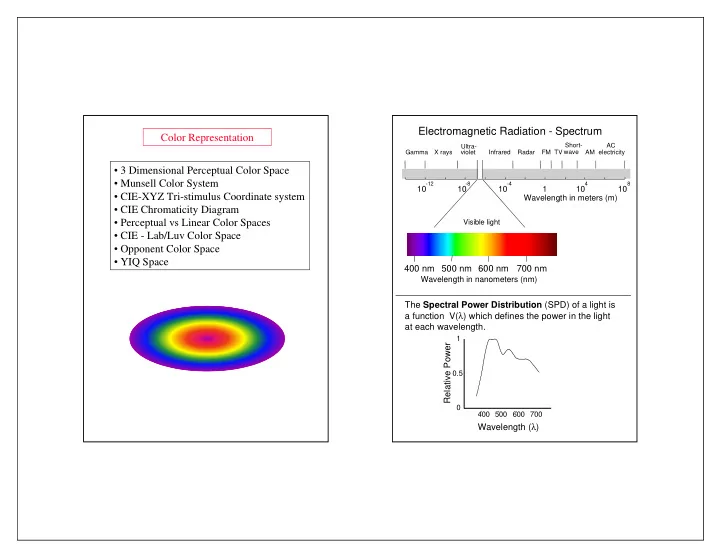

Electromagnetic Radiation - Spectrum Color Representation Short- AC Ultra- Gamma X rays violet Infrared Radar FM TV wave AM electricity • 3 Dimensional Perceptual Color Space • Munsell Color System -12 -8 -4 4 8 10 10 10 1 10 10 • CIE-XYZ Tri-stimulus Coordinate system Wavelength in meters (m) • CIE Chromaticity Diagram • Perceptual vs Linear Color Spaces Visible light • CIE - Lab/Luv Color Space • Opponent Color Space • YIQ Space 400 nm 500 nm 600 nm 700 nm Wavelength in nanometers (nm) The Spectral Power Distribution (SPD) of a light is a function V( λ ) which defines the power in the light at each wavelength. 1 Relative Power 0.5 0 400 500 600 700 Wavelength ( λ )
Rgb Image Examples of Spectral power Distributions 111 14 126 36 12 36 1 1 36 36 111 12 17 111 200 36 12 36 14 36 36 17 111 200 36 12 200 111 14 126 17 111 14 36 12 36 14 36 0.5 0.5 10 128 126 200 12 111 36 36 111 36 14 36 17 111 14 126 17 111 17 36 36 14 36 72 17 126 72 126 17 111 12 126 200 36 12 36 12 17 126 17 111 200 0 200 36 12 36 12 126 0 400 500 600 700 400 500 600 700 14 200 36 12 126 17 72 12 17 111 14 36 Blue Skylight Tungsten bulb 126 200 111 14 36 72 128 126 200 12 111 10 1 1 36 12 17 72 106 155 200 36 12 36 14 36 111 14 126 36 12 36 17 36 36 14 36 72 200 111 14 126 17 111 36 36 111 12 17 111 12 17 126 17 111 200 0.5 0.5 36 36 111 36 14 36 36 17 111 200 36 12 14 200 36 12 126 17 17 126 72 126 17 111 14 12 36 36 14 36 126 200 111 14 36 72 0 0 200 36 12 36 12 126 400 500 600 700 400 500 600 700 17 111 14 126 17 111 Red monitor phosphor Monochromatic light 36 12 17 72 106 155 72 12 17 111 14 36 12 36 126 200 36 12
Color Matching Trichromatic Color Theory Color Matching - behavioral basis for color Trichromatic: “tri”=three “chroma”=color representation. color vision is based on three primaries (i.e., it is 3 dimensional). Metamer - two lights that appear the same visually. They might have different SPDs Thomas Young (1773-1829) - (spectral power distributions). A few different retinal receptors operating with different wavelength sensitivities will allow humans to perceive the number of colors that they do. Tungsten light Monitor emission Suggested 3 receptors. 800 200 Helmholtz & Maxwell (1850) - Power Color matching with 3 primaries. 400 100 0 0 400 500 600 700 400 500 600 700 Wavelength (nm) The phosphors of the monitor were set to match the tungsten light.
