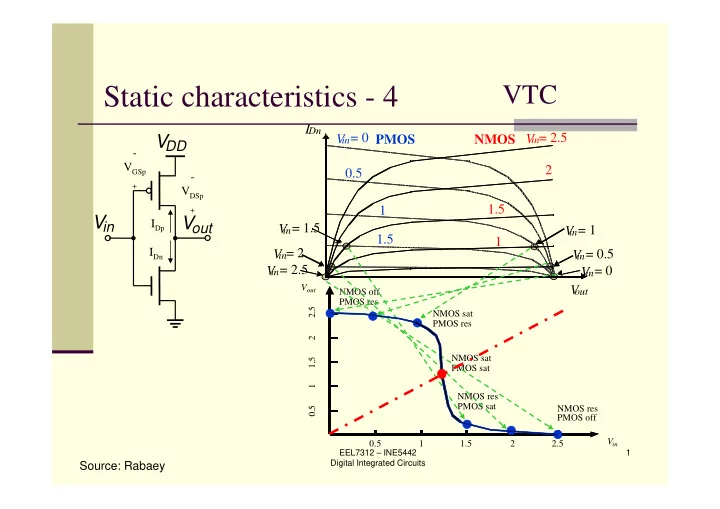

Static characteristics - 4 VTC I Dn in = 2.5 in = 0 V V PMOS V NMOS DD - V GSp 2 0.5 - + V DSp 1.5 1 + V in V out I Dp in = 1.5 V in = 1 V 1.5 1 I Dn in = 2 V V in = 0.5 in = 2.5 V in = 0 V V out V out NMOS off PMOS res 2.5 NMOS sat PMOS res 2 NMOS sat 1.5 PMOS sat 1 NMOS res PMOS sat 0.5 NMOS res PMOS off V 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 in EEL7312 – INE5442 1 Digital Integrated Circuits Source: Rabaey
Static characteristics - 5 Short-circuit current I Dn in = 2.5 in = 0 V V PMOS V NMOS DD - V GSp 2 0.5 - + V DSp 1.5 1 + V in V out I Dp in = 1.5 V in = 1 V 1.5 1 I Dn in = 2 V V in = 0.5 in = 2.5 V in = 0 V V out 2.5 IDD 2 1.5 1 0.5 V in 2 1.5 0.5 1 2.5 EEL7312 – INE5442 2 Source: Rabaey Digital Integrated Circuits
Static characteristics - 6 Switching threshold - 1 V DD - V GSp - + V DSp + V in V out I Dp I Dn EEL7312 – INE5442 3 Source: Weste & Harris Digital Integrated Circuits
Static characteristics - 7 Switching threshold - 2 V DD Experimental determination of V M : - V out short-circuit between input and output V GSp - + ⎛ ⎞ ⎛ ⎞ V DSp k W k W ( ) ( ) ( ) − − = 2 + λ ≅ 2 I n ⎜ ⎟ V V n ⎜ ⎟ V V 1 V Dn GSn Tn M Tn ⎝ ⎠ n DSn ⎝ ⎠ + 2 L 2 L V in V out n n I Dp ( ) ⎞ ) ( ) ⎞ ⎛ ( ⎛ k k W W 2 2 − − = + λ ≅ − p p I ⎜ ⎟ V V ⎜ ⎟ V V V 1 V Dp GSp Tp M Tp I Dn ⎝ ⎠ p DSp ⎝ ⎠ DD 2 2 L L p p λ << V 1 Usually V in DS V M ( ) W L / + k V V r V r = p p = → = + r Tn Tp DD ( ) I I V ; + + k W L / Dn Dp M 1 r 1 r n n Example: V DD =2.5 V, V Tp =-0.4 V, V Tn =0.43 V. What is V M for r= 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5? Answer: V M =0.98, 1.26, and 1.43 V, respectively. EEL7312 – INE5442 4 Source: Weste & Harris Digital Integrated Circuits
Static characteristics - 8 Noise margins - 1 V DD - V GSp - + V DSp + V in V out I Dp I Dn EEL7312 – INE5442 5 Source: Weste & Harris Digital Integrated Circuits
Static characteristics - 9 Noise margins - 2 Approximate calculation of V IL and V IH V DD V out - V GSp - + V OH V DSp + V in V out I Dp I Dn V M V in V OL V IL V IH For regeneration -g>1, g is the gain in transition region EEL7312 – INE5442 6 Source: Rabaey Digital Integrated Circuits
Static characteristics - 10 Scaling the supply voltage 2.5 0.2 VDD - V GSp 2 - 0.15 + V DSp 1.5 + V out (V) V Vin V out (V) I Dp out 0.1 1 I Dn 0.05 0.5 0 0 0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 V in (V) V in (V) Effects of supply voltage reduction: • Energy dissipation decreases but gate delay increases • dc characteristic becomes more sensitive to variations in device parameters • Signal swing reduces making the design more sensitive to external noise sources that do not scale EEL7312 – INE5442 7 Source: Rabaey Digital Integrated Circuits
