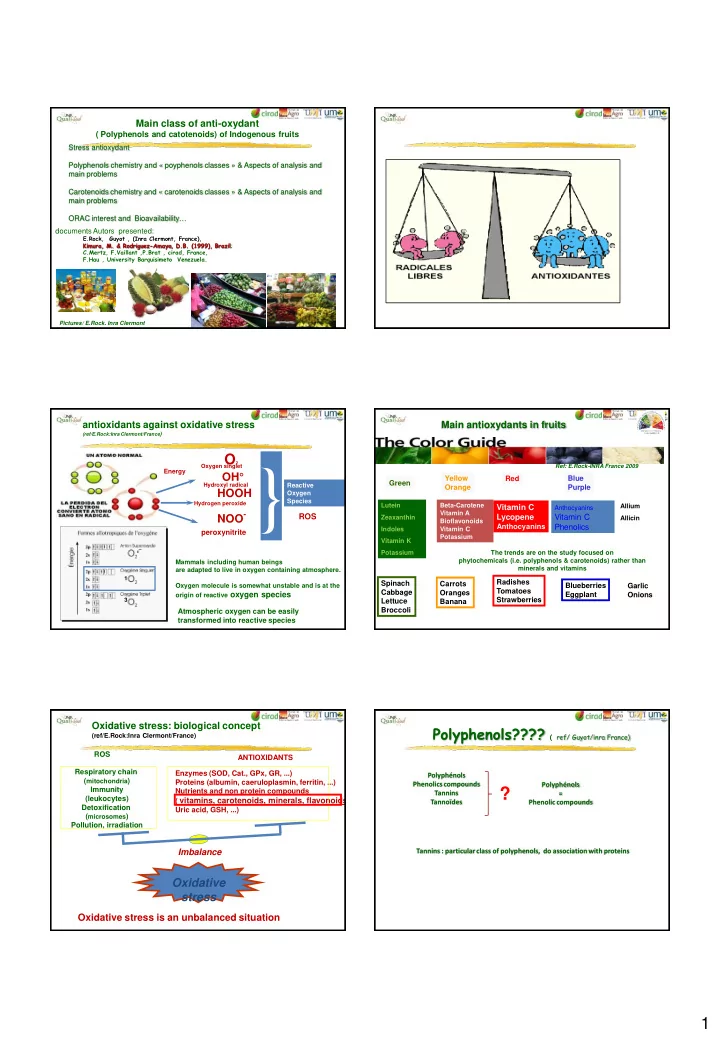

Main class of anti-oxydant ( Polyphenols and catotenoids) of Indogenous fruits Stress antioxydant Polyphenols chemistry and « poyphenols classes » & Aspects of analysis and main problems Carotenoids chemistry and « carotenoids classes » & Aspects of analysis and main problems ORAC interest and Bioavailability … documents Autors presented: E.Rock, Guyot , (Inra Clermont, France), Kimura, M. & Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. (1999), Brazil; C.Mertz, F.Vaillant ,P.Brat , cirad, France, F.Hau , University Barquisimeto Venezuela. Pictures/ E.Rock. Inra Clermont France antioxidants against oxidative stress Main antioxydants in fruits (ref/E.Rock:Inra Clermont/France ) O 2 NOO - } Oxygen singlet Ref: E.Rock-INRA France 2009 Energy OH° Yellow Blue Red Green White Hydroxyl radical Reactive Orange Purple HOOH Oxygen Species Hydrogen peroxide Lutein Beta-Carotene Allium Vitamin C Anthocyanins Vitamin A ROS Lycopene Vitamin C Zeaxanthin Allicin Bioflavonoids Anthocyanins Phenolics Indoles Vitamin C peroxynitrite Potassium Vitamin K •¯ Potassium The trends are on the study focused on phytochemicals (i.e. polyphenols & carotenoids) rather than Mammals including human beings minerals and vitamins are adapted to live in oxygen containing atmosphere. 1 Radishes Spinach Carrots Oxygen molecule is somewhat unstable and is at the Blueberries Garlic Tomatoes Cabbage Oranges origin of reactive oxygen species Eggplant Onions 3 Strawberries Lettuce Bananas Broccoli Atmospheric oxygen can be easily transformed into reactive species Oxidative stress: biological concept Polyphenols???? ( ref/ Guyot/inra France) (ref/E.Rock:Inra Clermont/France) ROS ANTIOXIDANTS Respiratory chain Enzymes (SOD, Cat., GPx, GR, ...) Polyphénols ( mitochondria ) Proteins (albumin, caeruloplasmin, ferritin, ...) Phenolics compounds Polyphénols Immunity ? Nutrients and non protein compounds Tannins = (leukocytes) ( vitamins, carotenoids, minerals, flavonoids Tannoïdes Phenolic compounds Detoxification Uric acid, GSH, ...) ( microsomes ) Pollution, irradiation Imbalance Tannins : particular class of polyphenols, do association with proteins Oxidative stress Oxidative stress is an unbalanced situation 1
POLYPHENOLS IN THE FOODS Some chemistry (2) ( ref: Guyot and al /inra-France) main combinations (ref/E.Rock:Inra Clermont/France) O structure and functionality O H H O O Hydrophil groups O H H H O H O H Esterification H O H OH O H O H H O O H C O H O H O H O H C C O H O O H O H • Physico-chimistry : solubility, O H O H O H H O O O H interact with polysaccharides, H O O C C O H O H O H O H protéins … O H H O O H O O O O H O H C H O H C H 2 O H Glycosylation O H O O H O H • Biochimistry reactivity:oxydation, H O O O H R etc … O H O H H O