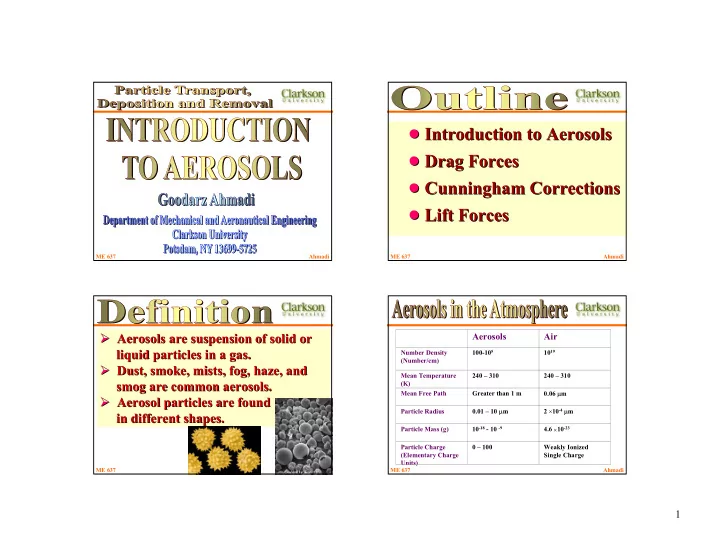

! Introduction to Aerosols Introduction to Aerosols ! ! Drag Forces Drag Forces ! ! Cunningham Corrections Cunningham Corrections ! ! Lift Forces Lift Forces ! ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi � Aerosols are suspension of � Aerosols are suspension of solid or solid or Aerosols Air liquid particles in a gas. liquid particles in a gas. Number Density 100-10 5 10 19 (Number/cm) � Dust, smoke, mists, fog, haze, and � Dust, smoke, mists, fog, haze, and Mean Temperature 240 – 310 240 – 310 smog are common aerosols. . smog are common aerosols (K) 0.06 µ m Mean Free Path Greater than 1 m � Aerosol particles are found � Aerosol particles are found 2 10 -4 µ m 0.01 – 10 µ m × Particle Radius in different shapes. . in different shapes 10 -18 - 10 -9 Particle Mass (g) 4.6 10 -23 × Particle Charge 0 – 100 Weakly Ionized (Elementary Charge Single Charge Units) ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi 1
λ = Mean Free Path λ Knudsen Number λ = Mean Free Path ν = = Kinematic Kinematic Viscosity Viscosity Knudsen Number 2 ν = Kn d d = Particle Diameter D = Diffusivity d = Particle Diameter D = Diffusivity Mach Number Mach Number v − p f | v | = M p = Particle Velocity f c v p = Particle Velocity v’ ’ = Thermal Velocity = Thermal Velocity v v Schmidt Number Schmidt Number ν f λ 2 n d = = f = Fluid (Air) Velocity Sc p v f = Fluid (Air) Velocity n = Number Density v n = Number Density D 4 f f Brown Number Brown Number v p , 2 | v ' p | c = Speed of Sound c = Speed of Sound = 1 / 2 = Br ( ) f , 2 f v | v ' | p − f Reynolds Number Reynolds Number | v v | d 4 M = = Re ν K n ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi Particle Diameter, µm 4 10 − 4 10 − 3 10 − 2 10 − 1 0 1 2 3 10 10 10 10 10 1 kT Electro. λ = = Infrared Microwaves X-Ray UV Vis Wave π 2 π 2 2 nd 2 d P Solid Fume Dust Definition m m Mist Spray Liquid Clay Silt Sand Gravel Soil p Molecular Molecular f = × -23 k 1.38 10 J / K f Atmospheric Smog Cloud/Fog Mist Rain Diameter Diameter Typical Viruses Bacteria Hair Particles Smoke Coal Dust Beach Sand Microscopy 23 . 1 T Size λ µ = Electron Microscopy Sieving Air ( m ) Air Analysis Ultra Centrifuge Sedimentation P methods ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi 2
µm Particle Diameter, 4 10 − 10 − 10 − 10 − 10 4 3 2 1 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 π F = 3 µUd Ultrasonic Settling Chamber Stokes Stokes Centrifuge Gas Cleaning Air Filter Method HE Air Filter Impact Separator F 24 Thermal Separator = = C D Drag Drag Electrostatic Separator D 1 Re ρ 2 Coefficient U A Coefficient × − 2 10 − 5 × − 9 × − 11 5 10 2 10 2 10 Air Diffusion 2 Coeff. cm 2 /s Water × − 12 × − × − × − 5 10 5 10 6 5 10 8 5 10 10 Reynolds Reynolds × − 10 − 6 2 10 4 0 . 6 Terminal 600 ρ = Ud Air Velocity cm/s − Number Number Re 10 − 10 × − 7 × 3 Water 6 10 6 10 12 S=2 µ ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi + 24 [ 1 3 Re/ 16 ] = C D Oseen Oseen Re C D + 0 . 687 24 [ 1 0 . 15 Re ] < < 1 Re 1000 = C D Re Newton Newton C D = 0 . 4 Re 3 < < × 5 10 Re 2 . 5 10 ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi 3
1000 For 1000 > For 1000 > Kn Kn > 0 > 0 πµ 3 Ud 100 Experiment Stokes Stokes- -Cunningham Cunningham = F D Drag Drag C CD Oseen 10 c Eq. (5) Stokes Cunningham Cunningham Newton 1 Correction Correction 0 λ 2 0 1 10 100 1000 10000 = + + − λ 1 . 1 d / 2 C 1 [ 1 . 257 0 . 4 e ] Re c d Predictions of various models for drag coefficient for a spherical particle. al particle. Predictions of various models for drag coefficient for a spheric ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi c Variations of C c with d for λ λ = 0.07 = 0.07 µ µm m 1000 Variations of C c with d for Diameter, µm C 100 c 10 µm 1.018 Cc 10 1 µm 1.176 0.1 µm 3.015 1 0.01 µm 23.775 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 Kn 0.001 µm 232.54 Variation of Cunningham correction with Knudsen number. Variation of Cunningham correction with Knudsen number. ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi 4