Static characteristics -11 Impact of Process Variations 2.5 “Good” PMOS 2 “Bad” NMOS 1.5 (V) Nominal out V Good NMOS 1 Bad PMOS 0.5 0 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 V in (V) W ′ β = Notes: k L k’ n ≈ 2 to 3 k’ p 1. For β n = β p and V Tp =-V Tn , V M =V DD /2 2. Source: Rabaey EEL7312 – INE5442 8 Source: Uyemura Digital Integrated Circuits
Dynamic operation - 1 V = 5 V DD M P High-to-low output transition v v = 5 V v (0+) = 5V v O I I O in a CMOS inverter M M C C N N (a) (b) vI v O + 5V + 5V 0 V 0 V t t 0 0 C: load capacitance + interconnect capacitance + capacitances associated with the inverter transistors Source: Jaeger EEL7312 – INE5442 9 Digital Integrated Circuits
Dynamic operation - 2 V = 5 V DD V = 5 V DD M M P P v v (0+) = 0V v O I Low-to- high output O transition in a CMOS inverter V = 0 V I M C N C (a) (b) vI v O + 5V + 5V t 0 V 0 V t 0 0 C: load capacitance + interconnect capacitance + capacitances associated with the inverter transistors EEL7312 – INE5442 10 Source: Jaeger Digital Integrated Circuits
Dynamic operation - 3 t PHL t PLH EEL7312 – INE5442 11 Source: Uyemura Digital Integrated Circuits
Propagation Dynamic operation - 4 delay - 1 V DD V GS = V DD ID(A) V GSn =V DD V out I D I C + 0 DS (V) V DD /2 V V DD V DSn __ dV t V / 2 = = − PHL DD dV CV /2 out I I ∫ ∫ C = − → = out DD dt C t D C dt PHL I I D Dav 0 V DD = → = 0 t V V V out DD DD 1 ( ) ∫ = = → = I I V dV t t V V /2 Dav D DS DS V /2 PHL out DD DD V / 2 DD EEL7312 – INE5442 12 Digital Integrated Circuits
Propagation Dynamic operation - 5 delay - 2 V DD V GS = V DD ID(A) CV /2 = DD t PHL I Dav V 1 DD ( ) ∫ = I I V dV Approach 1 Approach 1 Dav D DS DS V /2 DD V / 2 DD V out 0 V DD /2 DS (V) V V DD C I av ⎛ ⎞ k W ( ) − − ≅ 2 > I n ⎜ ⎟ V V V V for V D GS Tn DS GS Tn ⎝ ⎠ 2 L n ⎛ ⎞ W ( ) − − ≅ ⎡ − ⎤ ≤ 2 I ⎜ ⎟ ⎣ V V V V k V V /2 for V ⎦ D n GS Tn DS DS DS GS Tn ⎝ ⎠ L n V in = V DD ⎛ ⎞ k W ( ) 2 and that − ≅ = >> Let us assume that I n ⎜ ⎟ V V V I V Dav Dsat DD Tn DD Tn ⎝ ⎠ 2 L n C V /2 CV /2 C = ≈ ≈ In this case we have DD DD t ; t ⎛ ⎞ ⎛ ⎞ PHL PHL k W W ( ) I − 2 n ⎜ ⎟ V V ⎜ ⎟ V Dav k D D Tn DD ⎝ ⎠ n ⎝ ⎠ 2 L L n n Source: Rabaey EEL7312 – INE5442 13 Digital Integrated Circuits
Propagation Dynamic operation - 6 delay - 3 V DD ⎛ ⎞ ( ) k 2 and W + ≅ = >> − p I I ⎜ ⎟ V V that V V Dav Dsat DD Tp DD Tp ⎝ ⎠ 2 L Approach 1 Approach 1 p C V /2 CV /2 C I av = ≈ ≈ DD DD t ; t ⎞ ⎛ ⎞ ⎛ PLH ( ) PLH k W W I + 2 p ⎜ ⎟ V Dav ⎜ ⎟ V V k DD D D Tp p ⎝ ⎠ ⎝ ⎠ 2 L L n p + V t t out = PLH PHL t P C 2 C ≈ t ⎛ ⎞ PHL W ⎜ ⎟ V k DD n ⎝ ⎠ L Comments: n • k n ≈ 2-3 k p , k n,p = μ n,p ·C ox • Increasing V DD reduces t p but power goes up V in = V DD • t PLH can be ≈ t PHL by making (W/L) p ≈ 2-3(W/L) n BUT C is dependent on transistor dimensions • C includes load (fan-out), wire, inverter “self- capacitance” • C is non linear Source: Rabaey EEL7312 – INE5442 14 Digital Integrated Circuits
