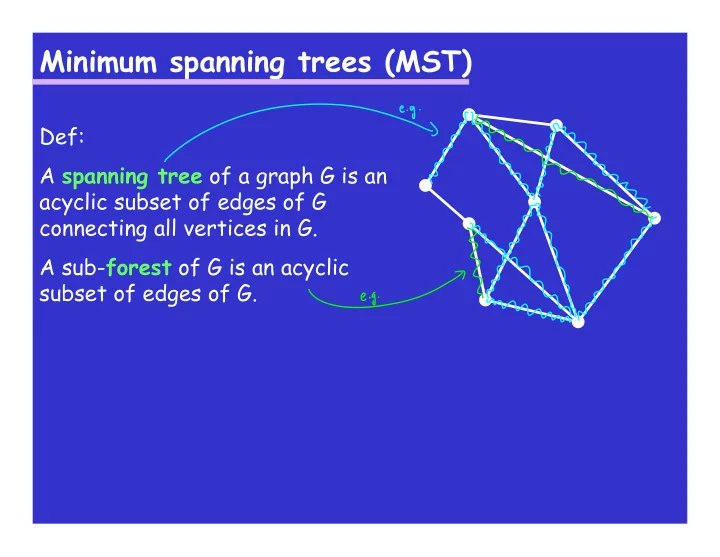

Minimum spanning trees (MST) Def: A spanning tree of a graph G is an acyclic subset of edges of G connecting all vertices in G. A sub- forest of G is an acyclic subset of edges of G.
Minimum spanning trees (MST) 1 Def: 15 7 8 A spanning tree of a graph G is an 4 acyclic subset of edges of G 3 5 7 connecting all vertices in G. 2 1 A sub- forest of G is an acyclic 1 6 subset of edges of G. 2 Def: Given is a weighted (undirected) graph G=(V,E,w) where w:E->Reals defines a weight of every edge in E. A minimum spanning tree of G is a spanning tree with the minimum total weight of edges.
Minimum spanning trees (MST) - Kruskal 1 15 7 8 4 3 5 7 2 1 1 6 2 Kruskal ( G=(V,E,w) ) 1. Let T= ∅ 2. Sort the edges in increasing order of weight 3. For edge e do 4. If T ∪ e does not contain a cycle then 5. Add e to T 6. Return T
Minimum spanning trees (MST) - Kruskal Lemma: Algo is correct. Kruskal ( G=(V,E,w) ) 1. Let T= ∅ 2. Sort the edges in increasing order of weight 3. For edge e do 4. If T ∪ e does not contain a cycle then 5. Add e to T 6. Return T
Minimum spanning trees (MST) - Kruskal 1 Implementation? 15 7 8 4 3 5 7 2 1 1 6 2 Kruskal ( G=(V,E,w) ) 1. Let T= ∅ 2. Sort the edges in increasing order of weight 3. For edge e do 4. If T ∪ e does not contain a cycle then 5. Add e to T 6. Return T
Minimum spanning trees (MST) - Kruskal 1 Implementation? 15 7 - Union-Find datastructure 8 4 Init (V) 3 5 7 1. for every vertex v do 2. boss[v]=v 2 1 1 3. size[v]=1 6 4. set[v]={v} 2 Union (u,v) 1. if size[boss[u]]>size[boss[v]] then 2. set[boss[u]]=set[boss[u]] union set[boss[v]] 3. size[boss[u]]+=size[boss[v]] 4. for every z in set[boss[v]] do 5. boss[z]=boss[u] 6. else do steps 2.-5. with u,v switched
Minimum spanning trees (MST) - Kruskal 1 Analysis of Union-Find 15 7 8 Lemma: 4 3 k Unions take O(k log k) time 5 7 2 1 1 6 2 Union (u,v) 1. if size[boss[u]]>size[boss[v]] then 2. set[boss[u]]=set[boss[u]] union set[boss[v]] 3. size[boss[u]]+=size[boss[v]] 4. for every z in set[boss[v]] do 5. boss[z]=boss[u] 6. else do steps 2.-5. with u,v switched
Minimum spanning trees (MST) - Kruskal 1 Analysis of Union-Find 15 7 8 Lemma: 4 3 k Unions take O(k log k) time 5 7 2 1 1 6 2 Corollary: The running time of Kruskal is: O(|E| log |E|) + O(|V| log |V|)
Minimum spanning trees (MST) - Prim 1 Prim ( G=(V,E,w) ) 15 1. Let T= ∅ , H= ∅ 7 8 2. For every vertex v do 4 3. cost[v]= ∞ , parent[v]=null 3 4. Let u be a vertex 5 7 5. Update (u) 6. For i=1 to n-1 do 2 1 1 7. u=vertex from H of 6 smallest cost (remove) Add (u,parent[u]) to T 2 • Update(u) • • Return T Update (u) 1. For every neighbor v of u 2. If cost[v]>w(u,v) then 3. cost[v]=w(u,v), parent[v]=u 4. If v not in H then 5. Add v to H
Minimum spanning trees (MST) - Prim Lemma: Prim is correct. Running time:
Single source shortest paths - Dijkstra 1 Input: G=(V,E,w) and a vertex s 15 (w non-negative) 7 8 4 Output: shortest paths from s to 3 every other vertex 5 7 2 1 1 6 Can use similar idea to Prim? 2
