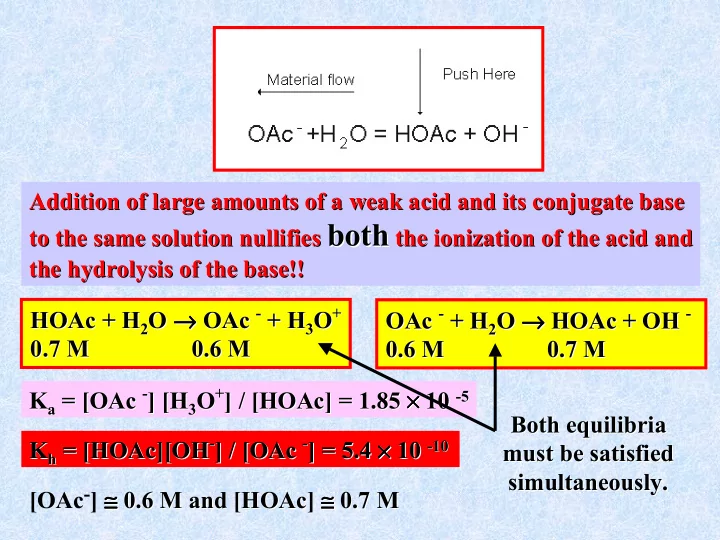

Addition of large amounts of a weak acid and its conjugate base Addition of large amounts of a weak acid and its conjugate base both the ionization of the acid and to the same solution nullifies both the ionization of the acid and to the same solution nullifies the hydrolysis of the base!! the hydrolysis of the base!! - + H - + H → → → OAc → + → HOAc → O → → → → OAc - O + OAc - O → → → → + OH - - → → HOAc + H + H 2 + H 3 + H 2 HOAc + OH HOAc 2 O 3 O OAc 2 O 0.7 M 0.6 M 0.7 M 0.6 M 0.6 M 0.7 M 0.6 M 0.7 M - ] [H + ] / [ × × × × 10 OAc - O + ] = 1.85 × × × × K a = [OAc ] [H 3 ] / [HOAc HOAc] = 1.85 10 - -5 5 K a = [ 3 O Both equilibria equilibria Both ][OH - - ] / [ OAc - - ] = 5.4 × 10 × × × ] = 5.4 × × × × K h = [HOAc HOAc][OH ] / [OAc 10 - K h = [ -10 10 must be satisfied must be satisfied simultaneously. simultaneously. [OAc - ] ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ 0.6 M and [ ≅ ≅ ≅ 0.7 M ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ ] ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ 0.6 M and [HOAc HOAc] 0.7 M
Thus have [H 3 O + + ] = ] = Thus have [H 3 O - ]} × K × × × ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ (0.70/0.60) × × × × (1.85 × 10 × × × OAc - ]} × × × × a ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ (0.70/0.60) × × × × (1.85 × × × × {[HOAc HOAc]/[ ]/[OAc K a 10 - -5 5 ) ) {[ 5 M} This result is accurate to 4 significant + ]=2.185x10 O + [H 3 ]=2.185x10 - -5 M} This result is accurate to 4 significant [H 3 O figures (gives same result as solving quadratic to this accuracy)! )! figures (gives same result as solving quadratic to this accuracy A solution containing substantial amounts of a weak acid A solution containing substantial amounts of a weak acid and its conjugate base is known as a buffer solution. and its conjugate base is known as a buffer solution. + ] = {[acid]/[salt]} O + Thus, have [H 3 ] = {[acid]/[salt]} K K a Thus, have [H 3 O a ratio of [acid] to [salt] and the ratio Depends only on K K a of [acid] to [salt] Depends only on a and the + ] will not O + If we dilute such a solution, [H 3 ] will not If we dilute such a solution, [H 3 O change since [acid] and [salt] change identically change since [acid] and [salt] change identically when such a solution is diluted! when such a solution is diluted!
