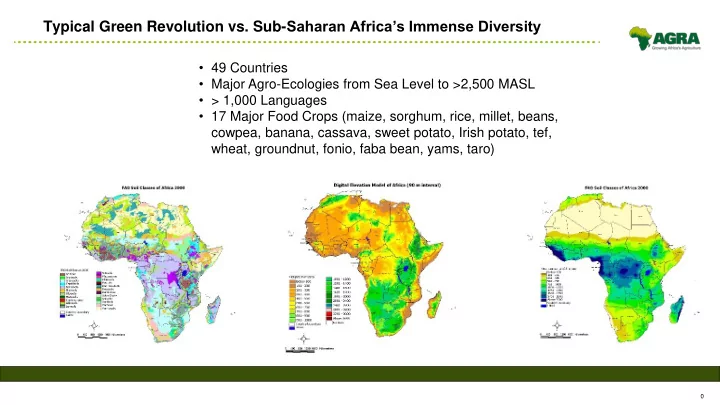

Typical Green Revolution vs. Sub- Saharan Africa’s Immense Diversity • 49 Countries • Major Agro-Ecologies from Sea Level to >2,500 MASL • > 1,000 Languages • 17 Major Food Crops (maize, sorghum, rice, millet, beans, cowpea, banana, cassava, sweet potato, Irish potato, tef, wheat, groundnut, fonio, faba bean, yams, taro) 0
CROPPING SEASONS IN SELECTED COUNTRIES January February April May July September October December Uganda Tanzania Tanzania(No) Rwanda Nigeria Ghana Ethiopia Mozambique Mali Malawi Kenya Burkina Faso First Season Second Season 1
Program for Africa’s Seed Systems (PASS) Value Chain R&D (Public Sector) Production and Marketing (Private Sector) Other Results: 2017 1 670 new crop 4 varieties developed 1, and released; 431 0 commercialized; 0 501 MSc/PhD’s 0 graduated; 114 private, African M seed companies T established; Identify strongest univs. Identify breeding teams Identify seed enterprises Identify service providers 19,174 agro-dealers Establish grant support Develop breeding strategy Est. prod., market strategy Establish grant support S trained, in Recruit top-level fellows Establish grant support Establish grant support Oversee training E operation. Curriculum oversight Breeding oversight Coordinate BDS training Oversee credit guarantee E Link breeders to SC’s . Monitor prod’n, marketing Link AD’s to seed co’s Thesis research oversight D Re-integrate students Assist commercialization Link to investment funds Create AD links to farmers 2
Benefits of Improved, Adapted Groundnut Varieties in Uganda On the left, improved On the right, variety bred by Dr. Farmer’s Variety David Okello, NARO 3
Benefits of Improved, Adapted Sorghum Varieties in West Africa Right, hybrid sorghum variety developed by Dr. Aboubacar Left, local land race. Toure, l’Institut de l’Economie Rurale. 4
Benefits of Improved, Adapted Bean Varieties in Rwanda In the foreground, improved bush bean variety developed by Musoni with improved climbing bean Augustine Musoni, Rwanda variety. Agricultural Board. In the center, local bean variety. 5
670 New Crop Varieties Bred and Released Maize, 177 Cassava, 86 Rice, 90 Sweet potato, 65 Sorghum, 36 Beans, 82 Wheat, 8 Millet, 14 Cowpea, 46 Chickpea, 2 Teff, 4 Groundnut, 26 Soybean, 14 Banana, 6 Faba bean, 4 Pigeon pea, 10 6
Scaling Up Improved Seed Supply via Private, Independent, African Seed Companies COMMUNICATION & PARTNERSHIP UPDATE Maslaha Seed Company, Nigeria Producing certified seed of: maize, rice, pearl millet, sorghum, and cowpea. 7
African Seed Companies, Cont. COMMUNICATION & PARTNERSHIP UPDATE Equator Seeds, Uganda Producing certified seed of: maize, beans, rice, soybean, sorghum, sesame, cowpea and finger millet. 8
African Seed Companies, Cont. Peacock Seeds, COMMUNICATION & PARTNERSHIP UPDATE Malawi Producing certified seed of: maize, beans, cowpea, and groundnut. 9
African Seed Companies, Cont. COMMUNICATION & PARTNERSHIP UPDATE Faso Kaba Seed Co, Mali Producing certified seed of: maize, cowpea, sorghum, millet, rice, and groundnut. 10