= πµ F 3 Ud K + µ µ f p 1 2 / 3 = πµ f F 3 Ud D e D + µ µ f p 1 / 6 = 1 / 3 d ( Volume ) e π = πµ f F 2 Ud For Bubbles For Bubbles D K=Correction Factor K=Correction Factor ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi p d u τ = − + τ f p ( u u ) g Drag dt Gravity Relaxation Time Relaxation Time Equation of Motion Equation of Motion 2 ρ p 2 mC d C Sd C ρ p τ = = = c c c = πµ p S d u 3 d ρ f πµ µ ν = f − p + 3 d 18 18 m ( u u ) m g dt C c τ ≈ × − µ 6 2 ( s ) 3 10 d ( m ) ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi 5
Stopping Distance = Penetration distance for Stopping Distance = Penetration distance for − τ p = f + τ − t / u ( u g )( 1 e ) an initial velocity of u u o an initial velocity of o − τ p = t / = τ − − t τ p p / u u e x u ( 1 e ) Terminal Velocity = Equilibrium Velocity after Large Time Terminal Velocity = Equilibrium Velocity after Large Time o o ρ p 2 d gC = τ p p x u = τ = t u g c o µ 18 µ ≈ µ p 2 x ( m ) 3 d ( m ) t µ ≈ 2 µ u ( m / s ) 30 d ( m ) ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi Diameter, Terminal τ sec Stopping Stopping − τ = + τ − p p p t / x x u ( 1 e ) µm Velocity Distance Distance o o u= 1 m/s u= 10 m/s − τ + + τ − τ − f t / ( u g )[ t ( 1 e )] 4 × 10 -8 0.05 0.39 µ m/s 0.04 µ m 0.0004 mm 9.1 × 10 -8 0.1 0.93 µ m/s 0.092 µ m 0.0009 mm 1 × 10 -6 0.5 10.1 µ m/s 1.03 µ m 0.0103 mm Components Components 3.6 × 10 -6 1 35 µ m/s 3.6 µ m 0.0357 mm τ g p f τ = τ − − − t / τ 7.9 × 10 -5 x / u [ t / ( 1 e )] 5 0.77 mm/s 78.6 µ m 0.786 mm α = f τ u 3.1 × 10 -4 10 3.03 mm/s 309 µ m 3.09 mm τ = − α τ − − − τ p f t / y / u [ t / ( 1 e )] 7.6 × 10 -3 50 7.47 cm/s 7.62 mm 76.2 mm ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi 6
0 0 α =0.1 α =0.1 -2 -2 -4 -4 α =1 y/utau y/utau α =1 -6 -6 -8 -8 α =2 -10 -10 α =2 -12 -12 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 x/utau t/tau Variations of the particle vertical position with time. Variations of the particle vertical position with time. Sample particle trajectories. Sample particle trajectories. ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi p πµ p d u 3 d 1 d u 1 + = − + − a f p f + τ = f − p + τ − ( m m ) ( u u ) ( m m ) g ( 1 ) ( u u ) g ( 1 ) dt C 2 S dt S c π ρ 3 f d Terminal Velocity Terminal Velocity f = m Fluid Mass Fluid Mass 6 ρ ρ p 2 f 1 d gC = τ − = − t u g ( 1 ) c ( 1 ) 1 a = f µ ρ p m m . S 18 Apparent Mass Apparent Mass 2 ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi 7
Lift − f p Ω 2 | u u | d d = << = << R 1 R 1 Ω es ν e ν u f u p 1 / 2 R γ 2 eG >> = & d = << ε 1 R 1 eG ν R Saffman (1965, 1968) (1965, 1968) Saffman es f f du du McLaughlin (1991) = ρν 1 / 2 2 f − p 1 / 2 McLaughlin (1991) F 1 . 615 d ( u u ) | | sgn( ) L ( Saff ) dy dy ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi McLaughlin (1991) McLaughlin (1991) Lift ⎧ − − ε 2 ε >> 1 0 . 287 for 1 F = L ⎨ − ε ε − ε << F 5 2 140 ln( ) for 1 ⎩ L ( Saff ) Leighton and Leighton and = ρ γ 4 2 F 0 . 576 d & Acrivos (1985) (1985) − Acrivos L ( L A ) = ρν γ 1 / 2 3 3 / 2 Saffman F 0 . 807 d & Saffman L ( Saff ) ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi 8
* 2 1.00E+03 u F * du γ = + = F L Experiment + = 1.00E+02 d L ν ρν 2 ν 1.00E+01 Saffman Mollinger 1.00E+00 Fl+ 1.00E-01 + = + + = + Hall 4 3 F 0 . 576 d F 0 . 807 d 1.00E-02 − L ( L A ) L ( Saff ) 1.00E-03 Leighton 1.00E-04 Hall (1988) Hall (1988) 1.00E-05 Mollinger Mollinger and and Nieuwstadt Nieuwstadt (1996) (1996) 0.1 1 10 + = + 2 . 31 d+ F 4 . 21 d + = + 1 . 87 F 15 . 57 d L ( Hall ) L ( MN ) ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi ! Introduction to Aerosols Introduction to Aerosols ! ! Drag Forces Drag Forces ! ! Cunningham Corrections Cunningham Corrections ! ! Lift Forces Lift Forces ! ME 637 Ahmadi ME 637 Ahmadi 9
Recommend
More recommend