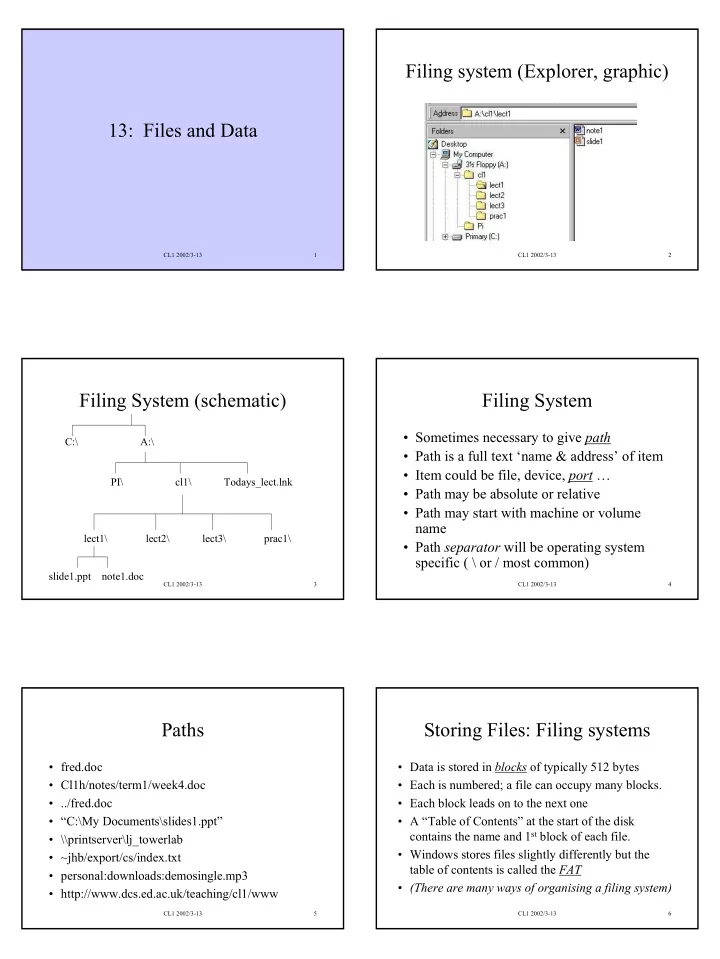

Filing system (Explorer, graphic) 13: Files and Data CL1 2002/3-13 1 CL1 2002/3-13 2 Filing System (schematic) Filing System • Sometimes necessary to give path C:\ A:\ • Path is a full text ‘name & address’ of item • Item could be file, device, port … PI\ cl1\ Todays_lect.lnk • Path may be absolute or relative • Path may start with machine or volume name lect1\ lect2\ lect3\ prac1\ • Path separator will be operating system specific ( \ or / most common) slide1.ppt note1.doc CL1 2002/3-13 3 CL1 2002/3-13 4 Paths Storing Files: Filing systems • fred.doc • Data is stored in blocks of typically 512 bytes • Cl1h/notes/term1/week4.doc • Each is numbered; a file can occupy many blocks. • ../fred.doc • Each block leads on to the next one • “C:\My Documents\slides1.ppt” • A “Table of Contents” at the start of the disk contains the name and 1 st block of each file. • \\printserver\lj_towerlab • Windows stores files slightly differently but the • ~jhb/export/cs/index.txt table of contents is called the FAT • personal:downloads:demosingle.mp3 • (There are many ways of organising a filing system) • http://www.dcs.ed.ac.uk/teaching/cl1/www CL1 2002/3-13 5 CL1 2002/3-13 6
A basic filing system Fragmentation Table of contents • Moving a disk read head is (relatively) slow File1 1 File2 4 • Files are accessed fastest when the blocks are File3 7 contiguous (all together) and the head doesn’t have to move far • Fragmentation is a process where parts of files are scattered over the disk and reduces efficiency and 3 4 Block 1 2 disk eventually needs defragmentation 2 3 5 – As follows… 6 8 5 6 7 8 … CL1 2002/3-13 7 CL1 2002/3-13 8 Fragmentation Filing system + free list Table of contents Delete File3 File1 1 File_a b file_c d file_e f file_g File2 4 Delete b, d and f: Free 7 Add new file h, length 3 blocks: 3 4 Block 1 2 2 3 5 Repeated deletion and addition of files leaves disk fragmented 6 8 5 6 7 8 … CL1 2002/3-13 9 CL1 2002/3-13 10 Free block list and non-deletion Formatting disk for initial use • Low-level formatting writes empty blocks of the right • All blocks not in use are linked together in a characteristics on the disk. special file called the free block list. • Partitioning designates areas for file systems • To delete a file all you need to do is: • (High-level) formatting writes an empty filing – Transfer the blocks to the free block list system on the disk partition, e.g. – Remove the file entry from the table of contents • This does not destroy the data in the file Free 1 All blocks in the partition • Such files can easily be undeleted • Remember this when giving a disk to someone else • Formatting a disk need not destroy files beyond recovery either CL1 2002/3-13 11 CL1 2002/3-13 12
The file locking problem Image files • An update is a read then a write • Grid of pixels • Each has to represent a colour • “A” reads item • Colour is defined by proportions of Red, Green • “B” reads item and Blue (RGB) • “A” writes back updated item • Describe each of R,G,B accurate to 1 part in 256 • “B” writes back differently updated item • Each pixel needs 3 bytes = 24 bits • “A”’s update is lost • Full screen @ 800*600 requires 1.44 Mbytes • Careful design of ‘atomic’ transactions • 3-5 minutes @ 56Kbits/sec (modem line) CL1 2002/3-13 13 CL1 2002/3-13 14 Colour maps and LUTs Data Compression • A diagram or slide could have only a few colours • Full-screen Web page • Rather than represent each pixel by 3 bytes, keep a – PC screen: 800*600 * 3 = 1.44 Mbytes lookup-table (LUT) or colour map of colours and – @ 56 Kbit/sec modem = about 4 minutes. for each pixel store the index in that table • Videoconference link (NetMeeting) • Similar process used in video cards and – Image: 160 * 128 * 1 = 