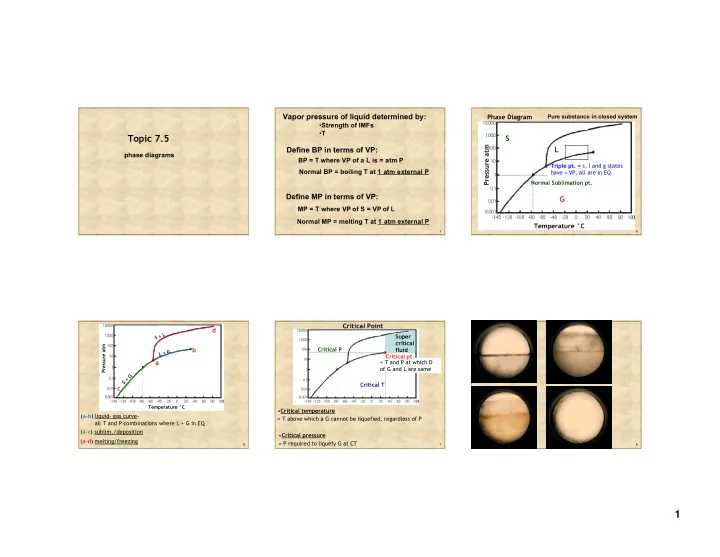

Vapor pressure of liquid determined by: Phase Diagram Pure substance in closed system • Strength of IMFs • T Topic 7.5 S Pressure atm L Define BP in terms of VP: phase diagrams . BP = T where VP of a L is = atm P Triple pt. = s, l and g states Normal BP = boiling T at 1 atm external P have = VP, all are in EQ Normal Sublimation pt. Define MP in terms of VP: G MP = T where VP of S = VP of L Normal MP = melting T at 1 atm external P Temperature °C 1 5 Critical Point d S + L Super critical . Pressure atm b Critical P fluid G + L Critical pt. a = T and P at which D of G and L are same G + S Critical T c Temperature °C • Critical temperature ( a-b ) liquid- gas curve- = T above which a G cannot be liquefied, regardless of P all T and P combinations where L + G in EQ ( a-c ) sublim./deposition • Critical pressure ( a-d ) melting/freezing = P required to liquefy G at CT 6 7 8 1
Slope of liquid/solid boundary line Phase diagram for water If slope positive, solid more dense than the liquid What happens to MP of CO 2 as P ↑ ? CO 2 MP ↑ - ↑ External P, particles compressed What happens - D ↑ to MP of H 2 O as P ↑ ? - ↑ P favors more D phase - S over L: so S has ↑ D MP ↓ If slope negative, solid less dense than the liquid: water - ↑ P, particles compressed - D ↑ -H 2 O unusual in that L molecules fit more tightly than S - L over S: so L has ↑ D 9 10 11 Problem A. Sketch a phase diagram for a substance based on the Pressure atm . . following information: Normal BP = 110°C Critical pt. Normal FP = -22°C 150 . . . Triple point = -20 °C and 0.100 atm liquid NFP NBP Critical point = 200°C and 150 atm 1 solid . . . Triple pt 0.100 . gas CP - 22 - 20 110 200 150 . . If a sample is placed in a container at 20°C and 0.98 atm, what L P (atm) phase(s) would exist? NFP liquid NBP 1 S The P of a sample is decreased from 140 atm to 0.095 atm at a . constant T of 130°C and then the T is decreased from 130°C to -60°C 0.100 at a constant P of 0.095 atm, what phase change(s) would take place? TP G vaporization and deposition - 22 - 20 200 110 If a sample of solid is dropped into liquid, what would happen? T °C L more D than S, ∴ S floats 12 13 14 2
Water has several solid forms Problem set 7.5 Problem E. . P Problem # 3 Which phase transitions could occur if a solid is heated at a pressure above its triple point? Melting and vaporization Do problem # 4 on PS 7.5 as independent practice in class 16 17 3
Recommend
More recommend