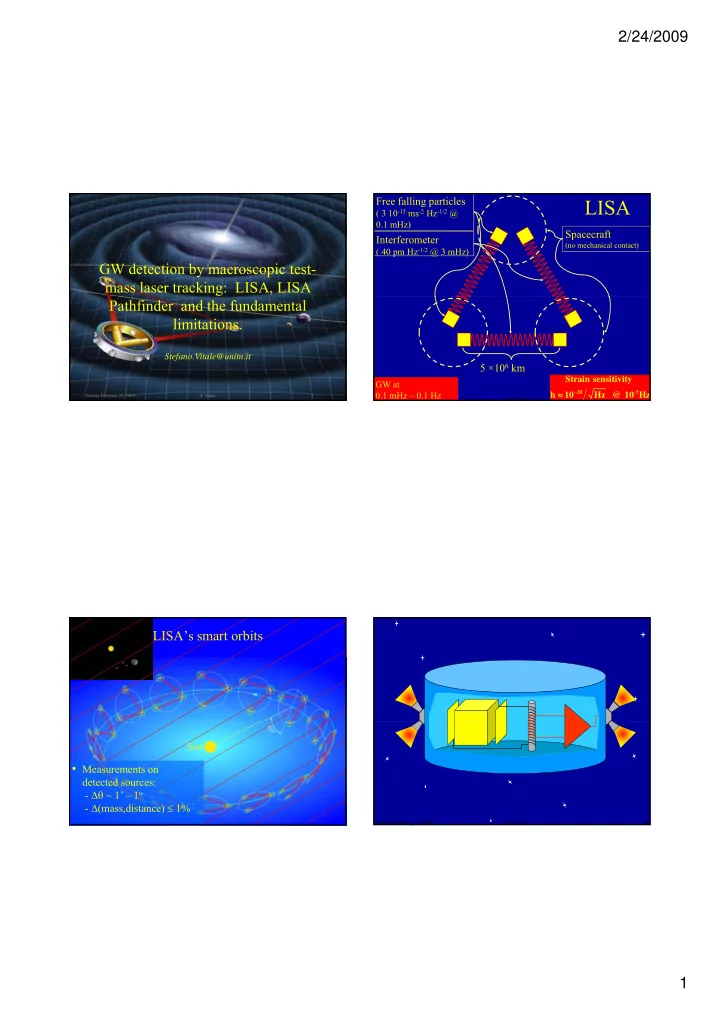

2/24/2009 Free falling particles LTP LTP LISA ( 3 10 -15 ms -2 Hz -1/2 @ 0.1 mHz) Spacecraft Interferometer (no mechanical contact) ( 40 pm Hz -1/2 @ 3 mHz) GW detection by macroscopic test- mass laser tracking: LISA, LISA Pathfinder and the fundamental limitations. Stefano.Vitale@unitn.it 5 ×10 6 km Strain sensitivity GW at ≈ − 0.1 mHz – 0.1 Hz 20 -3 h 10 Hz @ 10 Hz Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 1 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 2 LISA’s smart orbits • Measurements on detected sources: - Δθ ~ 1’ – 1 o - Δ (mass,distance) ≤ 1% Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 3 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 4 1
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP displacement sensor displacement sensor injection injection electrode Ac amplifier electrode Ac amplifier Test Test PSD PSD mass mass Ac bias Ac bias Optical readout along the sensitive axis Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 5 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 6 LTP LTP LTP LTP • Drag-free along sensitive direction • Test-mass control along the remaining ones • 2 kg Au-Pt test-mass • 4 mm gaps φ & z z θ & y θ η y φ η & x x Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 7 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 8 2
2/24/2009 The GW from difference of phase in adjacent arms The laser 2-ways Doppler link The standard GW interferometer A Laser Transponder Laser phase noise common to both arms: GW signal from difference: laser noise is suppressed Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 9 Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 10 LISA unequal arms confuse phases L ± 10 5 km L Need to recombine light emitted at equal times Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 11 Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 12 3
2/24/2009 LTP LTP Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 14 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 13 vitational Noise Newtonian Grav Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 16 Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 15 4
2/24/2009 Massive Binary Black Holes: strong signals Supermassive BH Contours of SNR, equal mass merger (optimal) In the center of (all) galaxies Form binaries upon Redshift � galaxies collision Strong SNR Galactic binaries Mass � Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 18 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 17 Black-hole merger tree Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 20 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 19 5
2/24/2009 LISA Pathfinder LISA Pathfinder. Experimental demostration of Hawking theorems: Growth of BH area No-hair theorem Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 21 Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 22 LTP LTP LTP LTP The basic element of one LISA arm: the “Doppler link” The basic element of one LISA arm: the “Doppler link” emitter am em-bea receiver Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 23 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 24 6
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP Measuring relative velocity along the line of sight Time delay: to be pictured in space-time � � � v v v emitter emitter emitter emitter c k c k c k ( ) ( ( ) ) ( ) ( ) ( ( ) ) ( ) ( ) Δν = − light ⋅ μ − − μ Δν = − Δν = − light light ⋅ ⋅ μ μ − − − − μ μ v t L c v t v v t t L c L c v v t t μ μ μ π emitter receiver π π emitter emitter receiver receiver 2 � 2 2 y light k � � light light k k am em-bea L t � v receiver receiver � � x v v receiver receiver Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 25 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 26 LTP LTP LTP LTP What does change relative velocity along the line of What does change relative velocity along the line of sight? sight? � � v v emitter emitter � � y y light light k k t t • Gravity: � � v v – Parallel transport receiver receiver x x Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 27 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 28 7
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP What does change relative velocity along the line of What does change relative velocity along the line of sight? sight? � � v v emitter emitter Rotation of the line of sight � � y y light light True forces that accelerate test-masses k k t t � � v v receiver receiver x x Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 29 29 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 30 LTP LTP LTP LTP What does change relative velocity along the line of The problem of staged links sight? � v emitter � Body Body Body y Test- Test- light Interferometer measurement noise (spacecraft, (spacecraft, (spacecraft, k mass mass optical bench..) optical bench..) optical bench..) • Links are split as test-masses cannot carry optics • Perfect split is insensitive to motion of body (bodies) • Misalignments, calibration errors mix motion of extra bodies in t � v receiver x Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 31 Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 32 8
