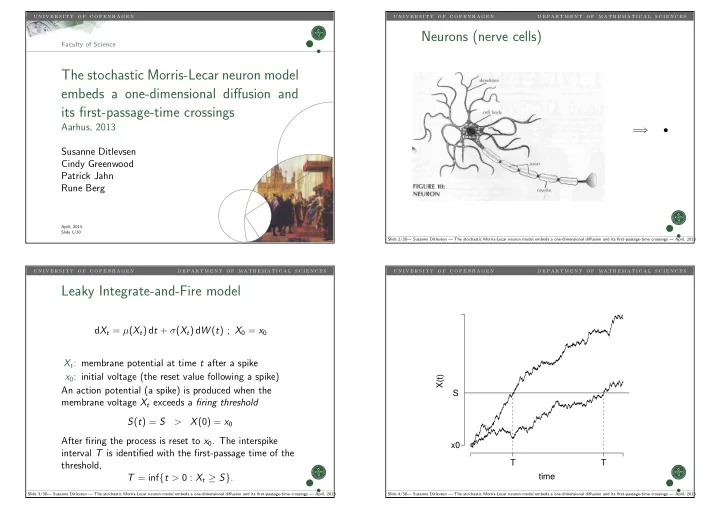

u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s Neurons (nerve cells) Faculty of Science The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings Aarhus, 2013 = ⇒ • Susanne Ditlevsen Cindy Greenwood Patrick Jahn Rune Berg April, 2013 Slide 1/30 Slide 2/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s Leaky Integrate-and-Fire model d X t = µ ( X t ) d t + σ ( X t ) d W ( t ) ; X 0 = x 0 X t : membrane potential at time t after a spike x 0 : initial voltage (the reset value following a spike) X(t) An action potential (a spike) is produced when the S membrane voltage X t exceeds a firing threshold S ( t ) = S > X (0) = x 0 After firing the process is reset to x 0 . The interspike x0 interval T is identified with the first-passage time of the T T threshold, time T = inf { t > 0 : X t ≥ S } . Slide 3/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 Slide 4/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013
u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s Two commonly used Leaky Two commonly used Leaky Integrate-and-Fire neuron models (I) Integrate-and-Fire neuron models (II) The Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process: The Feller process (also CIR or square root process): � � − X t � − X t − V I � � d X t = τ + µ d t + σ d W t ; X 0 = x 0 . d( X t − V I ) = + µ d t + σ X t − V I d W t ; τ X 0 = x 0 ≥ V I . where X t : membrane potential at time t after a spike where τ : membrane time constant, reflects spontaneous V I : inhibitory reversal potential voltage decay ( > 0) and µ : characterizes constant neuronal input σ 2 2 µ ≥ σ : characterizes erratic neuronal input x 0 : initial voltage (the reset value following a spike) Slide 5/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 Slide 6/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s Intracellular recording of membrane Spike generation potential (b) measured membrane voltage, V(t) 7 6 standard deviation 5 0 4 3 −50 2 1 0 500 0 time (ms) −10 −5 0 5 10 time (ms) Slide 7/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 Slide 8/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013
u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s Spike generation Estimation of spike intensity A Global Jump Diffusion Model (a) (b) ● ● 1 −2 ● τ ( X t )( a + g ( t ) − X t ) dt + σ ( X t ) dW t +( x ∗ − X t − ) µ ( X t − , dt ) , dX t = ● ● ● ● −3 0.2 ● ● ) ( 1 ms ) −4 λ ) ) ( λ ● log ( where µ ( X t − , dt ) is a Poisson random measure with ● λ ( ● −5 ● ● λ 0.1 intensity measure λ ( X t − ) dt . ● −6 ● ● ● ● Estimator: ● ● −7 ● ● ● ● ● ● 0 ● ● ● ● ● � l j =1 1 [ x − h 2 ] ( Y s j ) −55 −50 −45 −55 −50 −45 2 , x + h ˆ x (mV) x (mV) λ ( x ) := , � M i =1 ∆ 1 [ x − h 2 ] ( Y i ) 2 , x + h Final estimate: � x − ( − 38 . 25) � ˆ λ ( x ) = exp (15 . 3 + 0 . 4 x ) = exp 2 . 5 Slide 9/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 Slide 10/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s The Morris Lecar model 20 mV 1 dV t = C ( − g Ca m ∞ ( V t )( V t − V Ca ) − g K W t ( V t − V K ) data − g L ( V t − V L ) + I ) dt = ( α ( V t )(1 − W t ) − β ( V t ) W t ) dt dW t with the auxiliary functions given by model � � v − V 1 �� 1 m ∞ ( v ) = 1 + tanh 2 V 2 1 � v − V 3 � � � v − V 3 �� α ( v ) = 2 φ cosh 1 + tanh 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 2 V 4 V 4 time (s) 1 � v − V 3 � � � v − V 3 �� β ( v ) = 2 φ cosh 1 − tanh 2 V 4 V 4 Slide 11/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 Slide 12/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013
u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s (A) normalized conductance W t 0.5 20 0.4 membrane voltage, V(t) 0 0.3 −20 0.2 −40 ● 0.1 −40 −20 0 20 40 0 200 400 600 800 1000 membrane voltage V t time Slide 13/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 Slide 14/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s u n i v e r s i t y o f c o p e n h a g e n d e p a r t m e n t o f m a t h e m a t i c a l s c i e n c e s The stochastic Morris Lecar model 0.5 1 dV t = C ( − g Ca m ∞ ( V t )( V t − V Ca ) − g K W t ( V t − V K ) normalized conductance, W(t) 0.4 − g L ( V t − V L ) + I ) dt 0.3 dW t = ( α ( V t )(1 − W t ) − β ( V t ) W t ) dt � 0.2 2 α ( V t ) β ( V t ) + σ α ( V t ) + β ( V t ) W t (1 − W t ) dB t ● 0.1 −40 −20 0 20 40 membrane voltage, V(t) Slide 15/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013 Slide 16/30— Susanne Ditlevsen — The stochastic Morris-Lecar neuron model embeds a one-dimensional diffusion and its first-passage-time crossings — April, 2013
Recommend
More recommend