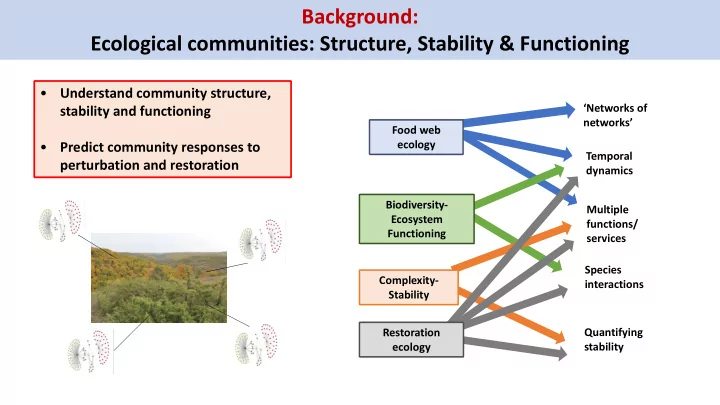

Background: Ecological communities: Structure, Stability & Functioning • Understand community structure, ‘Networks of stability and functioning networks’ Food web ecology • Predict community responses to Temporal perturbation and restoration dynamics Biodiversity- Multiple Ecosystem functions/ Functioning services Species Complexity- interactions Stability Quantifying Restoration ecology stability
Current project: Provisioning & Stability of multiple ecosystem services in agroecosystems ‘Networks of networks’ Food web ecology Temporal dynamics Biodiversity- Quantifying multiple Ecosystem Functioning functions/services Agroecology Complexity-Stability Species interactions Restoration ecology Quantifying stability
Current project: Provisioning & Stability of multiple ecosystem services in agroecosystems Methods Me Motivation Mo ES t trade-offs: C Crop yie ield ld – Po Pollination - Model f for c crop y yield d dynamics ( (ODE) Bi Biodiver ersi sity d d dP P ( t )+ σ P ( t ) u P ( t ) P ( t ) e e dt = r P P ( t )( 1 − k P ω sn A )+ σ P ( t ) u P ( t ) P ( t ) √ P ( t ) Mean & & S Stability o of E ES p provision d d W ( t )+ σ W ( t ) dt = r W W ( t )( 1 − W ( t ) u W ( t ) dW e e k W ω sn A )+ σ W ( t ) W ( t ) u W ( t ) √ W ( t ) Role o of s semi-natural h habitat ( (SNH) C ( t )=( 1 −ω sn ) A [ Z C + α C [ P ( t )/ A ] e e β C +[ P ( t )/ A ]]( 1 + σ C ( t ) u C ( t ) ) Qu Ques estio ions Resul Re ults What a are t the t trade-offs i in m mean a and s stability o of Insight i into t the e ecological m mechanisms d driving E ES multiple E ES i in a agroecosystems? D Do t they d depend trade-offs i tr in a agricultural s systems on t the a amount o of S SNH a and c crop p pollination de depe pende dence? SNH, c crop p pollination d dependence a and c crop r relative responsiveness t to b biodiversity l levels d drive E ES t trade-of offs What i is t the o optimum a amount o of S SNH t to p provide a h high a and s stable c crop y yield? Implications f for a agricultural p pollination
Recommend
More recommend