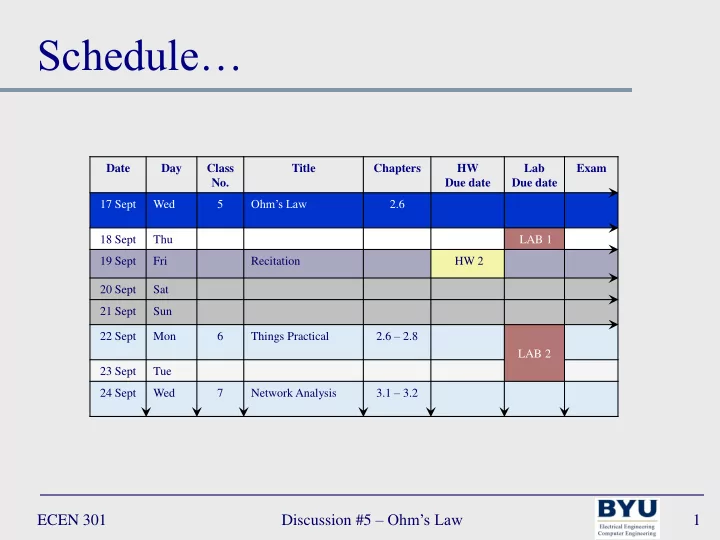

Schedule… Date Day Class Title Chapters HW Lab Exam No. Due date Due date Ohm’s Law 17 Sept Wed 5 2.6 18 Sept Thu LAB 1 19 Sept Fri Recitation HW 2 20 Sept Sat 21 Sept Sun 2.6 – 2.8 22 Sept Mon 6 Things Practical LAB 2 23 Sept Tue 3.1 – 3.2 24 Sept Wed 7 Network Analysis Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 1
Divided We Fall Matthew 12:25-26 25 And Jesus knew their thoughts, and said unto them, Every kingdom divided against itself is brought to desolation; and every city or house divided against itself shall not stand: Nephi 7:2 2 And the people were divided one against another; and they did separate one from another into tribes, every man according to his family and his kindred and friends; and thus they did destroy the government of the land. Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 2
Lecture 5 – Resistance & Ohm’s Law Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 3
Open and Short Circuits Short circuit : a circuit element across which the voltage is zero regardless of the current flowing through it Resistance approaches zero Flow of current is unimpeded ex: an ideal wire + i • In reality there is a small resistance R = 0 v v = 0 – Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 4
Open and Short Circuits Undesirable short circuit – accidental connection between two nodes that are meant to be at different voltages. The resulting excessive current causes: overheating, fire, or explosion Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 5
Open and Short Circuits Open circuit : a circuit element through which zero current flows regardless of the voltage applied to it Resistance approaches infinity No current flows ex: a break in a circuit + i • At sufficiently high voltages arcing occurs R ∞ v i = 0 – Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 6
Open and Short Circuits Example : What happens to R 2 and R 3 if R 1 is shorted? V s = 2 V, R 1 = 2 Ω , R 2 = R 3 = 4 Ω , i 1 = 500mA R 2 and R 3 = ¼ W rating, R 1 = ½ W rating + v 1 – R 1 i 1 i 3 i 2 + + + _ v s v 2 v 3 R 3 R 2 – – Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods ECEN 301 7
Open and Short Circuits Example : What happens to R 2 and R 3 if R 1 is shorted? V s = 2 V, R 1 = 2 Ω , R 2 = R 3 = 4 Ω , i 1 = 500mA R 2 and R 3 = ¼ W rating, R 1 = ½ W rating v i R 1 1 1 + v 1 – 500 2 mA v 2 i R 1 i 1 2 1 V R i 3 i 2 2 1 + + 0 + v s v v _ v s 1 2 v 2 v 3 R 3 4 R 2 v v v – – 2 2 1 250 mA 1 V Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods ECEN 301 8
Open and Short Circuits Example : What happens to R 2 and R 3 if R 1 is shorted? V s = 2 V, R 1 = 2 Ω , R 2 = R 3 = 4 Ω , i 1 = 500mA R 2 and R 3 = ¼ W rating, R 1 = ½ W rating + v 1 – P i v P i v R 1 i 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 i 3 i 2 500 1 mA V 250 1 mA V + + + 500 mW 250 mW _ v s v 2 v 3 R 3 R 2 1 1 – – W W 2 4 Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods ECEN 301 9
Open and Short Circuits Example : What happens to R 2 and R 3 if R 1 is shorted? V s = 2 V, R 1 = 2 Ω , R 2 = R 3 = 4 Ω , i 1 = 500mA R 2 and R 3 = ¼ W rating, R 1 = ½ W rating 0 v v s 2 P i v v v 2 2 2 2 s 500 2 mA V i 1 2 V i 3 i 2 1 W v + + 2 i + _ v s 2 v 2 v 3 R 3 R R 2 2 – – 2 BAD! R 2 and 4 R 3 are damaged 500 mA Discussion #7 – Node and Mesh Methods ECEN 301 10
Series Resistors Series Rule : two or more circuit elements are said to be in series if the current from one element exclusively flows into the next element. From KCL: all series elements have the same current N R R EQ n 1 n R 2 R 3 R n R N R 1 ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ ∙ R EQ Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 11
Series Resistors Demonstration of series rule : apply KVL and Ohm’s law on the circuit + v 1 – i 0 V v v v 1 2 3 s V v v v R 1 1 2 3 s ( ) ( ) ( ) i R i R i R + + 1 2 3 V s 1.5V _ v 2 R 2 ( ) i R R R 1 2 3 – i R – v 3 + EQ V s R R 3 EQ i Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 12
Series Resistors Voltage divider : the voltage across each resistor in a series circuit is directly proportional to the ratio of its resistance to the total series resistance of the circuit R n v V n s R R R R R 1 2 3 n N R n V s R EQ R n NB : the ratio will always be <= 1 R EQ Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 13