H H O O O H O H O H Thousands of molecules in the diet Hydrophob group Polymerisation Main class of polyphenols of interest in fruits Main class of polyphenols ( ref Wikipedia/ internet) Phenols acid simple C O O H C O O H Main class of polyphenols: Phenolic acids C6-C1ou C6-C3 simple polyphénol and phenolic O H O H acid flavonoids Cafeic acid Benzoic acid Gallic acid Vanillic acid coumarins & naphtaquinones tanins Main class of polyphenols Some chemistry (1) ( ref: Guyot and al /inra-France) Phenol group H Basic structure of this OH H C Main class of polyphenols: phenolic compound C C simple polyphénol and phenolic acid C C C H R : can be a sugar, organic acid flavonoids R H coumarins & nathataquinones Ex : Catéchin H H tanins C OH C C H POLY phénols C C H O C O C C C CH OH H C C CH C C H OH H 2 O H 2
Main class of polyphenols of interest in fruits Main class of polyphenols of interest in fruits ( ref Wikipedia/ internet) ( ref Wikipedia/ internet) Flavonoids(anti-oxydants+++) with or no aglycone, heterosides, methoxylation) Coumarins and naphta quinones Flavonols Coumarine aromatic compounds Flavones Isoflavones Flavonoids Flavanones C6-C3-C6 Flavanols Anthocyanids Naphta quinone Flavanone /hetrosides form:: cytotoxic, anti bacterian,.anti fungi, hesperidine, naringine) Flavonol ( rutine) Aglycones: quercetol, kamepferol Quercetol or (Quercetine) (aglycone form) Main class of polyphenols Main class of polyphenols of interest in fruits ( ref Wikipedia/ internet) Flavonoids(anti-oxydants+++) Flavanols , anthocyandols (with or no aglicones, gallates, polymeres, heterosides) Main class of polyphenols: simple polyphénol and phenolic acid flavonoids coumarins & nathataquinones Catéchine heterosid form: epicathechin Anthocyanidol : aglycone form: tanins exemple:pelargonidol, delphinidol or Anthocyanidin: hererosides forms: exemple :anthocyanes cyanidol 3,5 di glucoside Main class of polyphenols of interest in fruits Main class of polyphenols of interest in fruits ( ref Wikipedia/ internet) Tanins… class Acide ellagique Tanins complex: - ellagitanin and epicatechine - condensed tanins : flavonols polymer Gallo tanin 3
IMPORTANT PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF Basic polyphenols analysis CAROTENOIDS Kimura, M. & Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. (1999), Brazil; HPLC – UV : individual molecules analysis Quench singlet Scavenge or interact RT: 0.00 - 42.97 SM: 7B RT: 3.00 - 40.00 SM: 7B 18.73 NL: 18.65 NL: 100 3.91E7 100 8.14E6 oxygen with free radicals Base Peak F: 95 Base Peak F: 95 - c ESI Full - Advantages : very wel difrenciation - c ESI Full 90 ms [ 90 Après ms [ 50.00- 50.00- Avant 85 85 2000.00] MS 2000.00] MS OX0_DP04 - - 18.18 OX2-DP04 bteween polyphenolic compounds. 