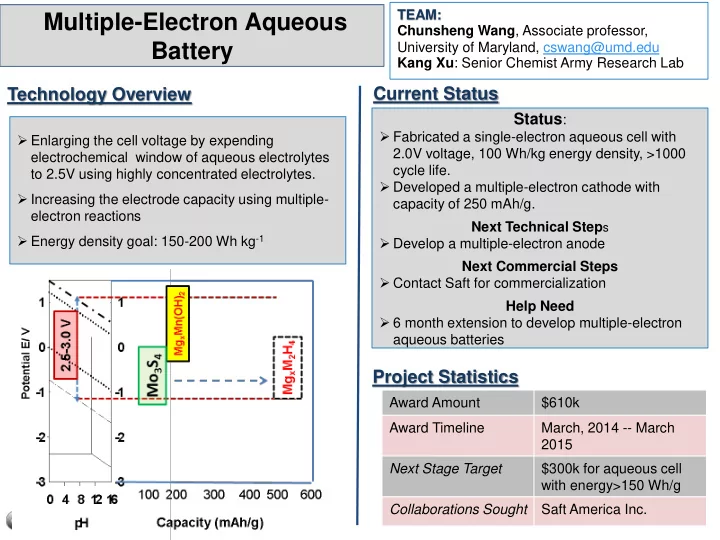

TEAM: Multiple-Electron Aqueous Chunsheng Wang , Associate professor, Battery University of Maryland, cswang@umd.edu Kang Xu : Senior Chemist Army Research Lab Technology Overview Current Status Status : Fabricated a single-electron aqueous cell with Enlarging the cell voltage by expending 2.0V voltage, 100 Wh/kg energy density, >1000 electrochemical window of aqueous electrolytes cycle life. to 2.5V using highly concentrated electrolytes. Developed a multiple-electron cathode with Increasing the electrode capacity using multiple- capacity of 250 mAh/g. electron reactions Next Technical Step s Energy density goal: 150-200 Wh kg -1 Develop a multiple-electron anode Next Commercial Steps Contact Saft for commercialization Help Need 6 month extension to develop multiple-electron aqueous batteries Project Statistics Award Amount $610k Award Timeline March, 2014 -- March 2015 Next Stage Target $300k for aqueous cell with energy>150 Wh/g Collaborations Sought Saft America Inc.
2.0V Aqueous single-electron lithium ion batteries 2.7V aqueous electrolyte (pH=7) Charge/discharge curves of 2.0V Cycling performance of high-voltage single-electron full cell. Capacity is aqueous Li-ion batteries based on the total mass of anode and cathode 2
2.0V aqueous single-electron lithium ion batteries Novel aqueous battery technologies beyond state-of-the-art aqueous Li-ion batteries 3
Multiple-electron MnO 2 Cathodes for Mg 2+ /H + batteries 0.0 -0.1 H + E vs.Ag/AgCl (V) Mg 2+ -0.2 -0.3 -0.4 WE: MnO2 CE: active carbon -0.5 RE: Ag/AgCl Electrolyte: 1M KOH-H2O -0.6 0 50 100 150 WE: MnO2, CE: active carbon Capacity (mAh/g) Electrolyte: Mg(NO3)2-Mg(OH2) Current: 100 mA/g 200mA/g 0.4 0.2 79% capacity comes from Mg 2+ E vs.Ag/AgCl (V) Mg 2+ insertion, the rest comes from H + 0.0 insertion -0.2 WE: MnO2 H + CE: active carbon -0.4 RE: Ag/AgCl Current: 200 mA/g Electrolyte: Mg(NO3)2-Mg(OH)2-H2O -0.6 0 20 40 60 80 100 Discharge capacity(mAh/g) 4
Multiple-electron Mo 3 S 4 Anodes for Mg 2+ /H + batteries Cycle stability of Mo 3 S 4 for Mg Mg insertion/extraction behavior of Mo 3 S 4 at insertion/extraction at 100 mA/g in 0.1M 100 mA/g in 0.1M Mg(BH 4 ) 2 /1.5M Mg(BH 4 ) 2 /1.5M LiBH 4 /diglyme organic LiBH 4 /diglyme organic electrolyte electrolyte 5
Project Status and Achievements Publications 1.5 1.5 1. T. Gao, F. Han, Y. Zhu, L. 1.0 1.0 2H 2 O = O 2 + 4H Suo, C. Luo, K. Xu and C. + + 4e Wang, Hybrid Mg 2+ /Li + - 0.5 0.5 Battery with Long Cycle Life H 2 O Potential E/ V MnO 2 cathode 0.0 0.0 and High Rate Capability, H 2 = 2H + 2e Advanced Energy Materials , -0.5 -0.5 - 2014, MgxMo 3 S 4 anode DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201401 -1.0 -1.0 507. Highlighted by -1.5 -1.5 Materials View. -2.0 -2.0 Mg-M alloys 2. L. Suo, et al, High energy Mg(OH) 2 aqueous Li-ion batteries. -2.5 -2.5 MgH 2 Submitted Mg -3.0 -3.0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 pH
Recommend
More recommend