Example: 1 liter of 0.25 M HCl HCl, add 0.600 moles of , add 0.600 moles of NaOAc NaOAc(s) (s) Example: 1 liter of 0.25 M Assume no volume change occurs upon addition of salt. Assume no volume change occurs upon addition of salt. OAc - - ], [ O + + ], [OH ], [OH - - ] Find [OAc ], [HOAc HOAc], [H ], [H 3 ] Find [ 3 O + + + + NaOAc → → → Na HCl → → H → → → → Na + OAc - - → → → O + Cl - - → → → → + OAc H 2 O + HCl H 3 + Cl NaOAc H 2 O + 3 O + → - + H → HOAc → → → OAc - O + → → → (1) OAc + H 3 HOAc + H + H 2 O (1) 3 O 2 O 0.600 0.250 ~ 0 initially 0.600 0.250 ~ 0 initially Recognizing a buffer Recognizing a buffer K a = [ OAc − ][ H 3 O + ] when you see it. Not when you see it. Not = 1 . 85 × 10 − 5 [ HOAc ] always an easy task. always an easy task. Equation far to the right Equation far to the right + → - + H Buffer conditions! → → HOAc → → Buffer conditions! OAc - O + → → → (2) OAc + H 3 HOAc + H + H 2 O (2) 3 O 2 O ~ .350 ~ 0 ~ .250 ~ .350 ~ 0 ~ .250 - ] = .350 [ OAc - [OAc ] = .350 [HOAc HOAc] = .250 ] = .250 [
[ HOAc ] [ OAc − ] ≈ 1 . 855 × 10 − 5 . 25 [ H 3 O + ] = K a 5 M = 1.325x10 - -5 M = 1.325x10 . 35 O + + ] by a buffer solution Clamping of [H 3 ] by a buffer solution Clamping of [H 3 O 1) Add 1 ml of 1 M HCl HCl to 1 liter of pure H to 1 liter of pure H 2 O: 1) Add 1 ml of 1 M 2 O: + concentration changes + ] ≅ ≅ 0.001 ≅ ≅ O + ] ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ O + [H 3 0.001 Or, the H H 3 concentration changes [H 3 O Or, the 3 O 7 to 10 3 (4 orders of magnitude)! From 10 - -7 to 10 - -3 (4 orders of magnitude)! From 10 2) Now add 1 ml of 1M HCl HCl to one liter of solution containing to one liter of solution containing 2) Now add 1 ml of 1M 0.7 moles of HOAc HOAc and 0.6 moles of and 0.6 moles of NaOAc NaOAc. . 0.7 moles of ≅ 0.7M and [ ≅ ≅ ≅ OAc - - ] ≅ ≅ ≅ 0.6M ≅ ] ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ ] ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ Remember, this is a buffer, so [HOAc HOAc] 0.7M and [OAc 0.6M Remember, this is a buffer, so [ + → - + H → → HOAc → → OAc - O + → → → Initially: + H 3 HOAc + H + H 2 O Initially: OAc 3 O 2 O 0.600 0.001 0.700 0.600 0.001 0.700 Max change in + added reacts with Max OAc - - change in HOAc HOAc occurs if all H occurs if all H + added reacts with OAc → → → → HOAc → → → → HOAc: Reaction : Reaction stoichiometry stoichiometry is as follows: is as follows: + → - + H OAc - O + → HOAc → → → → → → + H 3 HOAc + H + H 2 O OAc 3 O 2 O ≅ ≅ 0 0.599 ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ ≅ 0 0.701 0.599 0.701