80 IO 4 IO 4 80 75 oxydation 75 oxydation 70 70 65 65 21.07 Relative Abundance 60 Relative Abundance 60 23.95 55 55 - limits: 50 50 16.87 26.19 45 45 40 40 - expensive 35 35 15.35 30 30 15.35 25 25 20 - Need standard molecules ( if exist) 20 14.40 CAROTENOIDS 15 19.75 15 Absorb light Lipophilic 10 27.19 10 28.51 14.49 30.53 - Sample preparation very long 5 5 3.15 12.06 31.99 35.54 39.65 13.17 20.65 24.24 7.83 8.91 0.57 3.28 6.20 8.72 11.00 27.89 29.62 33.55 36.47 37.86 41.89 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Time (min) Time (min) Chromatogrammes LC-MS « Base peak » Bind to hydrophobic Dosage de Folin-ciocalteu, total Polyphénol Easily isomerized content ( no diference between the Pp class, surfaces And oxidized A.Ascorbic) HPLC analysis …. examples (ref: C Mertz and al, 2007) POSSIBLE PROTECTIVE MECHANISMS AGAINST CHRONIC DISEASES - Extraction acetone/water/ formic acid Quenching of singlet oxygen - Qualitative (LC/MS) and quantitative analysis of major compounds Scavenging of peroxyl radicals ellagitannins and anthocyanins (blackberry) Modulation of carcinogen metabolism hydroxycinnamic acids (tree tomato, naranjilla), Inhibition of cell proliferation anthocyanins and kaempferol glycoside (red tree tomato) Enhancement of cell differentiation via - Analysis of minor compounds in blackberries retinoids liq-liq extraction with ethyl acetate Stimulation of cell-to-cell communication flavonols ( quercetin and kaempferol glycosides) Enhancement of the immune reponse ellagic acid glycosides Ref: Mertz and al, 7th International Food Data Conference. Sao Paulo, Oct.2007 Carotenoids Biology Compound Pro-Vitamin A Chemopreventive Induction Relative status activity of junctional inhibition of (Inhibition of C communication lipid peroxidation proliferation) The carotenoids ….. __________________________________________________________________________________ b -Carotene ++++ ++++ ++++ ++ Main reference in the area: Canthaxanthine - ++++ ++++ +++ Lutein - + +++ +++ Kimura, M. & Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. (1999), Brazil Lycopene - +(+) ++ +++ Vit E - + + ++++ Retinoic acid ++++ ++ +++ ND Acycloretinoic acid - +(+) + ND Kimura, M. & Rodriguez-Amaya, D.B. (1999), Brazil; 4
PRINCIPAL CAROTENOIDS IN FOODS CAROTENOIDS CONSIDERED IMPORTANT TO HUMAN HEALTH b -Carotene Lycopene OH OH OH b -Cryptoxanthin HO HO Lutein OH OH Lycopene OH OH HO HO Zeaxanthin HO HO Lutein CAROTENOIDS CONSIDERED IMPORTANT TO HUMAN HEALTH The and Antioxydant value b -Carotene And bioavailability approach OH b -Cryptoxanthin Total Carotenoid Total Carotene b -carotene The Antioxydant value Provitamins A Principal Carotenoids (Provitamin and Non-Provitamin A Carotenoids) Cis – and trans - isomers Complete carotenoid composition EVOLUTION OF CAROTENOID ANALYSIS 5
Recommend
More recommend