Certified Seed Production(MT), 2007-2017 160,000 141,942.6 126,408.0 140,000 128,939.0 125,054.7 120,000 100,000 80,605.4 80,000 57,991.6 60,000 40,437.0 40,000 25,844.8 20,000 9,748.5 5,663.5 2,346.3 0 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 11 11
Certified Seed Production by Country (MT) in 2017 Ethiopia 57,347 Uganda 26,703 Nigeria 23,115 Burkina Faso 7,620 Tanzania 5,791 Malawi 3,405 Zambia 3,173 Kenya 3,048 Mali 2,851 Niger 2,783 Ghana 2,247 Mozambique 1,966 South Sudan 1,591 Rwanda 185 Sierra Leone 72 DRC 25 Liberia 20 0 10,000 20,000 30,000 40,000 50,000 60,000 12 12
114 Seed Companies Operating Across 18 Countries 13
Varieties Released by Crop (670 Vars.) Maize, 177 Cassava, 86 Sweet potato, 65 Rice, 90 Sorghum, 36 Beans, 82 Millet, 14 Wheat, 8 Chickpea, 2 Cowpea, 46 Teff, 4 Groundnut, 26 Soybean, 14 Banana, 6 Pigeon pea, 10 Faba bean, 4 14
5 Innovations That Helped to Scale: 1. Develop capacity at national level 15
5 Innovations That Helped to Scale: 2. Approach seed supply for smallholder farmers as a business 16
5 Innovations That Helped to Scale: 3. Train African seed companies to produce high-quality seed, at-scale, including hybrids. 17
Seed Companies That Have Purchased Seed Processing Equipment. Increase in or new capacity estimated at 8,000MT annual capacity per location. (33) Companies U of Nairobi Value Seeds 10/13 Chris Kaijuka 5/14 5/13 Goldagric PREMIER SEED Agri Seed Africasia Manoa Pearl Seed 10/13 (2) 1/12 5/14 6/14 Seed 12/11 Western Seed Meru Agro 8/13 Uganda DA-ALLGREE N Alheri 7/11 3/14 Boman 11/11 2/12 USAID-COOPS Seed Nigeria 1/14-(4) Niger Dryland Seeds(2) 3/13 Ethiopia 8/11 Suba Agro Plant Fresco 9/11 NAFASO 2/13 Tanzania 6/11 Kenya Burkina Funwe Faso 4/13 Peacock Enterprise Ltd 9/11 Seed Tech 8/11 FASO KABA Malawi 7/11 Wienco Dengo Commercial Mali 7/11 10/12 Sementes Nzara Yapera M&B Seeds 10/12 10/11 Mozseed Ghana Mozambique 6/14 Dryer 18
5 Innovations That Helped to Scale: 4. Increase farmer awareness of the value of higher-yielding seed and fertilizer. 19
5 Innovations That Helped to Scale: 5. Build marketing chains where farmers live 20
New Model for Scaling Technologies in Africa: Private Sector-led Extension • Elements of a new approach include: • Trusted local advisory services; • Inclusive , “whole village” approach; • Small “sample” packs to reduce “adoption risk” • Practical technology demo’s under local conditions; • Partnerships between public and private actors, and farmers; • Farmer feedback via farmer field days. Village 1 Village 2 Village 4 Village 3 21
Funding Only the Most Direct Actions in Scaling Seeds Cuts out the Public Sector and Ignores the Need for New Technologies. 22
Lessons Learned on the Journey to Scaling Technologies 1. Public – private partnerships actually work, and take it further; 2. Political will is critical, and can be nurtured; 3. There is huge untapped potential for SME growth in African agri-business; 4. National agricultural research systems are a huge source of innovation; 23
Recommend
More recommend