Color Matching Experiment The Human Eye test match Lens - + Cornea Fovea Optic Nerve + - Vitreous Pupil Humor - + Optic Disc Iris Retina Ocular Muscle Three primary lights are set to match a test light. Test light Match light 1 1 ~ 0.75 0.75 = 0.5 0.5 0.25 0.25 0 0 400 500 600 700 400 500 600 700
The Human Retina Retinal Photoreceptors Cones - • High illumination levels (Photopic vision) • Less sensitive than rods. cones rods • 5 million cones in each eye. • Only cones in fovea (aprox. 50,000). • Density decreases with distance from fovea. • 3 cone types differing in their spectral sensitivity: L , M, and S cones. horizontal bipolar Cone Spectral Sensitivity amacrine ganglion 1 L M Relative sensitivity S 0.75 light 0.5 0.25 0 400 500 600 700 Wavelength (nm)
Color Representations 3D Color Spaces • Color Order Systems G Cubic Color Spaces (Munsell, HLS, HSV) B R • Linear Color Spaces (RGB, XYZ) Brightness • Perceptual Color Spaces Hue (Luv, Lab) Polar Color Spaces • Opponent Color Spaces (YIQ) black-white • Subtractive Color Spaces blue-yellow (CMYK) Opponent Color Spaces red-green
Color Description Munsell Color System Hue (red, green, yellow, blue ...) Equal perceptual steps in Hue Saturation Value. Hue: R, YR, Y, GY, G, BG, B, PB, P, RP Saturation (pink,bright red, ....) (each subdivided into 10) Value: 0 ... 10 (dark ... pure white) Chroma: 0 ... 20 (neutral ... saturated) Lightness (black, gray, white ....) 10/ White Value 5/ 10R 5R 5YR /8 /10 10YR 10RP 1/ /6 /4 /2 5Y 5RP G Hue R 10P 10Y Saturation B 5P 5GY /2 10PB 10GY /4 Brightness Example: 5PB /6 5G 5YR 8/4 10B /8 10G /10 5B 10GB 5GB Black
HSV/HSB Color Space Munsell Book of Colors HSV = Hue Saturation Value (Smith ‘78) HSB = Hue Saturation Brightness V green yellow 120 ° cyan 1.0 red 0 ° Blue magenta 240 ° H 0.0 S black HLS Color Space V green yellow HLS = Hue Lightness Saturation 120 ° cyan 0.5 red 0 ° Blue magenta 240 ° H 0.0 S black TekHVC = Hue Saturation Chroma (Luv)
CIE-RGB Linear Color Spaces Choose 3 primaries as the basis SPDs. Colors in 3D color space can be described as linear combinations of 3 basis colors. 3 Primary Intensity 2 a • + c • = + b • 1 0 400 500 600 700 The representation of : Wavelength (nm) Stiles & Burch (1959) Color matching Experiment. Primaries are: 444.4 525.3 645.2 10 deg field. (a, b, c) is then given by: Given the 3 primaries, we can describe any light with 3 values (CIE-RGB): (85, 38, 10) (21, 45, 72) (65, 54, 73)
CIE Color Standard - 1931 RGB to XYZ CIE - Commision Internationale d’Eclairage RGB to XYZ is a linear transformation 1931 - defined a standard system for color representation. XYZ tristimulus coordinate system . X 0.490 0.310 0.200 R = 0.177 0.813 0.011 Y G X Y Z Z 0.000 0.010 0.990 B R = monochromatic primary 700nm G = monochromatic primary 546.1nm B = monochromatic primary 435.8nm Given the 3 primaries, we can describe any light with 3 positive values (CIE-XYZ): (Primaries are normalized so that equal amounts are required to match equal energy illuminant E). (55, 46, 10) (39, 41, 72) (63, 56, 73) (from Jain)
CIE Chromaticity Diagram Color Naming X = x X X+Y+Z 0.9 Y 520 = y Y 530 X+Y+Z 510 540 Z 0.9 = z Z 550 520 X+Y+Z 530 505 560 green 540 510 x+y+z = 1 570 yellow- 550 500 green y 580 505 0.5 560 y yellow 590 570 495 500 orange 600 0.5 580 610 white cyan 490 red 650 pink 590 495 600 485 magenta 610 blue 490 650 480 purple 470 485 450 480 0.0 1.0 0.5 x 470 450 0.0 0.0 0.5 1.0 x A common representative of color signal: [x,y,Y]
Television Primaries and Gamut Blackbody Radiators and CIE standard Illuminants R G B - Primaries used for PAL 1 1 1 CIE Standard Illuminants: R G B - Primaries used for NTSC 2 2 2 A - tungsten light D65 - reference white for PAL B - Sunset C - reference white for NTSC C - blue sky D65 - Average daylight E - Equal energy white (x=y=z=1/3) 0.8 NTSC G 2 PAL 0.8 G 1 0.6 y 0.6 0.4 R 1 D65 R 2 E 4000 3000 5000 C y 2000 6000 0.4 7000 0.2 8000 A B 10000 B 1 E 20000 C D65 B 2 0.2 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 x 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 x
Recommend
More recommend