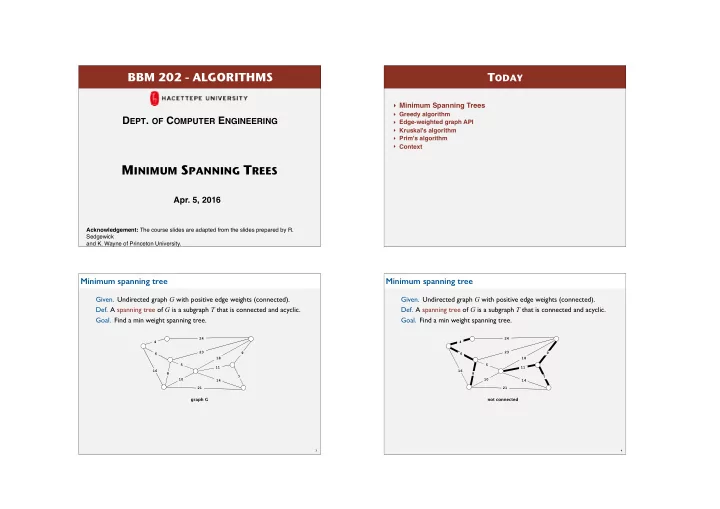

BBM 202 - ALGORITHMS T ODAY ‣ Minimum Spanning Trees ‣ Greedy algorithm D EPT . OF C OMPUTER E NGINEERING ‣ Edge-weighted graph API ‣ Kruskal's algorithm ‣ Prim's algorithm ‣ Context M INIMUM S PANNING T REES Apr. 5, 2016 Acknowledgement: The course slides are adapted from the slides prepared by R. Sedgewick and K. Wayne of Princeton University. Minimum spanning tree Minimum spanning tree Given. Undirected graph G with positive edge weights (connected). Given. Undirected graph G with positive edge weights (connected). Def. A spanning tree of G is a subgraph T that is connected and acyclic. Def. A spanning tree of G is a subgraph T that is connected and acyclic. Goal. Find a min weight spanning tree. Goal. Find a min weight spanning tree. 24 24 4 4 23 23 9 9 6 6 18 18 5 5 11 11 16 16 8 8 7 7 10 10 14 14 21 21 graph G not connected 3 4
Minimum spanning tree Minimum spanning tree Given. Undirected graph G with positive edge weights (connected). Given. Undirected graph G with positive edge weights (connected). Def. A spanning tree of G is a subgraph T that is connected and acyclic. Def. A spanning tree of G is a subgraph T that is connected and acyclic. Goal. Find a min weight spanning tree. Goal. Find a min weight spanning tree. 24 24 4 4 23 23 9 9 6 6 18 18 5 5 11 11 16 16 8 8 7 7 10 10 14 14 21 21 not acyclic spanning tree T: cost = 50 = 4 + 6 + 8 + 5 + 11 + 9 + 7 Brute force. Try all spanning trees? 5 6 Network design Models of nature MST of bicycle routes in North Seattle MST of random graph http://www.flickr.com/photos/ewedistrict/21980840 http://algo.inria.fr/broutin/gallery.html 7 8
Medical image processing Applications MST is fundamental problem with diverse applications. • Dithering. MST describes arrangement of nuclei in the epithelium for cancer research • Cluster analysis. • Max bottleneck paths. • Real-time face verification. • LDPC codes for error correction. • Image registration with Renyi entropy. • Find road networks in satellite and aerial imagery. • Reducing data storage in sequencing amino acids in a protein. • Model locality of particle interactions in turbulent fluid flows. • Autoconfig protocol for Ethernet bridging to avoid cycles in a network. • Approximation algorithms for NP-hard problems (e.g., TSP , Steiner tree). • Network design (communication, electrical, hydraulic, cable, computer, road). http://www.ics.uci.edu/~eppstein/gina/mst.html http://www.bccrc.ca/ci/ta01_archlevel.html 9 10 Cut property M INIMUM S PANNING T REES Simplifying assumptions. Edge weights are distinct; graph is connected. ‣ Greedy algorithm ‣ Edge-weighted graph API Def. A cut in a graph is a partition of its vertices into two (nonempty) sets. ‣ Kruskal's algorithm A crossing edge connects a vertex in one set with a vertex in the other. ‣ Prim's algorithm ‣ Context Cut property. Given any cut, the crossing edge of min weight is in the MST. crossing edges separating gray from white vertices are drawn in red e minimum-weight crossing edge must be in the MST 12