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP An Input-Output Description An Input-Output Description Parasitic Parasitic Displacement Displacement Differential Differential readout noise Equivalent force readout noise Forces Forces Difference of Difference of Relative Relative Force Force GW- GW- Displacement p Displacement p Diff Differential i l Diff Differential i l D Doppler Arm l A D Doppler Arm l A Acceleration Acceleration Other bodies Other bodies displacement displacement Equivalent force Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 33 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 34 LTP LTP LTP LTP Differential acceleration performance Differential acceleration performance Parasitic acceleration of test- masses A “Universal” plot Measurement noise δ ≈ ω δ a 2 x eq Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 35 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 36 9
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP GP-A Cassini Firenze February 23, S. Vitale Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 37 38 LTP LTP LTP LTP Microscope GOCE-Grace Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 39 Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 40 10
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP Testing on Ground • Surface forces – Mostly originated from the nearest surroundings of test-mass • Volume forces – Magnetics – Locally generated gravitation Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 41 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 42 LTP LTP LTP LTP Test-mass nearest Assessing surface parasitic forces on ground: the torsion surroundings and shield: pendulum the GRS Test-mass Disturbing surroundings (GRS) Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 43 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 44 11
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP ≤ − 15 10 N Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 45 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 46 Work-function patches create stray voltages LTP LTP LTP LTP Couple to test-mass noisy charge and create force. Fluctuate over time Force per unit charge or test-mass potential 0-force: stray voltage has been compensated Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 47 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 48 12
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP 40 micron Silica Fiber Q=10 6 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 49 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 50 LTP LTP LTP LTP Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 51 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 52 13
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 53 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 54 LTP LTP LTP LTP LISA Pathfinder • Take one spacecraft • Take one LISA Doppler Link • Squeeze it into the spacecraft Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 55 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 56 14
2/24/2009 LTP LTP Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 57 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 58 LTP LTP LTP LTP Implement LISA Geodesic Link within a factor 10 Limited by features of Find a route to test (extra forces, poorer environment) project to LISA Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 59 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 60 15
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP Pathfinder → LISA • Fly nominal LISA hardware on Pathfinder: – Maximize returns of the test – Shortens time to develop LISA • Identify quantitatively leading sources of noise: – Physical model allows extrapolation to LISA – Will allow accurate understanding of LISA data Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 61 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 62 LTP LTP LTP LTP Gravitational balance Practicing routing and packaging Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 63 Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 64 16
2/24/2009 LISA Hardware LTP LTP LTP LTP Firenze February 23, S. Vitale 65 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 66 LTP LTP LTP LTP Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 67 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 68 17
2/24/2009 LTP LTP LTP LTP 40 micron Silica Fiber Q=10 6 40 micron Silica Fiber Q=10 6 LPF Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 69 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 70 LTP LTP LTP LTP Pathfinder interferometry and the Potential local LISA readout relevance to LISA Test- Test- Spacecraft Spacecraft mass mass 5×10 6 km • LISA link is 3-stage • LISA pathfinder has no spacecraft → spacecraft link • A test of the local interferometric readout for LISA • A test of the test-mass → spacecraft → test-mass split link Albert Einstein Institute Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 71 Firenze February 23, 2009 S. Vitale 72 18
Recommend
More recommend