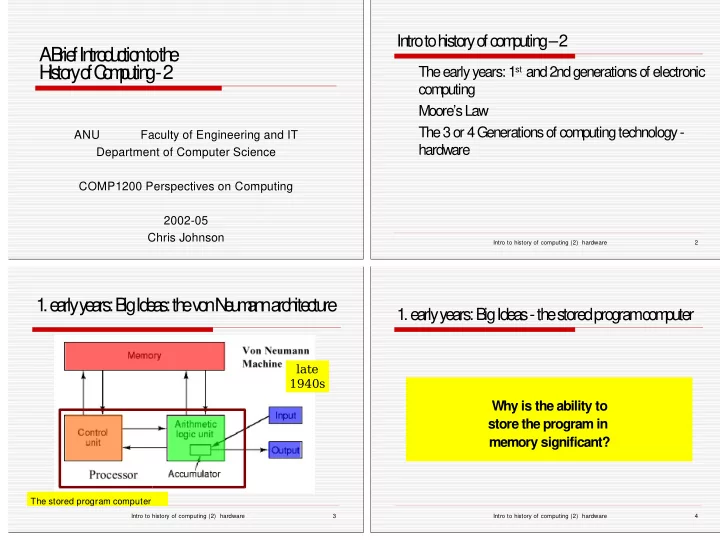

In tro to h isto ry o f co m p u tin g – 2 A B rie f In tro d u c tio n to th e H is to ry o f C o m p u tin g - 2 The early years: 1 st and 2nd generations of electronic computing Moore’s Law The 3 or 4 Generations of computing technology - ANU Faculty of Engineering and IT hardware Department of Computer Science COMP1200 Perspectives on Computing 2002-05 Chris Johnson Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 2 1 . e a rly y e a rs : B ig Id e a s : th e v o n N e u m a n n a rc h ite c tu re 1 . e a rly ye a rs: B ig Id e a s - th e sto re d p ro g ra m co m p u te r late 1940s Why is the ability to store the program in memory significant? The stored program computer Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 3 Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 4
1 . e a rly y e a rs : s m a ll id e a s ... 1 . e a rly ye a rs: G e n e ra tio n s o f e le ctro n ic co m p u tin g electronic valves (1943)1948 1. (vacuum tubes) “I think there is a world market for m aybe five computers” individual solid-state transistors 1959 2. IBM’s chairman Thomas J Watson, 1943 integrated solid-state circuits 1964 3. LSI, MSI, VLSI ( 133 Million PCs were sold in 2000 ) 4. VLSI & the Personal Computer 1981 Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 5 Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 6 1 . e a rly ye a rs: th e 1 st g e n e ra tio n 1 . e a rly ye a rs: 1 st g e n e ra tio n – va lve s (va cu u m tu b e s) example: Bendix G-15 1956 Burroughs B205, ca. 1954 300 built This module represents one 2,160 x 29 bit words decimal digit in the (about 8KBytes storage) ALU accumulator speed: 2 kHz max 180 tube packages (valves) University of Virginia museum Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 300 germanium diode 7 Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 8 packages
1 . e a rly ye a rs: 1 st g e n e ra tio n h a rd w a re 1 . e a rly ye a rs: 1 st g e n e ra tio n so ftw a re based on vacuum tubes: like small light bulbs, 2, 3 - 5 programs writen as numeric codes (machine contacts common language) and in primitive assembly languages (diode, triode,..., pentode) (a few words and code names: A1, M100) slow: computer logic needs internal switching of tube system software tiny: small subroutine libraries for states: limited to kHz speeds numeric routine (e.g.SIN, TAN) and I/O formatting expensive, so computers had only small ALU (e.g. convert internal number to decimal digits) unreliable: vacuum tubes fail frequently, randomly - like manual operation: load next program from paper light bulbs tape by physical switches at console: no “operating runs hot, required a lot of power & cooling system” physically big showed that electronic computing was useful Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 9 Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 10 1 . 1 st a n d 2 nd TYPICAL INPUT/OUTPUT 1 . e a rly y e a rs : 2 nd g e n e ra tio n g e n e ra tio n I/O : in p u t/o u tp u t USED A SINGLE TYPEWRITER-LIKE DEVICE WITH MECHANICAL KEYBOARD, from approximately 1959 FAN-FOLD PAPER. PAPER TAPE, MAYBE PUNCH transistor a general purpose electronic amplification CARD READER AND PUNCH. ONE PERSON AT A TIME. device: EARLY INTERFACE cooler, faster, smaller, much more reliable than DEVICES WERE THE SAME AS COMMUNICATIONS valves TELETYPES, RUNNING AT SPEED OF 10-30 CHARACTERS computer systems software: came with PER SECOND. manufacturer-supplied Operating System for batch NO GRAPHICS AT ALL. ONLY ONE FONT operation, (like this Courier) still needed an operator to load paper and magnetic - Usually had only tapes and paper cards – no online backing store files UPPERCASE CHARACTERS. Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 11 Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 12
1 . 2 nd g e n e ra tio n - tra n s is to rs 1 . 3 rd g e n e ra tio n e le c tro n ic s software: by end of generation (early 1960s) each ability to manufacture Integrated Circuit containing many transistors m anufacturer sold com pilers for machine on single “chip” of silicon: 1964 fewer physical components, less soldering, independent, application-oriented programm ing cheaper, more reliable manufacturing languages for their machines: - fit more logic on each circuit board FORTRAN, COBOL, Algol, LISP computers now used custom-designed integrated circuits (ICs) no easy portability of programs, allowed circuits to work faster: MHz not kHz m agnetic tapes for fast secondary storage 4 microsecond ADD (0.25 MIPS) [IBM 360/50: 1965] no general computer networks 0.75 microsec ADD (1.25 MIPS) [IBM 360/75: 1968] computers more reliable, physically smaller, larger memory Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 13 Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 14 360/50: 256K Byte (1965) 360/75: 1 M Byte (1968) 1 . 3 rd g e n e ra tio n : vo n N e u m a n n a rch ite ctu re p lu s virtu a l 1 . 3 rd g e n e ra tio n c o m p u te rs m e m o ry I/O Secondary controllers Virtual IBM 360 storage memory use for online file 1968 storage Online file storage Conducting a war by computer Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 15 Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 16 Vietnam, circa 1968 Philip Jones Griffiths
1 . 3 rd g e n e ra tio n sto ra g e a n d so ftw a re add fast online secondary storage – disks - use for scratch files, database, general user files and Virtual Mem ory [Atlas - UK 1961] Operating Systems - yes! High level Languages – yes yes yes! hundreds of langauges were created. Intro to history of computing (2) hardware 17
Recommend
More recommend