I. Overview of photosynthesis L06: Photosynthesis & Respiration - PDF document
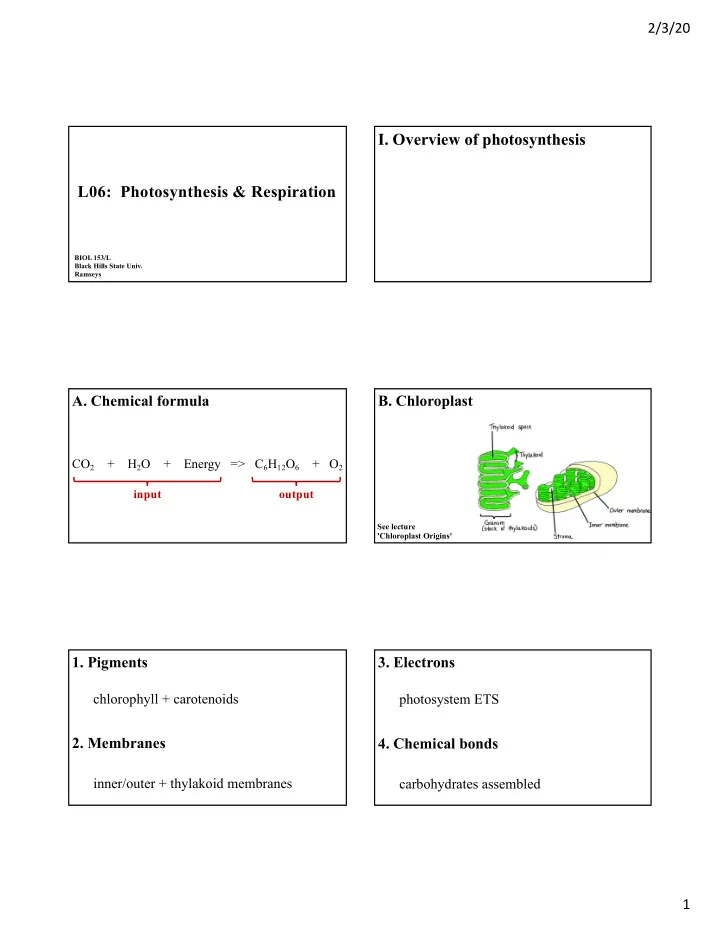
2/3/20 I. Overview of photosynthesis L06: Photosynthesis & Respiration BIOL 153/L Black Hills State Univ. Ramseys A. Chemical formula B. Chloroplast CO 2 + H 2 O + Energy => C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 input output See
2/3/20 I. Overview of photosynthesis L06: Photosynthesis & Respiration BIOL 153/L Black Hills State Univ. Ramseys A. Chemical formula B. Chloroplast CO 2 + H 2 O + Energy => C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 input output See lecture 'Chloroplast Origins' 1. Pigments 3. Electrons chlorophyll + carotenoids photosystem ETS 2. Membranes 4. Chemical bonds inner/outer + thylakoid membranes carbohydrates assembled 1
2/3/20 C. Action spectrum 1. Types of electromagnetic radiation 1. Types of electromagnetic radiation 2. Wavelengths used by plants blue light: ~400 - 500 nm red light: ~600 - 700 nm D. Biochemical pathways 2. Wavelengths used by plants why are plants green? 2
2/3/20 1. Light reactions II. Overview of respiration light energy converted to ATP + NADPH 2. Dark Reactions ATP + NADPH assembles carbohydrates A. Chemical formula B. Mitochondria C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 => CO 2 + H 2 O + Energy input output See lecture 'Origin of Chloroplasts' 1. Membranes 3. Chemical bonds inner/outer membranes (cristae) Carbohydrates disassembled 2. Electrons respiration ETS See lecture 'Origin of Chloroplasts' 3
2/3/20 1. Aerobic (high ATP yield) C. Biochemical pathways Glycolysis => Respiration (cytosol) (mitochondria) 2. Anaerobic (low ATP yield) Glycolysis => Fermentation (cytosol) (cytosol) III. P&R as opposing biochem forces ouput of photosynthesis = input for respiration (and vice versa) Fig. 6-5 Raven p. 95 IV. Measurement of P&R • Option #1: Biomass organic molecules made ( P ) terrestrial : straightforward super insightful! minus aquatic : straightforward organic molecules burned ( R ) 4
2/3/20 • Option #2: Gas exchange Leaf disk assay O 2 produced ( P ) terrestrial : leaf challenging disk or aquatic : CO 2 produced ( R ) straightforward water column Scenario #1: P > R Scenario #2: R > P • more O 2 made vs. consumed • more O 2 consumed vs. made • O 2 accumulates in leaf • O 2 disappears in leaf • bouyant bubbles • no bouyount bubbles • leaf floats • leaf drops V. Terrestrial consequences of P&R photosynthetic organisms transformed earth (geological time) 5
2/3/20 VI. Aquatic consequences of P&R A. Sources of oxygen • Atmosphere Waves (lake surface) photosynthetic organisms transform water bodies • Small photosynthetic plankton: P (daily + seasonally) • Large photosynthetic plants: P C. Changes through day B. Sources of carbon dioxide • Decomposition • Heterotrophic organisms: R • Photosynthetic organisms: R Wind Wind Wind Wind Waves (lake surface) Waves (lake surface) Waves (lake surface) Waves (lake surface) High O 2 High CO 2 Phyto- Phyto- plankton plankton Summer (Day) Summer (Night) Summer (Day) Summer (Night) 6
2/3/20 D. Changes through seasons Wind Snow Waves (lake surface) Ice Phyto- plankton Summer (Day) Winter (Day) Wind Snow Waves (lake surface) Ice Min O 2 Low O 2 High O 2 Phyto- plankton Summer (Day) Winter (Day) 7
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.