Series Resistors Voltage divider : the voltage across each resistor in a series circuit is directly proportional to the ratio of its resistance to the total series resistance of the circuit + v 1 – i R 1 R R R + + 1 2 3 v V v V v V V s 1.5V _ v 2 R 2 1 2 3 s s s R R R – EQ EQ EQ – v 3 + R 3 Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 14
Series Resistors Example1 : Determine v 3 V s = 3V, R1 = 10 Ω , R 2 = 6 Ω , R 3 = 8 Ω – v 1 + i R 1 + + V s _ v 2 R 2 – + v 3 – R 3 Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 15
Series Resistors Example1 : Determine v 3 V s = 3V, R1 = 10 Ω , R 2 = 6 Ω , R 3 = 8 Ω – v 1 + i Using oltage Divider : Using Series Rule : V R 1 R R EQ R R R 3 v V 1 2 3 3 s R + + 10 6 8 EQ V s _ v 2 R 2 8 24 3 – 24 + v 3 – 1 V R 3 Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 16
Parallel Resistors Parallel Rule : two or more circuit elements are said to be in parallel if the elements share the same terminal s From KVL: the elements will have the same voltage 1 1 1 1 1 1 R EQ 1 1 1 1 R R R R R 1 2 3 EQ N R R R R 1 2 3 N NB : the parallel + + + + + + combination of two R n R 1 R 2 R 3 R N R EQ – resistors is often – – – – – written: R 1 || R 2 Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 17
Parallel Resistors Demonstration of parallel rule : apply KCL and Ohm’s law on the circuit KCL at node a : 0 i i i i 1 2 3 s Node a i i i i s 1 2 3 + v v v i 1 i 3 i 2 R R R 1 2 3 + + + 1 1 1 v v i s R 3 R 1 R 2 R R R 1 2 3 – – – 1 v – R EQ v R EQ i s Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 18
Parallel Resistors Current divider : the current in a parallel circuit divides in proportion to the resistances of the individual parallel elements 1 R n i i n s 1 1 1 1 1 R R R R R 1 2 3 n N 1 R n i s 1 R EQ R R EQ EQ NB : the ratio will always be <= 1 i R s R n n Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 19
Parallel Resistors Current divider : the current in a parallel circuit divides in proportion to the resistances of the individual parallel elements R 1 / EQ i R i 1 i i 2 s 1 s R 1 / R 2 EQ R i 1 i 3 i 2 R EQ EQ i i i s + + + R 3 s R 1 i s R 3 R 1 R 2 3 – – – NB : it makes sense that the smaller the resistor, the larger the amount of current that will flow. Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 20
Parallel Resistors Example2 : find i 1 R 1 = 10 Ω , R 2 = 2 Ω , R 3 = 20 Ω , I s = 4A i 1 i 3 i 2 – – – i R 3 R 1 R 2 + + + s Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 21
Parallel Resistors Example2 : find i 1 R 1 = 10 Ω , R 2 = 2 Ω , R 3 = 20 Ω , I s = 4A Using current divider : NB : all elements share terminals 1 1 R EQ 1 1 1 R 1 i i R R R 1 1 s 1 2 3 i 1 i 3 i 2 1 R EQ 1 1 1 – – – 1 10 2 20 i R 3 R 1 R 2 10 4 1 + + + 13 s 2 10 1 20 20 40 20 65 13 0 . 615 A Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 22
Parallel Resistors Example2 : find i 1 R 1 = 10 Ω , R 2 = 2 Ω , R 3 = 20 Ω , I s = 4A Verify tha t KCL holds with current dividing : 0 i i i i 1 2 3 s i i i i s 1 2 3 1 / 1 / 1 / R R R i 1 i 3 i 2 1 2 3 i i i s s s 1 / 1 / 1 / R R R – EQ EQ EQ – – 1 / 1 / 1 / i R 3 R R R R 1 R 2 1 2 3 i s + 1 / + + R EQ s 1 / R EQ i s 1 / R EQ i s Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 23
Parallel Resistors The parallel combination of resistors is often written: For two resistors: R 1 || R 2 For three resistors: R 1 || R 2 || R 3 etc. In each case R EQ for the parallel combination must be found 1 1 || || R R R || R R 1 2 3 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 + + + + + R R R R R 1 2 3 R 1 R 2 R 3 R 1 R 2 1 2 1 – – – – – 1 R R R R R R R R 2 3 1 3 1 2 2 1 R R R R R 1 2 3 + + 1 2 R R R R 1 || R 2 R 1 || R 2 || R 3 R R 1 2 3 – 1 2 – R R R R R R R R 2 3 1 3 1 2 2 1 Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 24
Parallel Resistors Example3 : find v v s = 5V, R 1 = 1k Ω , R 2 = 1k Ω + R 1 – + + + + _ v s v R 2 R 3 i s – – – Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 25
Parallel Resistors Example3 : find v v s = 5V, R 1 = 1k Ω , R 2 = 1k Ω + R 1 – + R 1 – + + + + + + _ _ v s v s v v R 2 R 3 R 2 || R 3 i s i s – – – – Discussion #5 – Ohm’s Law ECEN 301 26
Recommend
More recommend