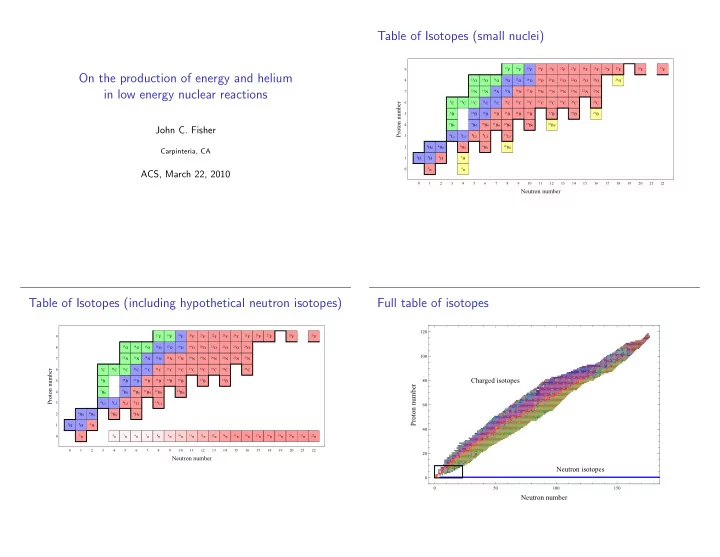

Table of Isotopes (small nuclei) 9 17 F 18 F 19 F 20 F 21 F 22 F 23 F 24 F 25 F 26 F 27 F 29 F 31 F On the production of energy and helium 8 13 O 14 O 15 O 16 O 17 O 18 O 19 O 20 O 21 O 22 O 23 O 24 O 26 O in low energy nuclear reactions 12 N 13 N 14 N 15 N 16 N 17 N 18 N 19 N 20 N 21 N 22 N 23 N 7 9 C 10 C 11 C 12 C 13 C 14 C 15 C 16 C 17 C 18 C 19 C 20 C 22 C Proton number 6 8 B 10 B 11 B 12 B 13 B 14 B 15 B 17 B 19 B 21 B 5 4 7 Be 9 Be 10 Be 11 Be 12 Be 14 Be 16 Be John C. Fisher 3 6 Li 7 Li 8 Li 9 Li 11 Li 3 He 4 He 6 He 8 He 10 He 2 Carpinteria, CA 1 H 2 H 3 H 5 H 1 1 n 4 n 0 ACS, March 22, 2010 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 Neutron number Table of Isotopes (including hypothetical neutron isotopes) Full table of isotopes 120 17 F 18 F 19 F 20 F 21 F 22 F 23 F 24 F 25 F 26 F 27 F 29 F 31 F 9 8 13 O 14 O 15 O 16 O 17 O 18 O 19 O 20 O 21 O 22 O 23 O 24 O 100 7 12 N 13 N 14 N 15 N 16 N 17 N 18 N 19 N 20 N 21 N 22 N 23 N 6 9 C 10 C 11 C 12 C 13 C 14 C 15 C 16 C 17 C 18 C 19 C 20 C 22 C Proton number Charged isotopes 8 B 10 B 11 B 12 B 13 B 14 B 15 B 17 B 19 B 80 5 Proton number 7 Be 9 Be 10 Be 11 Be 12 Be 14 Be 4 3 6 Li 7 Li 8 Li 9 Li 11 Li 60 2 3 He 4 He 6 He 8 He 1 1 H 2 H 3 H 40 1 n 4 n 5 n 6 n 7 n 8 n 9 n 10 n 11 n 12 n 13 n 14 n 15 n 16 n 17 n 18 n 19 n 20 n 21 n 22 n 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 20 Neutron number Neutron isotopes 0 0 50 100 150 Neutron number
Question: How could you detect neutron isotopes? Liquid-drop model ◮ From their decay and reaction products ◮ Suppose that neutrons in a neutron isotope are bound about 1/2 as strongly as they are in an ordinary charged isotope. ◮ These depend on how strongly isotopes are bound ◮ The volumetric neutron isotope mass excess then would be ◮ We need a model ∆( A n) ≈ 8 . 071A − 7A ≈ A ◮ We need also a surface energy proportional to A 2 / 3 . ◮ Hypothesize: A 2 / 3 . ◮ Now we have the hypothetical neutron isotope mass excess ∆( A n) = A + A 2 / 3 Neutron isotope detection by radioactive decay Alpha particle shower (exothermic ββα ) Etch pits on a detector chip in air under a nickel cathode (Oriani) ◮ 200 n − → 196 n + 4 He ◮ 196 n − → 192 n + 4 He ◮ 192 n − → 188 n + 4 He ◮ And so on. A neutron isotope decays by emitting a series of energetic alpha particles. Overall: 200 n − → 50( 4 He) ◮ ◮ We can detect the alpha particles.