- ] = 0.599 OAc - [HOAc HOAc] = 0.701 and [ ] = 0.701 and [OAc ] = 0.599 [ [ acid ] [ anion ] K a = 0.701 − 5 0.599 1.85 × 10 + ] = O + and [H 3 ] = and [H 3 O + ] = 2.17 × × 10 O + ] = 2.17 × × × × × × New [H 3 10 - -5 5 New [H 3 O .700 5 = 2.16 O + + ] = 1.85 × × × × 10 × 10 × × × ] = 1.85 × × × × = 2.16 × × × × Before addition of HCl HCl, [H , [H 3 10 - -5 10 - -5 5 Before addition of 3 O .600 “No No” ” change in [H change in [H 3 O + + ] when buffered! ] when buffered! “ 3 O 4 change in H + concentration!! If not buffered, get 10 4 change in H 3 O + concentration!! If not buffered, get 10 3 O + is being the H + “Physically Physically” ” the H is being “ “stored stored” ” as as undissociated HOAc undissociated HOAc: : “ + → - + H OAc - O + → → HOAc → → → → → + H 3 HOAc + H + H 2 O OAc 3 O 2 O - also find pH does not change because the OH - reacts If add OH - also find pH does not change because the OH - reacts If add OH OAc - - ! with HOAc HOAc to give H to give H 2 O and OAc ! with 2 O and
H 2 O(100mL) H 2 O(100mL) Add strong Add strong 13 13 Unbuffered Unbuffered base to: base to: 12 12 1) Pure water 1) Pure water 11 11 2) 0.1 M/0.1 M 2) 0.1 M/0.1 M 10 10 Acetate buffer Acetate buffer 9 9 pH pH 3) 1.0 M/1.0M 3) 1.0 M/1.0M / 0.10 COOH / 8 8 0.10 M 0.10 M CH CH 3 3 COOH 0.10 M M NaCH NaCH 3 3 COO (100mL) COO (100mL) Acetate buffer Acetate buffer 7 7 6 6 Buffered Buffered 5 5 0 0 10 10 20 20 30 30 40 40 Volume 0.10 M M NaOH NaOH ( (mL mL) ) Volume 0.10 / 1.0 COOH / 1.0 1.0 M M CH CH 3 3 COOH 1.0 M M NaCH NaCH 3 3 COO (100mL) COO (100mL) Buffered: small change in pH compared to unbuffered unbuffered. . Buffered: small change in pH compared to Higher buffer concentration resists pH changes more effectively. Higher buffer concentration resists pH changes more effectively.
12 11 10 9 100.0 100.0 mL mL of of Equivalence point 8 0.1000 M M HCl HCl 0.1000 7 titrated with titrated with 6 pH 0.1000 0.1000 M M NaOH NaOH. . 5 4 3 2 1 0 At start 0 50 100 At start Volume 0.1000 M Volume 0.1000 M NaOH NaOH ( (mL mL) ) [H 3 O + + ]=10 ]=10 - -1 1 M [H 3 O M Titration of a strong acid by a strong base. Titration of a strong acid by a strong base.
Titration Curve for aWeak aWeak Acid HA (red curve/points) Acid HA (red curve/points) Titration Curve for - → → → → → H → → → HA + OH - HA + OH H 2 2 O + A O + A - - Mix of HA Mix of HA - in and A - in and A buffer buffer QuickTime™ and a Animation decompressor region region are needed to see this picture. Mostly Mostly HA HA at start at start
Indicators Indicators + ]. Dye molecules whose color changes with pH or [H + ]. Dye molecules whose color changes with pH or [H Useful way to follow pH changes. Useful way to follow pH changes. + + In → H → O → → → → O + + In - - → → HIn + H + H 2 H 3 (Indicators are themselves weak HIn 2 O 3 O acids or bases.) - yellow, In - yellow, HIn HIn red red In In = Indicator In = Indicator K I = [ H 3 O + ][ In − ] [ HIn ] - form, to red, Ratio of yellow, In - form, to red, HIn HIn form, controlled only by form, controlled only by Ratio of yellow, In [H 3 O + + ] for a given K ] for a given K I [H 3 O I - ] / [ + ] [In - O + ] / [HIn HIn] = K ] = K I / [H 3 ] [In I / [H 3 O
Bonus * Bonus * Bonus * Bonus * Bonus * Bonus Bonus * Bonus * Bonus * Bonus * Bonus * Bonus
Recommend
More recommend