Single source shortest paths - Dijkstra 1 15 Dijkstra ( G=(V,E,w), s ) 7 1. Let H= ∅ 8 2. For every vertex v do 4 3 3. dist[v]= ∞ 5 7 4. dist[s]=0 5. Update (s) 2 1 1 6. For i=1 to n-1 do 6 7. u=extract vertex from H of smallest cost 2 8. Update(u) • Return dist[] Update (u) 1. For every neighbor v of u 2. If dist[v]>dist[u]+w(u,v) then 3. dist[v]=dist[u]+w(u,v) 4. If v not in H then 5. Add v to H
Single source shortest paths - Dijkstra 1 Lemma: Dijkstra is correct. 15 7 8 4 3 5 7 2 1 1 6 2 Running time:
All pairs shortest paths – Floyd-Warshall 1 Input: G=(V,E,w), w non-negative 15 7 8 Output: shortest paths between 4 all pairs of vertices 3 5 7 2 1 1 6 2
All pairs shortest paths – Floyd-Warshall 1 Input: G=(V,E,w), w non-negative 15 7 8 Output: shortest paths between 4 all pairs of vertices 3 5 7 2 1 1 6 Idea 1: • Use Dijkstra from every vertex 2
All pairs shortest paths – Floyd-Warshall 1 Input: G=(V,E,w), w non-negative 15 7 8 Output: shortest paths between 4 all pairs of vertices 3 5 7 2 1 1 6 Idea 1: • Use Dijkstra from every vertex 2 Idea 2: • How about dynamic programming?
All pairs shortest paths – Floyd-Warshall 1 Heart of the algorithm: 15 7 8 the length of the 4 shortest path 3 S[i,j,k] = 5 7 from i to j using only vertices ≤ k 2 1 1 6 2
All pairs shortest paths – Floyd-Warshall 1 Heart of the algorithm: 15 7 8 the length of the 4 shortest path 3 S[i,j,k] = 5 7 from i to j using only vertices ≤ k 2 1 1 6 2 How to compute S[i,j,k] ? S[i,j,k] =
All pairs shortest paths – Floyd-Warshall 1 15 Floyd-Warshall ( G=(V,E,w) ) 7 8 1. For i=1 to |V| do 4 3 2. For j=1 to |V| do 5 7 3. S[i,j,0] = w(i,j) 4. For k=1 to |V| do 2 1 1 5. For i=1 to |V| do 6 6. For j=1 to |V| do 7. S[i,j,k] = min { 2 8. S[i,j,k-1], 9. S[i,k,k-1]+S[k,j,k-1] } 10.Return ? w(i,j) if k = 0 S[i,j,k] = min { S[i,j,k-1], S[i,k,k-1] + S[k,j,k-1] } if k > 0
Single source shortest paths – Bellman-Ford -1 Input: 4 7 -7 directed G=(V,E,w) and a vertex s 4 3 5 -3 Output: 2 • FALSE if exists reachable 1 1 6 negative-weight cycle, 2 • distance to every vertex, otherwise.
Single source shortest paths – Bellman-Ford -1 Input: 4 7 -7 directed G=(V,E,w) and a vertex s 9 3 5 -3 Output: 2 • FALSE if exists reachable 1 1 6 negative-weight cycle, 2 • distance to every vertex, otherwise.
Single source shortest paths – Bellman-Ford -1 4 7 -7 8 3 5 -3 Bellman-Ford ( G=(V,E,w), s ) 2 1 1 6 1. For every vertex v 2. d[v] = ∞ 2 3. d[s]=0 4. For i=1 to |V|-1 do 5. For every edge (u,v) in E do 6. If d[v]>d[u]+w(u,v) then 7. d[v]=d[u]+w(u,v) 8. For every edge (u,v) in E do 9. If d[v]>d[u]+w(u,v) then 10. Return NEGATIVE CYCLE 11.Return d[]
Single source shortest paths – Bellman-Ford -1 Lemma: Bellman-Ford is correct. 4 7 -7 Running time: 8 3 5 -3 Bellman-Ford ( G=(V,E,w), s ) 2 1 1 6 1. For every vertex v 2. d[v] = ∞ 2 3. d[s]=0 4. For i=1 to |V|-1 do 5. For every edge (u,v) in E do 6. If d[v]>d[u]+w(u,v) then 7. d[v]=d[u]+w(u,v) 8. For every edge (u,v) in E do 9. If d[v]>d[u]+w(u,v) then 10. Return NEGATIVE CYCLE 11.Return d[]
Recommend
More recommend