Cut property: correctness proof Greedy MST algorithm • Start with all edges colored gray. Simplifying assumptions. Edge weights are distinct; graph is connected. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. Def. A cut in a graph is a partition of its vertices into two (nonempty) sets. A crossing edge connects a vertex in one set with a vertex in the other. 0-7 0.16 2-3 0.17 Cut property. Given any cut, the crossing edge of min weight is in the MST. 1 1-7 0.19 3 0-2 0.26 5 5-7 0.28 Pf. Let e be the min-weight crossing edge in cut. 7 1-3 0.29 • Suppose e is not in the MST. 2 the MST does 1-5 0.32 not contain e • Adding e to the MST creates a cycle. 2-7 0.34 0 f • Some other edge f in cycle must be a crossing edge. 4-5 0.35 1-2 0.36 • Removing f and adding e is also a spanning tree. 6 4 4-7 0.37 • Since weight of e is less than the weight of f , e 0-4 0.38 that spanning tree is lower weight. an edge-weighted graph 6-2 0.40 • Contradiction. ▪ 3-6 0.52 adding e to MST 6-0 0.58 creates a cycle 6-4 0.93 13 14 Greedy MST algorithm Greedy MST algorithm • Start with all edges colored gray. • Start with all edges colored gray. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. crossing edges crossing edge (sorted by weight) 1 1 3 3 5 5 0-2 0.26 in MST 1-3 0.29 7 7 2 2 2-7 0.34 1-2 0.36 0 0 6-0 0.58 6-4 0.93 6 6 4 4 min-weight grey vertices form crossing edge MST edges one side of cut 0-2 15 16
Greedy MST algorithm Greedy MST algorithm • Start with all edges colored gray. • Start with all edges colored gray. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. crossing edges (sorted by weight) 1 1 3 3 5 5 5-7 0.28 in MST 1-5 0.32 7 7 2 2 4-5 0.35 min-weight 0 0 crossing edge 6 6 4 4 MST edges MST edges 0-2 0-2 5-7 17 18 Greedy MST algorithm Greedy MST algorithm • Start with all edges colored gray. • Start with all edges colored gray. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. crossing edges (sorted by weight) 1 1 3 3 5 5 6-2 0.40 in MST 3-6 0.52 7 7 2 2 6-0 0.58 6-4 0.93 0 0 6 6 4 4 min-weight crossing edge MST edges MST edges 0-2 5-7 0-2 5-7 6-2 19 20
Greedy MST algorithm Greedy MST algorithm • Start with all edges colored gray. • Start with all edges colored gray. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. crossing edges (sorted by weight) 1 1 3 3 5 5 0-7 0.16 in MST 2-3 0.17 7 7 2 2 2-7 0.34 min-weight 4-5 0.35 0 0 crossing edge 1-2 0.36 4-7 0.37 6 6 4 4 3-6 0.52 MST edges MST edges 0-2 5-7 6-2 0-2 5-7 6-2 0-7 21 22 Greedy MST algorithm Greedy MST algorithm • Start with all edges colored gray. • Start with all edges colored gray. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. crossing edges min-weight (sorted by weight) crossing edge 1 1 3 3 5 5 2-3 0.17 in MST 1-7 0.19 7 7 2 2 1-5 0.32 1-2 0.36 0 0 6 6 4 4 MST edges MST edges 0-2 5-7 6-2 0-7 0-2 5-7 6-2 0-7 2-3 23 24
Greedy MST algorithm Greedy MST algorithm • Start with all edges colored gray. • Start with all edges colored gray. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. crossing edges (sorted by weight) 1 1 3 3 5 5 1-7 0.19 in MST 1-3 0.29 7 7 2 2 1-5 0.32 min-weight 4-5 0.35 0 0 crossing edge 1-2 0.36 4-7 0.37 6 6 4 4 0-4 0.38 6-4 0.93 MST edges MST edges 0-2 5-7 6-2 0-7 2-3 0-2 5-7 6-2 0-7 2-3 1-7 25 26 Greedy MST algorithm Greedy MST algorithm • Start with all edges colored gray. • Start with all edges colored gray. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Find a cut with no black crossing edges, and color its min-weight edge black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. • Repeat until V - 1 edges are colored black. crossing edges (sorted by weight) 1 1 3 3 5 5 4-5 0.35 in MST 4-7 0.37 7 7 2 2 0-4 0.38 min-weight 6-4 0.93 0 0 crossing edge 6 6 4 4 MST edges MST edges 0-2 5-7 6-2 0-7 2-3 1-7 0-2 5-7 6-2 0-7 2-3 1-7 4-5 27 28
Recommend
More recommend