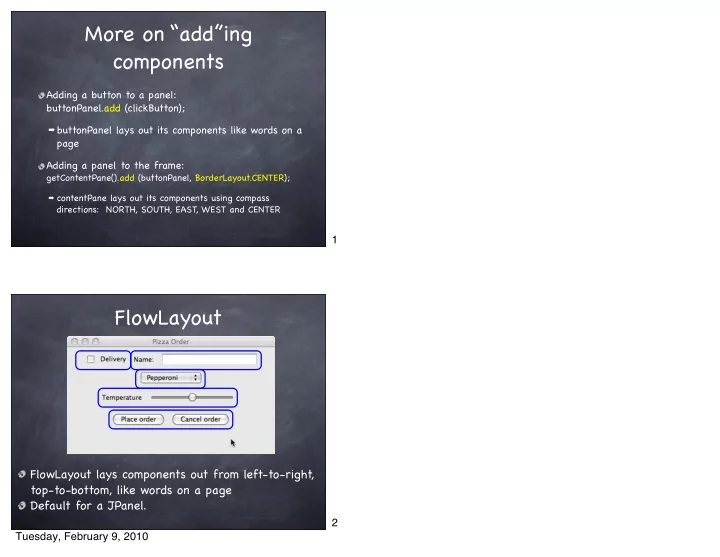

More on “add”ing components Adding a button to a panel: buttonPanel.add (clickButton); ➡ buttonPanel lays out its components like words on a page Adding a panel to the frame: getContentPane().add (buttonPanel, BorderLayout.CENTER); ➡ contentPane lays out its components using compass directions: NORTH, SOUTH, EAST, WEST and CENTER 1 FlowLayout FlowLayout lays components out from left-to-right, top-to-bottom, like words on a page Default for a JPanel. 2 Tuesday, February 9, 2010
BorderLayout NORTH WEST EAST SOUTH BorderLayout lays out components using compass directions + CENTER Default for a JFrame’ s content pane. 3 BorderLayout Rules One component per compass point Component expands to fill the entire area 4 Tuesday, February 9, 2010
What Gives??? EAST There are 2 buttons in the EAST! The buttons do not fill the entire east area! Conclusion: My professor lied to me! 5 Grouping Components with JPanel JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel.add (new JButton("Place order")); buttonPanel.add (new JButton("Cancel order")); contentPane.add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.EAST); 6 Tuesday, February 9, 2010
FlowLayout A JPanel uses FlowLayout as its layout manager rather than BorderLayout. With BorderLayout, we say: contentPane.add (buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); With FlowLayout, we omit the compass direction: buttonPanel.add(easy); Components are added from left to right. 7 FlowLayout There are 2 buttons in the button panel. buttonPanel.add (orderButton); There is 1 button panel in the EAST. buttonPanel.add (cancelButton); FlowLayout sizes components in a more natural way. Conclusion: My professor didn’ t lie to me! 8 Tuesday, February 9, 2010
BoxLayout JPanel buttonPanel = new JPanel(); buttonPanel.setLayout(new BoxLayout(buttonPanel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS)); buttonPanel.add (new JButton("Place order")); buttonPanel.add (new JButton("Cancel order")); contentPane.add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.EAST); 9 BoxLayout BoxLayout constructor: BoxLayout(Container target, int axis) target is the component whose layout we are setting axis is either BoxLayout.X_AXIS or BoxLayout.Y_AXIS colorPanel.setLayout ( new BoxLayout (colorPanel, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS)); 10 Tuesday, February 9, 2010
JPanel gives “natural” size contentPane.add(comboBox, BorderLayout.SOUTH); toppingsPanel.add (comboBox); contentPane.add(toppingsPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); 11 GridLayout Specify # of rows and # of columns to create a grid Each component gets the same size 12 Tuesday, February 9, 2010
GridLayout JPanel sliderPanel = new JPanel(); / / Use 3 rows and as many columns as necessary. sliderPanel.setLayout (new GridLayout(3, 0)); redSlider = new JSlider(...); redLabel = new JLabel("Red", JLabel.RIGHT); redValueLabel = new JLabel("0", JLabel.LEFT); / / Do similar stuff for blue and green / / Add red components. Each component goes / / in the next place in the grid. sliderPanel.add(redLabel); sliderPanel.add(redSlider); sliderPanel.add(redValueLabel); / / Add green and blue components Container contentPane = getContentPane(); contentPane.add(sliderPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH); 13 JLabels public void begin() { ... redSlider = new JSlider(...); redLabel = new JLabel("Red", JLabel.RIGHT); redValueLabel = new JLabel("0", JLabel.LEFT); ... } public void stateChanged(ChangeEvent evt) { / / Get component color values & update label int redValue = redSlider.getValue(); redValueLabel.setText("" + redValue); / / Repeat for blue and green / / Create the new color and make it the color for colorRect Color newColor = new Color(redValue, greenValue, blueValue); colorRect.setColor(newColor); } 14 Tuesday, February 9, 2010
JLabel JLabel constructor: JLabel(String text) JLabel(String text, int horizontalAlignment) where horizontalAlignment is JLabel.LEFT, JLabel.RIGHT or JLabel.CENTER Changing the label void setText(String text) A JLabel is for output only; there are no listeners or event handling associated with JLabels 15 Layout Manager Summary BorderLayout - uses compass points FlowLayout - naturally-sized components, laid out left-to-right BoxLayout - X_AXIS or Y_AXIS GridLayout - fixed # of rows and columns, all cells equal size 16 Tuesday, February 9, 2010
Recommend
More recommend