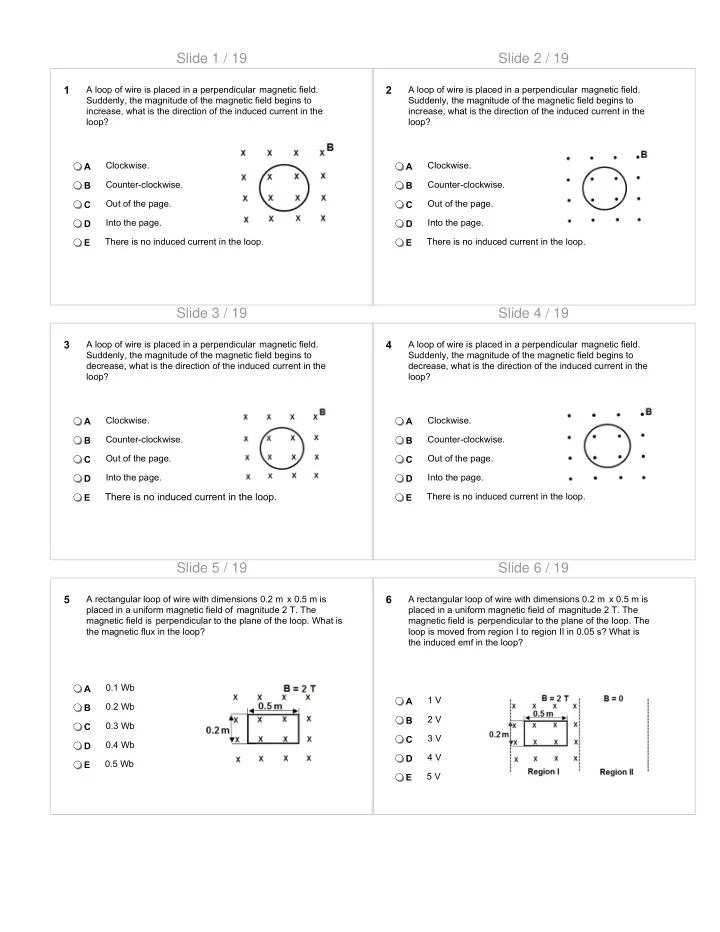

Slide 1 / 19 Slide 2 / 19 1 A loop of wire is placed in a perpendicular magnetic field. 2 A loop of wire is placed in a perpendicular magnetic field. Suddenly, the magnitude of the magnetic field begins to Suddenly, the magnitude of the magnetic field begins to increase, what is the direction of the induced current in the increase, what is the direction of the induced current in the loop? loop? Clockwise. Clockwise. A A Counter-clockwise. Counter-clockwise. B B Out of the page. Out of the page. C C Into the page. Into the page. D D E There is no induced current in the loop. E There is no induced current in the loop. Slide 3 / 19 Slide 4 / 19 3 A loop of wire is placed in a perpendicular magnetic field. 4 A loop of wire is placed in a perpendicular magnetic field. Suddenly, the magnitude of the magnetic field begins to Suddenly, the magnitude of the magnetic field begins to decrease, what is the direction of the induced current in the decrease, what is the direction of the induced current in the loop? loop? Clockwise. Clockwise. A A B Counter-clockwise. B Counter-clockwise. Out of the page. Out of the page. C C Into the page. Into the page. D D There is no induced current in the loop. There is no induced current in the loop. E E Slide 5 / 19 Slide 6 / 19 5 A rectangular loop of wire with dimensions 0.2 m x 0.5 m is 6 A rectangular loop of wire with dimensions 0.2 m x 0.5 m is placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 2 T. The placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 2 T. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. What is magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of the loop. The the magnetic flux in the loop? loop is moved from region I to region II in 0.05 s? What is the induced emf in the loop? A 0.1 Wb 1 V A 0.2 Wb B 2 V B 0.3 Wb C 3 V C 0.4 Wb D 4 V D 0.5 Wb E 5 V E
Slide 7 / 19 Slide 8 / 19 8 A magnet bar with the north pole faced 7 A bar magnet is moved towards a vertical downward is held above a horizontal conducting ring that is suspended at the circular coil. Which of the following end of a string. What happens to the ring statements about the induced current is true during the time when the magnet (viewed from above)? approaches it? T he induced current flows in a clockwise direction. A The ring will move toward the magnet. A The induced current flows in a counter-clockwise B direction. The ring will move away from the magnet. B The induced current flows first in a clockwise and The ring will remain stationary. C C then in a counter-clockwise direction. The ring will tend to turn in clockwise direction. D The induced current flows first in a counter- D The ring will tend to turn in counter-clockwise clockwise and then in a clockwise direction. E direction. There is no induced current in the coil. E Slide 9 / 19 Slide 10 / 19 9 A bar magnet with the north pole faced 10 A metal rod with a length of L moves at a constant velocity downward is dropped above a horizontal through a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B. The magnetic circular coil. Which of the following statements field is perpendicular to the rod. Which of the following is true about the induced current is true (viewed from about the electric potential in the rod? above)? The induced current flows in a clockwise direction. A The induced current flows in a counter-clockwise B direction. Point A has higher potential. A The induced