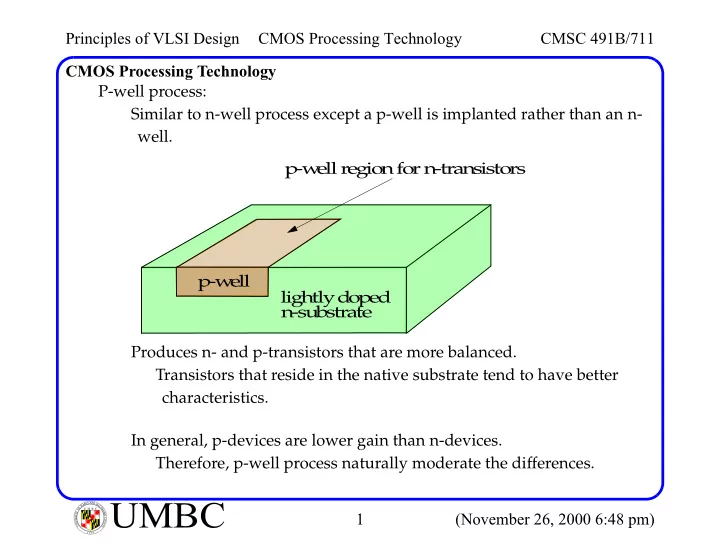

Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology P-well process: Similar to n-well process except a p-well is implanted rather than an n- well. p-w ell region for n-transistors p-w ell lightly doped n-substrate Produces n- and p-transistors that are more balanced. Transistors that reside in the native substrate tend to have better characteristics. In general, p-devices are lower gain than n-devices. Therefore, p-well process naturally moderate the differences. L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 1 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology Twin-tub process: Allows independent optimization of gain, threshold voltage, etc. of n- type and p-type devices. GND V DD Epitaxy: High purity p+ n+ p+ n+ p+ n+ silicon grown p-well n-well with accurately epitaxial layer determined dopant n+ substrate concentrations Both types of substrate contacts are REQUIRED in this process. L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 2 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology Silicon-On-Insulator (SOI) process: Instead of silicon substrate, use an insulating substrate. Silicon can be grown on: Sapphire or SiO 2 which in turn has been grown on silicon. 1) lightly doped n-type Si (n-) Sapphire L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 3 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology poly 2) 5) p- n- n- n- Sapphire Sapphire photoresist n-island p-island 3) 6) n+ n+ n- p- n- Sapphire Sapphire Thinox 7) 4) p+ p+ n+ n+ p- n- Sapphire Sapphire O xidation + m etalization L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 4 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology Advantages: • Closer packing of p- and n-transistors, due to absence of wells. • Absence of latch-up problems (to be discussed). • Only “sidewall” areas of source and drain diffusions contribute to parasitic junction capacitance, faster devices. • Leakage currents to substrate and adjacent devices almost eliminated. • Enhanced radiation tolerance. Disadvantages: • No substrate diodes, inputs more difficult to protect. • Device gains are lower, I/O structures must be larger. • Density of contemporary digital processes is actually determined by num- ber and density of metal interconnection layers. • Sapphire and silicon on SiO 2 substrates are considerably more expensive. L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 5 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology CMOS Enhancements: • More levels of metal interconnect, 2, 3, 4, ... Eases automated routing and improves power and clock distribution to modules. “Vias” are used to connect upper layers of metal to metal 1. “Contact cuts” are made from metal 1 to diffusion or poly. via contact metal 1 metal 2 p + Aggressive processes allow the stacking of vias on top of contacts. L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 6 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology CMOS Enhancements: • Lower poly sheet resistance. Poly resistance between 20 and 40 Ohms. If poly combined with a refractory metal, resistance (and delay) can be reduced. Silicide (silicon and tantalum) used as gate material, between 1 and 5 Ohms. Can be extended to source and drain, called salicide (Self ALigned SILI- CIDE). Silicide Poly p-substrate L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 7 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology CMOS Enhancements: • Local interconnect. Silicide used to make direct connection between poly and diffusion, no contact or metal. e.g. six transistor SRAM cell: m etal 1 V D D p-diff local interconnect poly w ord line bit bit L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 8 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology Static memory and analog circuits require passive components: Resistors: Undoped poly; tera ohm values are possible. Capacitors: Second layer of thinox and poly (poly 2). Trench capacitors allow memory densities of 64Mbit and higher. Book covers structures to implement: • EPROM • BiCMOS • thin-film transistors • 3-D CMOS We will cover in advanced topics (time permitting). L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 9 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology Layout or Design Rules: Design rules specify geometric constraints on the layout artwork. Provide a communication channel between the IC designer and the fab- rication process engineer. Objective: To obtain a circuit with optimum yield. To minimize the area of the circuit. To provide long term reliability of the circuit. Design rules represent the best compromise between performance and yield: More conservative rules increase yield. More aggressive rules increase performance. Design rules represent a tolerance that ensures high probability of cor- rect fabrication - rather than a hard boundary between correct and incorrect fabrication. L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 10 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology Layout or Design Rules: Two approaches to describing design rules: • Lambda-based rules: Allow first order scaling by linearizing the resolu- tion of the complete wafer implementation. To move a design from 4 micron to 2 micron, simply reduce the value of lambda. Worked well for 4 micron processes down to 1.2 micron processes. However, in general, processes rarely shrink uniformly. Probably not sufficient for submicron processes. • Micron rules: List of minimum feature sizes and spacings for all masks, e.g., 3.25 microns for contact-poly-contact (transistor pitch) and 2.75 micron metal 1 contact-to-contact pitch. Micron rules can result in as much as a 50% size reduction over lambda rules. Normal style for industry. L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 11 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology Latch-Up: Parasitic circuit effect that causes V DD and GND to short. Can result in self-destruction, at best a malfunction requiring a power cycle. in V G N D D D out p+ n+ n+ p+ p+ n+ n-w ell N PN PN P p-substrate Parasitic bipolar transistors formed between n and p MOS transistors. L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 12 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Principles of VLSI Design CMOS Processing Technology CMSC 491B/711 CMOS Processing Technology Latch-Up: Latch-up is triggered by supply voltage transients which cause V DD to overshoot or GND to dip by ~0.7V above or below the supply. Not likely to occur in core logic. You can prevent this condition by making liberal use of substrate con- tacts: • Every well MUST have a substrate contact. • Every substrate contact should be connected to metal directly to a sup- ply pad. • Place substrate contacts as close as possible to the source contacts. I/O circuitry is more susceptible and must be protected. • Guard rings are used in the I/O pads to reduce gain of parasitic transis- tors. • I/O pad design should be left to experts. L A N R Y D UMBC A B M A L F T U M B C I O M Y O T R 13 (November 26, 2000 6:48 pm) I E S R C E O V U I N N U T Y 1 6 9 6
Recommend
More recommend