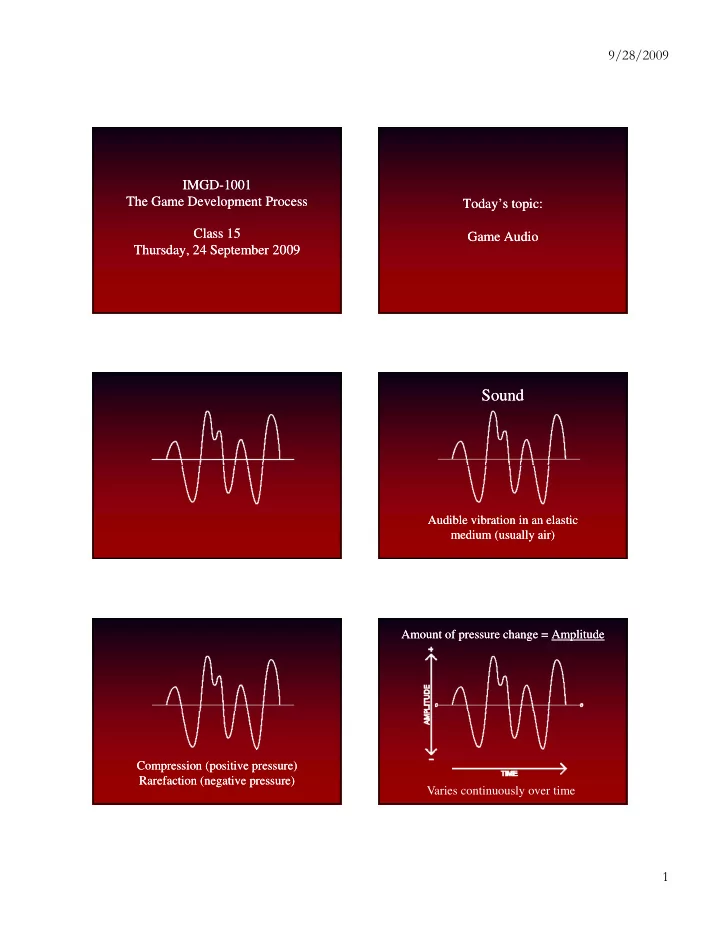

9/28/2009 IMGD IMGD- -1001 1001 The Game Development Process The Game Development Process Today’s topic: Today’s topic: Class 15 Class 15 Game Audio Game Audio Thursday, 24 September 2009 Thursday , 24 September 2009 Sound Sound Audible vibration in an elastic Audible vibration in an elastic medium (usually air) medium (usually air) Amount of pressure change = Amount of pressure change = Amplitude Amplitude Compression (positive pressure) Compression (positive pressure) Rarefaction (negative pressure) Rarefaction (negative pressure) Varies continuously over time 1
9/28/2009 Rate Rate of vibration/pressure of vibration/pressure change = change = Frequency Frequency Frequency range of human hearing: Frequency range of human hearing: Approximately 20 to 20,000 Hz Approximately 20 to 20,000 Hz Measured in cycles per second (Hertz or Hz) Digital audio Digital audio Analog recording and playback Analog recording and playback Experimental recordings: Late ‘60s Experimental recordings: Late ‘60s Jazz/classical: Early 70s Jazz/classical: Early 70s First symphonic recording: 1976 First symphonic recording: 1976 First major label recording: 1979 First major label recording: 1979 Ry Cooder s Ry Cooder’s Ry Cooder’s Bop Till You Drop Ry Cooder s Bop Till You Drop Bop Till You Drop Bop Till You Drop Compact Disc Compact Disc Jointly created by Sony/Phillips Jointly created by Sony/Phillips Introduced October 1, 1982 Introduced October 1, 1982 Billy Joel’s Billy Joel’s 52nd Street 52nd Street Biggest seller Biggest seller Transducers: Convert one type of energy to another All All transducers introduce distortion transducers introduce distortion Beatles Beatles 1 (30M+ copies) (30M+ copies) Digital audio Digital audio based on based on sampling sampling Amplitude of signal is measured (and usually recorded) Amplitude of signal is measured (and usually recorded) at precise time intervals, converted to stream of numbers at precise time intervals, converted to stream of numbers 2
9/28/2009 Digital recording and playback Digital recording and playback Extremely accurate, low Extremely accurate, low noise and distortion noise and distortion Almost immeasurable wow or flutter Almost immeasurable wow or flutter Easily edited and manipulated Easily edited and manipulated Essentially perfect replication Essentially perfect replication Digital sampling (“digitizing”) Digital sampling (“digitizing”) Sample rate Sample rate How often to sample? How often to sample? Number of samples taken per second Number of samples taken per second Depends on desired frequency range Depends on desired frequency range Also measured in Hertz Also measured in Hertz Nyquist frequency = Sample rate Nyquist frequency = Sample rate Sample resolution Sample resolution p required to fully express a signal required to fully express a signal i d i d f ll f ll i i l l Range of numbers used to describe Range of numbers used to describe 2X maximum required frequency 2X maximum required frequency each sample each sample 2X 20 kHz = 40 kHz minimum sample 2X 20 kHz = 40 kHz minimum sample Measured in binary bits Measured in binary bits rate to represent full human range rate to represent full human range 8 bits = 256 values ( 8 bits = 256 values (± ± 127) 127) 16 bits = 65,536 values ( 16 bits = 65,536 values (± ± 32K) 32K) 24 bits = 16,777,216 values 24 bits = 16,777,216 values Home audio formats Home audio formats How much to sample? How much to sample? Compact Disc Compact Disc Depends on desired dynamic range Depends on desired dynamic range Sample rate: 44.1 kHz Sample rate: 44.1 kHz Dynamic range = Difference Dynamic range = Difference Sample resolution: 16 bits Sample resolution: 16 bits between softest and loudest sounds between softest and loudest sounds Dynamic range: >90 dB Dynamic range: >90 dB Dynamic range: >90 dB Dynamic range: >90 dB Measured in decibels (dB); 1 dB = Measured in decibels (dB); 1 dB = Two channels for stereo Two channels for stereo faintest perceptible sound faintest perceptible sound “CD quality” “CD quality” Real Real- -world range: 10 world range: 10- -20 dB (anechoic 20 dB (anechoic HD/BluRay DVD HD/BluRay DVD chamber) to 140 dB (beside jet engine) chamber) to 140 dB (beside jet engine) Up to 8 channels 96 Up to 8 channels 96 kHz 24 kHz 24- -bit audio bit audio Each bit of sampling resolution Each bit of sampling resolution approximately doubles dynamic range approximately doubles dynamic range Dynamic range: >120 dB Dynamic range: >120 dB 3