20Kbytes applications; only so many colours can be displayed at once – @ 56 Kbit modem = 1 frame / 3 secs • (can get strange effects when different • Doesn’t happen (!); what’s going on? applications are using different colour maps) • Data Compression CL1 2002/3-13 15 CL1 2002/3-13 16 Run-length encoding File and Image Compression • (see Compression slide) Image: 11 * 11 = 121 pixels. • Run-length encoding Transmit (no encoding): width=11,height=11, data= 0,0,0, … 0,1,0 … • Inefficient if no runs, e.g. 0,1,0 … 0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0 … – 1234 1234 1234 1234 … = 123 pieces of real information (width, height, 121 pixel values) • Better techniques Transmit (with run-length encoding): width=11,height=11, 0(27),1(1), 0(10), 1(1), 0(10), … =32 pieces of real information (width, height, 15 * (value * length)) Simple run-length encoding CL1 2002/3-13 17 CL1 2002/3-13 18
Compression BSTW Compression (lossless) • Saves transmission time and space • File is read word by word • Lossless: Can recover original data exactly • Once read, words are put in a table – Data, text, executable program • Words that repeat are referred to by their position in the table – E.g. Lempel-Ziv (used by Zip programs) • Lossy: Information is lost • Table position is adjusted on-the-fly to put frequent words at the top (shorter reference) – Pictures of real world; video link; MP3 music – Only care that it is good enough . Specify quality • Compression & decompression programs – E.g. JPEG, MPEG both know the rules by which this is done CL1 2002/3-13 19 CL1 2002/3-13 20 File and Image Compression Teddy bears • Simple run-length encoding – Lossless; not very efficient for images (no runs) • GIF – Lempel-Ziv encoding – Lossless; can be very efficient • JPEG – Lossy (losses increase each time it is rewritten) – Have trade-off: quality v. compression CL1 2002/3-13 21 CL1 2002/3-13 22 Teddy Bears Choice of image formats • JPG – Lossy; Ideal for real-world images, pictures • BMP – Degree of compatibility with Windows • GIF – Lossless; max 256 colours; Diagrams, clip art • TIFF – Lossless; good colour rendition (24-bit) ‘reference’ format – browsers won’t handle it; large files • Kodak Photo-CD – Filing system+format; picture stored at several resolutions CL1 2002/3-13 23 CL1 2002/3-13 24
Other formats Single (private) key encryption (DES) Sender Original message • MPEG, AVI, QuickTime – video Sender’s Key Encrypt • MP3, WAV – music and sound • DXF – AutoCAD drawing exchange … Lòce ŷ eOjz91 … • CSV – Comma Separated Variable Send as attachment – spreadsheet, database, any simple tables Sender’s Key Decrypt Recipient • CODECS – on-the-fly coder/decoders for real-time video Original message Key is weak spot – has to be sent to recipient somehow CL1 2002/3-13 25 CL1 2002/3-13 26 Dual (public) key encryption (PGP) Public Key encryption (e.g. PGP) Sender Original message • I publish public key that encrypts only Recipient’s Public Key Encrypt • You use my public key to encrypt and send me encrypted file … Lòce ŷ eOjz91 … • I use my associated private key to decrypt it (no contact) • Limitation: Can’t publish a single encrypted Send as attachment document for all to read Recipient’s Private Key Recipient Decrypt • Key-signing parties: People get together and validate each other’s keys; validation is part of key Original message Public key is weak point – could be compromised. Key- CL1 2002/3-13 27 CL1 2002/3-13 28 signing parties guard against this Key Points • Filing system – blocks; how they’re linked • Formatting, fragmentation, free list • Why deleting file doesn’t wipe data • Colours – RGB • Choice of image file formats • Lossy and lossless data compression • Encryption and vulnerability CL1 2002/3-13 29
Recommend
More recommend