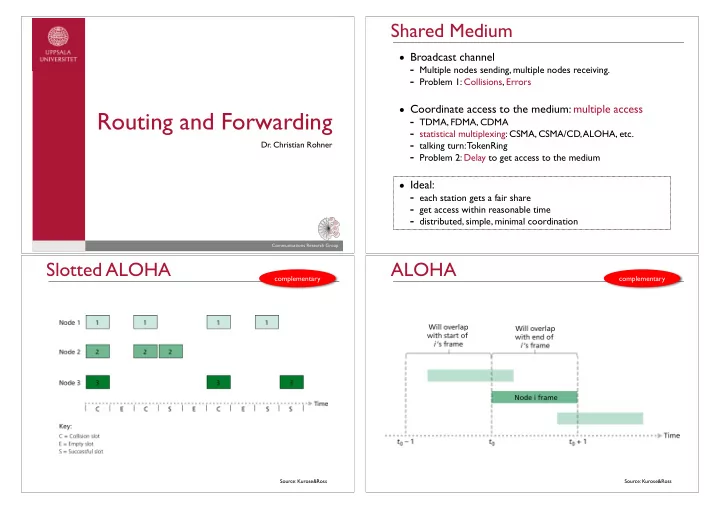

Shared Medium • Broadcast channel - Multiple nodes sending, multiple nodes receiving. - Problem 1: Collisions, Errors • Coordinate access to the medium: multiple access Routing and Forwarding - TDMA, FDMA, CDMA - statistical multiplexing: CSMA, CSMA/CD, ALOHA, etc. - talking turn: TokenRing Dr. Christian Rohner - Problem 2: Delay to get access to the medium • Ideal: - each station gets a fair share - get access within reasonable time - distributed, simple, minimal coordination Communications Research Group Slotted ALOHA ALOHA complementary complementary Source: Kurose&Ross Source: Kurose&Ross
Ethernet Carrier Sense Multiple Access Originally: Single wire [1976, Metcalfe] CSMA/CD - send at any time (no wait) - do not transmit if others are transmitting (carrier sensing CS) - stop if collision (collision detection CD) - random backoff Connectionless, unreliable Source: Kurose&Ross CSMA/CD Efficiency complementary Source: Kurose&Ross
Performance Tuning Ethernet Frame complementary complementary Vergleich CSMA mit CSMA/CD, beta=0.01 resp. 0.1 1 CSMA/CD 0.8 0.6 S CSMA Preamble: �� wake-up, synchronisation (64 bit) 0.4 CSMA/CD Addresses: �� 48bit 0.2 Type: � � � � � IP , ARP , AppleTalk, etc. CSMA Data: � � � � � 46...1500Byte 0 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 CRC: � � � � 32bit - no ACK, no retransmission! G connectionless, unreliable � = P*R / L P: Propagation Time R: Channel Rate L: Frame Length Source: Kurose&Ross Hub (Self learning) Switch • “Ethernet in a Box” Packet: Cache: Queue(s) src dst src port A 1 port 1 2 3 B 2 ... ... Store and Forward Segment Forward to selected port only: 1. listen to all traffic 2. store source and incomming port in cache 3. lookup destination in cache table - if not found: forward to all but incomming port - else: forward only to port stored in cache 4. age cache
Spanningtree Algorhyme from Radia Perlman updated • election of a root Bridge (lowest ID) I think that I shall never see • election of a designated Bridge for every segment a graph more lovely than a tree. > shortest distance to root > lowest ID A tree whose crucial property • removal of loops by blocking ports on segments other is loop-free connectivity. than the one closest to the root Bridge or for which the A tree that must be sure to span bridge is designated Bridge. so packet can reach every LAN. First, the root must be selected. Segment The Bridges are exchanging HELLO messages designated including: By ID, it is elected. - their ID 15 closest to root - ID of the bridge assumed to be root Bridge Least-cost paths from root are traced. - length of best known path to root Bridge 3 - etc. 27 In the tree, these paths are placed. A mesh is made by folks like me, closest to root then bridges find a spanning tree. Routing and Forwarding Three Switching Techniques • Routing: determine the route or path a packet has to follow. • Forwarding: move a packet from an input link to an appropriate output link (determined by the routing). Routing Forwarding
Recommend
More recommend