9/28/2009 “CD quality” data rate “CD quality” data rate Compressed digital audio Compressed digital audio 44,100 samples per second 44,100 samples per second Lossless compression Lossless compression 16 bits (2 bytes) per sample 16 bits (2 bytes) per sample Preserves data perfectly Preserves data perfectly 2 channels 2 channels Compression ratio Compression ratio Compression ratio: 2:1 typical Compression ratio: 2:1 typical : 2:1 typical : 2:1 typical 44,100 x 2 x 2 = 176,400 bytes/sec 44,100 x 2 x 2 = 176,400 bytes/sec Lossy compression Lossy compression or 10.584 MB per minute or 10.584 MB per minute Discards some data to increase Discards some data to increase Typical pop song 30 Typical pop song 30- -40 MB if 40 MB if compression ratio compression ratio uncompressed uncompressed The trick is: What to throw away? The trick is: What to throw away? The game changer: MP3 (1994) The game changer: MP3 (1994) Lossy compression algorithm based Lossy compression algorithm based The MP3 Phenomenon The MP3 Phenomenon on auditory masking on auditory masking First Web appearance: Late ‘94 First Web appearance: Late ‘94 Loud low Loud low- -frequency sounds can make frequency sounds can make softer high softer high-frequency sounds inaudible f f h h f h h f frequency sounds inaudible d d d bl d bl Winamp, mp3.com (Summer ’97) Winamp, mp3.com (Summer ’97) Perceptual coding: Throw away high Perceptual coding: Throw away high First portable players (Spring ’98) First portable players (Spring ’98) frequencies that “can’t be heard frequencies that “can’t be heard 32 MB Eiger MPMan F10, Rio PMP300 32 MB Eiger MPMan F10, Rio PMP300 anyway” anyway” Napster (June ‘99) Napster (June ‘99) Compression ratio Compression ratio: 10:1 : 10:1 or better or better Created by Shawn Fanning (19), Created by Shawn Fanning (19), Pop song becomes a 3 MB file Pop song becomes a 3 MB file Northeastern University Northeastern University Game audio: Early days Game audio: Early days Game audio: Today Game audio: Today Apple II and PC: Click the speaker Apple II and PC: Click the speaker All game audio is digital All game audio is digital Atari, C64, early consoles: FM synths Atari, C64, early consoles: FM synths Music, SFX, VO delivered pre Music, SFX, VO delivered pre- -rendered rendered Macintosh (January 1984) Macintosh (January 1984) Typical assets Typical assets AdLib PC sound card (1976) AdLib PC sound card (1976) AdLib PC sound card (1976) AdLib PC sound card (1976) .wav (bigger, no decoding) .wav (bigger, no decoding) (bi (bi d d di di ) ) Creative Labs Sound Blaster (1989) Creative Labs Sound Blaster (1989) .mp3 (small, decoded, requires license) .mp3 (small, decoded, requires license) AdLib with digital audio + game port AdLib with digital audio + game port .ogg (small, decoded, no license) .ogg (small, decoded, no license) CD CD- -ROM (1985) ROM (1985) .flac (smaller, decoded) .flac (smaller, decoded) Real Real- -time mixing, effects, time mixing, effects, CD CD- -R (1990) R (1990) spatialization spatialization MIDI/music synthesis MIDI/music synthesis 4
9/28/2009 Tonight’s assignment: Tonight’s assignment: Questions? Questions? Continue reading Rollings/Morrs Continue reading Rollings/Morrs Continue reading Rollings/Morrs Continue reading Rollings/Morrs Friday: Friday: Continue Project 4 Continue Project 4 Game design Game design 5
Recommend
More recommend