Worldwide The molecular mechanism underlying the development and - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Worldwide The molecular mechanism underlying the development and progression of gastric cancer in Mizoram, a high-risk region for gastric cancer in Northeast India is unknown Tobacco consumption in various forms is widely prevalent Tobacco
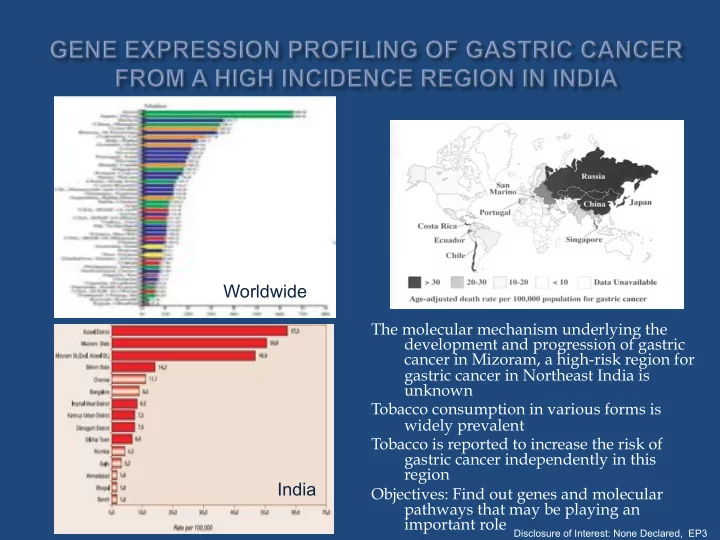
Worldwide The molecular mechanism underlying the development and progression of gastric cancer in Mizoram, a high-risk region for gastric cancer in Northeast India is unknown Tobacco consumption in various forms is widely prevalent Tobacco is reported to increase the risk of gastric cancer independently in this region India Objectives: Find out genes and molecular pathways that may be playing an important role Disclosure of Interest: None Declared, EP3
Pathogenesis of Gastric Ca Trends in overall age standardized Cornea pathway (Intestinal) death rates - Europe Bacteria • Incidence is declining • Early detection, Dietary �������������������� Better surgery ������������������� ���������� • Decreased salt, increased fruits, vegetables Bacteria • Improved food storage Dietary • Decreased smoking Tobacco Genetic Predisposition • Treatment of H. pylori • SNPs in PSCA gene has been associated with diffuse gastric In NE India cancer • CDH1 mutation is seen in • No reported decrease in incidence 70-90% sporadic and 10-30% • CDH1 mutation was not found in our familial cases earlier studies • Targeted prevention is feasible • Pathogenetic mechanism may be for high-risk subpopulation with different in NE India inherited CDH1 mutation EP3
Risk factors ! Cases (n=112) ! Controls (n=66) ! Multivariate ! Microarray was done using n (%) ! n (%) ! OR2 (95% CI) ! P value ! oligonucleotide based Cancer H.pylori Positive a ! 75 (67) ! 42 (64) ! 1.19 (0.59-2.39) ! 0.63 ! OciChips TM with tumor tissues Tobacco Smoking b ! 63 (56) ! 32 (48) ! 1.54 (0.79-3.02) ! 0.21 ! and corresponding normals Tobacco Chewing c ! 77 (69) ! 34 (52) ! 2.11 (1.09-4.05) ! 0.026 ! Deregulated Pathways Betel-quid Chewing d ! 60 (54) ! 30 (45) ! 1.27 (0.68-2.38) ! 0.45 ! Alcohol RYK, SH2D2A, 29 (26) ! 18 (27) ! 0.89 (0.42-1.81) ! 0.72 ! Consumption e ! Apoptosis CSNK1E, LRP12, Tobacco conferred a significant increase risk HSPE1,FGB, PXN, CHP of upto two fold Immune RFX1,CXCL10, C3AR1, response MALT1 Variables ! Interaction ! OR2(95% CI) ! p -value ! Tobacco Angiogenesis SH2D2A, ANG chewing b ! Cell H. pylori -ve X Non chewer ! 1.0 ! CD151, PXN, WASF1 H. pylori -ve X Chewer ! 3.7(1.52-9.03) ! 0.004 ! adhesion H. pylori +ve X Non chewer ! 4.06(1.41-11.69) ! 0.009 ! Wnt H. pylori +ve X Chewer ! 7.12(5.02-36.31) ! ≤ 0.0001 ! CHP, CSNK1E, RYK signaling Betel- Notch quid JAG2, HES1 signaling chewing c ! H. pylori -ve X Non chewer ! 1.0 ! Hedgehog CSNK1E, BMP7 H. pylori -ve X Chewer ! 2.01(0.76-5.31) ! 0.16 ! signaling H. pylori +ve X Non chewer ! 2.67(0.98-7.25) ! 0.06 ! ATP6V1G2, HBXIP, Viral H. pylori +ve X Chewer ! 3.52(1.16-10.68) ! 0.026 ! ACE2 response Tobacco chewers who were also Cell CDC2L1, JAG2, IL9 H. pylori positive conferred a seven fold risk proliferation EP3
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.