current flows first in a clockwise and B Point B has higher potential. C then in a counter-clockwise direction. Point C has higher potential. C The induced current flows first in a counter- D Point A and B have the same potential. D clockwise and then in a clockwise direction. Point A and C have the same potential. E There is no induced current in the coil. E Slide 11 / 19 Slide 12 / 19 11 A metal rod with a length of L moves at a constant velocity 12 A metal rod with a length of L moves at a constant velocity through a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B. The through a uniform magnetic field of magnitude B. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the rod. What is the magnetic field is perpendicular to the rod. What is the induced potential difference between point A and B? electric field in the rod? A Bv A Bv vL vL B B BL BL C C BLv BLv D D Potential difference is zero. There is no electric field in the rod. E E
Slide 13 / 19 Slide 14 / 19 13 A circular loop of wire is 14 A steady current, I, flows though a straight placed in a perpendicular wire. A circular loop of wire is placed next uniform magnetic field. to the wire. Which of the following will not Which of the following will produce an induced current in the loop? not produce an induced current in the loop? Move the loop away from the wire. A Move the loop to region II. A Move the loop toward the wire. B Rotate the loop with respect to its diameter. B Increase the electric current in the wire. C Rotate the loop with respect to its center. C D Decrease the electric current in the wire. Stretch the loop and change its area. D Move the loop in parallel to the wire. E None from the above. E Slide 15 / 19 Slide 16 / 19 16 A current-carrying wire lies on a horizontal table. A circular 15 A current-carrying wire lies on a horizontal table. A circular coil is coil is placed next to the loop. The current vanishes suddenly. placed next to the loop. The current suddenly grows stronger. What is the direction of the induced current in the coil? What is the direction of the induced current in the coil? Clockwise. A A Clockwise. Counter-clockwise. B Counter-clockwise. B There is no induced current in the coil. C There is no induced current in the coil. C The induced current changes its direction from The induced current changes its direction from D D clockwise to counter-clockwise. clockwise to counter-clockwise. The induced current changes its direction from The induced current changes its direction from E E counter-clockwise to clockwise. counter-clockwise to clockwise. Slide 17 / 19 Slide 18 / 19 17 A rectangular loop of 18 Coil A is connected to a circuit including: a battery, a switch, and wire is moved at a a resistor. Coil B lies in the same plane as coil A. What is the constant speed from direction of the induced current in coil B at the moment when the region I to region II switch is closed? and then to region III. Which of the following is true about the magnetic force direction acting on the loop when it Region I to Region II to Clockwise. crosses the boundary Region II Region III A between the regions? A B Counter-clockwise. Left Right B Left Left There is no induced current in the coil. C C The induced current changes its direction from Right Right D clockwise to counter-clockwise. D Right Left The induced current changes its direction from E E Zero Zero counter-clockwise to clockwise.
Slide 19 / 19
Recommend
More recommend