 k z OF s-Welle V(z) z p-Welle z=0 a 4.7 Tight binding bandstructure 4.8 Examples - metall 4. Electrons in solids 4. Electrons in solids 107 109 Aluminium-Bandstruktur mit 1 s-artigen, 3 p-artigen und 5 d-artigen Basisfunktionen (j = 1 . . . 9) nach: D. A. Papaconstantopoulos, Cu, fcc: 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1, s(p) and d bands, metal Handbook of the band structure of elemental solids, Plenum Press (New York) 1986.
4. Electrons in solids 4.8 Examples - semiconductor 4. Electrons in solids 4.8 Occupied states – photoelectron spectroscopy 110 112 vertical transition Ge, 4s2 4p2, → sp3 hybridized, absolute band gap, semiconductor 4.8 Examples – Fermi surfaces 4.8 Unoccupied states 4. Electrons in solids 4. Electrons in solids 111 113 Fermi surfaces Inverse photoemission (IPES) Two-photon photoemission (2PPE) Al
4.8 Examples - metall 4. Electrons in solids 4.8 Examples – Fermi surfaces 4. Electrons in solids 109 111 Fermi surfaces Al Cu, fcc: 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1, s(p) and d bands, metal 4. Electrons in solids 4.8 Examples - semiconductor 4.8 Occupied states – photoelectron spectroscopy 4. Electrons in solids 110 112 vertical transition Ge, 4s2 4p2, → sp3 hybridized, absolute band gap, semiconductor
4.8 Unoccupied states 4. Electrons in solids 113 Inverse photoemission (IPES) Two-photon photoemission (2PPE)
Recommend
More recommend