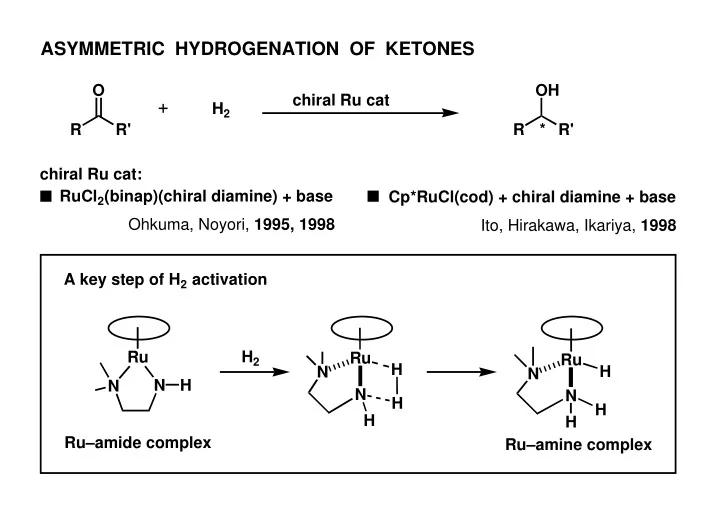

ASYMMETRIC HYDROGENATION OF KETONES O OH chiral Ru cat H 2 R R' R * R' chiral Ru cat: ■ ■ RuCl 2 (binap)(chiral diamine) + base Cp*RuCl(cod) + chiral diamine + base Ohkuma, Noyori, 1995, 1998 Ito, Hirakawa, Ikariya, 1998 A key step of H 2 activation Ru H 2 Ru Ru H H N N N H N N N H H H H Ru–amide complex Ru–amine complex
EFFECT OF LIGAND STRUCTURES ON ACTIVITY conv, % a conv, % a conv, % a amine amine amine none 37 57 <1 (CH 3 ) 2 N NHCH 3 N NH 2 3 41 0 H 2 N NH 2 (CH 3 ) 2 N NHTs NH 2 2 98 0 CH 3 O NH 2 CH 3 HN NH 2 (CH 3 ) 2 N N(CH 3 ) 2 0 6 100 Ph 2 P NH 2 (CH 3 ) 2 N NH 2 (CH 3 ) 2 N OH acetophenone:Ru:diamine:KOH = 100:1:1:1 P H 2 = 1 atm, 30 °C,1 h, Conditions: a Determined by 1 H NMR. 2-propanol
CATALYST PRECURSOR FOR THE HYDROGENATION Ru cat OH O (CH 3 ) 2 N(CH 2 ) 2 NH 2 + H 2 2-propanol C 6 H 5 C 6 H 5 10 atm 30 °C, 2 h ketone:Ru:diamine = 1000:1:1 TOF = 100 TOF = product mol/cat mol·h Ru cat: H 3 C CH 3 O O Ru Ru
SOLVENT EFFECT ON THE TURNOVER NUMBERS TON a solvent methanol 70 ethanol 300 2-propanol 200 tert -butyl alcohol 20 THF 65 CH 3 CN 30 DMF 70 CH 2 Cl 2 0 hexane 0 Conditions: Ru cat 0.2 mol%, H 2 10 atm, 30 °C, 2 h Ru cat = (Cp*RuOCH 3 ) 2 + (CH 3 ) 2 N(CH 2 ) 2 NH 2 a TON = product mol/cat mol
ISOTOPE LABELING EXPERIMENTS Cp*RuCl(cod) (CH 3 ) 2 N(CH 2 ) 2 NH 2 O OH KOH + H 2 or D 2 C 6 H 5 C 6 H 5 solvent H 1 atm 30 °C, 2–3 h (D) ketone:Ru:diamine:KOH = 100:1:1:1 ~100% yield D content, % a H 2 or D 2 solvent OH H 2 0 D OH D 2 7 OD D 2 90 a Determined by 1 H NMR and D NMR.
A POSSIBLE MECHANISM Ru H N Cp*RuCl(cod) H HN H 2 + (CH 3 ) 2 N(CH 2 ) 2 NH 2 ROH + KOH ROH Ru Ru Ru H N N H H N HN N H 2 N O H R H (Cp*RuOCH 3 ) 2 + C 6 H 5 (CH 3 ) 2 N(CH 2 ) 2 NH 2 C 6 H 5 OH Ru C 6 H 5 N C H O NH O H
ASYMMETRIC HYDROGENATION WITH CHIRAL Ru CATALYSTS Cp*RuCl(cod) chiral diamine chiral diamine O OH S KOH + H 2 2-propanol C 6 H 5 R C 6 H 5 R N NH 2 R 10 atm 30 °C, 6–18 h C 2 H 5 ketone:Ru:diamine:KOH = 100:1:1:1 examples: OH OH 72% ee ( R ) 73% ee ( R ) C 6 H 5 C 6 H 5 OH OH 79% ee ( R ) 81% ee ( R ) C 6 H 5 C 6 H 5 OH OH 79% ee ( R ) 88% ee ( R ) C 6 H 5 C 6 H 5
EFFECT OF STRUCTURES OF DIAMINES ON THE ee VALUES N NH 2 N N N(CH 3 ) 2 NH 2 H H C 2 H 5 72% ee ( R ) 13% ee ( S ) 3% ee ( R ) N N N N H H CH 3 13% ee ( R ) 40% ee ( S )
ENANTIO–FACE SELECTION OF KETONE R Ru H R N H N S H OH R H Ar R O Ar catalyst precursor possible transition state
Recommend
More recommend