The Oriani shower Full table of isotopes ◮ 63 pits 120 ◮ about 200 alphas in full 4 π shower 80 ◮ about 800 neutrons in parent neutron isotope 40 0 0 200 400 600 800 ◮ Consistent with decay mode Neutron number ◮ Consistent with large neutron isotopes ◮ Consistent with helium production Neutron isotope detection by growth reactions Neutron isotope detection by lithium-6 reactions ◮ Isotope growth (deuterium fuel) Isotope growth 2 H + A n → A+1 n + 1 H 6 Li + A n → A+1 n + 5 Li − − 2 H + A+1 n − → A+2 n + 1 H 6 Li + A+1 n − → A+2 n + 5 Li 2 H + A+2 n − → A+3 n + 1 H 6 Li + A+2 n − → A+3 n + 5 Li 2 H + A+3 n − → A+4 n + 1 H 6 Li + A+3 n − → A+4 n + 5 Li ◮ Neutron isotope growth is accompanied by emission of Isotope decay energetic protons. A+4 n − → A n + 4 He ◮ Isotope decay also occurs Overall (steady state) A+4 n − → A n + 4 He 4( 6 Li) − → 4( 5 Li) + 4 He ◮ Overall (steady state) → 4( 1 H) + 5( 4 He) + 14MeV − 4( 2 H) − → 4( 1 H) + 4 He + 20MeV
Neutron isotope detection by lithium-7 reactions Some useful things to study ◮ Energetic protons and alphas Isotope growth ◮ Explore basic reactions 7 Li + A n → A+2 n + 5 Li − ◮ Helium and heat 7 H + A+2 n − → A+4 n + 5 Li ◮ Identify and quantify nuclear fuels Isotope decay ◮ Transmutation (more expensive) A+4 n − → A n + 4 He ◮ Confirm and extend reaction dynamics Overall (steady state) 2( 7 Li) − → 2( 5 Li) + 4 He → 2( 1 H) + 3( 4 He) + 7MeV − Helium and heat Comments on neutron isotopes ◮ For theoreticians Steady state reactions for selected fuel isotopes ◮ Ordinary nuclear physics with more isotopes 2 H: 4( 2 H) − → 4( 1 H) + 4 He + 20MeV ◮ For experimenters 6 Li: 4( 6 Li) − → 4( 1 H) + 5( 4 He) + 14MeV ◮ Opportunity for fundamental research 7 Li: 2( 7 Li) − → 2( 1 H) + 3( 4 He) + 7MeV ◮ For entrepreneurs 9 Be: 4( 9 Be) − → 9( 4 He) + 23MeV ◮ It’s risky to ignore lithium and beryllium and other fuels 13 C: 4( 13 C) − → 4( 12 C) + 4 He + 9MeV 17 O: 4( 17 O) − → 4( 16 O) + 4 He + 12MeV 18 O: 2( 18 O) − → 2( 16 O) + 4 He + 5MeV 232 Th: Complex, ambiguous, 238 U: not worked out.
Recommend
More recommend