Propagation Dynamic operation - 7 delay - 4 Source: Rabaey EEL7312 – INE5442 15 Digital Integrated Circuits
Propagation Dynamic operation - 8 delay - 5 What’s R on ? V DD V GS = V DD ID(A) t pHL = f(R on .C L ) Approach 2 Approach 2 = 0.69 R on C L V out R − 1 V out ln(0.5) o C L 0 DS (V) 1 V DD V DD /2 V V DD R − R on 1 mid Approach by Uyemura Uyemura Approach by 0.5 0.36 ⎛ ⎞ dI W ( ) − = = − V in = V DD 1 D ⎜ ⎟ R k V V on n ⎝ ⎠ DD Tn t dV L R on C L = DS V n 0 DS Modeling capacitor discharge Approach by Rabaey Approach by Rabaey as in an RC circuit! 1 ( ) ≡ + R R R C on 0 mid ≈ 2 t ⎛ ⎞ PHL W ⎜ ⎟ V k Source: Rabaey EEL7312 – INE5442 16 DD n ⎝ ⎠ L Digital Integrated Circuits n
Propagation Dynamic operation - 9 delay - 6 V DD Approach by Uyemura Uyemura Approach by ⎛ ⎞ ( ) dI W − = = − 1 D ⎜ ⎟ + R k V V ( ) on n p , ( ) n p ( ) DD Tn p ( ) ⎝ ⎠ dV L = DS V n p ( ) 0 DS t pHL = 0.69 R on,n C L V out t pLH = 0.69 R on,p C L C L R on ⎡ ⎤ ⎢ ⎥ + ⋅ t t 0.69 C 1 1 ⎢ ⎥ = = + PHL PLH L t ⎢ ⎛ ⎞ ⎛ ⎞ ⎥ P ( ) W W V in = V DD 2 2 ( ) − ⎜ ⎟ ⎜ ⎟ + k V V k V V ⎢ ⎥ n ⎝ ⎠ DD Tn p ⎝ ⎠ DD Tp ⎣ L L ⎦ n p ⋅ 0.69 C 1 1 ≈ + L t [ ] ⎛ ⎞ ⎛ ⎞ P W W 2 V ⎜ ⎟ ⎜ ⎟ DD k k n p ⎝ ⎠ ⎝ ⎠ L L n p Source: Uyemura EEL7312 – INE5442 17 Digital Integrated Circuits
Dynamic operation - 10 Experimental setup S 1 2 + G B 1 VDD = 5.0 V - 3 D + B G CL 0 VPULSE S - 0 EEL7312 – INE5442 18 Digital Integrated Circuits
Dynamic operation - 11 Inverter Propagation Delay * this is the Propagationdelay.cir file * PMOS transistor description MP 3 2 1 1 modelp W=2u L=1u .model modelp pmos (level=1 VT0=-0.65 TOX=7.5n KP=60u lambda=0.0) * NMOS transistor description MN 3 2 0 0 modeln W=2u L=1u .model modeln nmos (level=1 VT0=0.5 TOX=7.5n KP=150u lambda=0.0) * dc source vDD 1 0 dc 5.0 *load capacitance CL 3 0 0.01p *signal source v0 2 0 dc 0 pulse 0 5 0 1ps 1ps 200ps 400ps .end EEL7312 – INE5442 19 Digital Integrated Circuits
Dynamic operation - 12 SpiceOpus (c) 6 -> source Propagationdelay1.cir SpiceOpus (c) 7 -> tran 1ps 500ps SpiceOpus (c) 8 -> setplot new New plot Current tran2 Inverter Propagation Delay (Transient Analysis) tran1 Inverter Propagation Delay (Transient Analysis) const Constant values (constants) SpiceOpus (c) 9 -> setplot tran2 SpiceOpus (c) 10 -> plot v(2) v(3) xlabel t[s] ylabel 'Input, Output [V]' EEL7312 – INE5442 20 Digital Integrated Circuits
21 Why? Digital Integrated Circuits EEL7312 – INE5442 tPHL ≈ 2.5·tPLH Dynamic operation - 12 Why?
Recommend
More recommend