
Photosynthesis
Plants
Leaf Structure
Stomata
Plant Adaptations for Photosynthesis
Desert Plant Adaptations
Solar Energy • Solar energy travels to Earth in different wavelengths of light
Pigments • A pigment is a protein molecule that absorbs light • The primary pigments in green plants are chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b
Chlorophyll Pigments • Chlorophyll pigments absorb blue-violet and red regions of the visible spectrum best
Other Plant Pigments • Cooler temperatures cause plants to produce less chlorophyll, revealing “hidden” pigments • Carotenes – red and orange • Xanthophylls – yellow • Anthocyanins – purple, red, blue (pH dependent) • Fucoxanthins - brown
Purpose of Photosynthesis • To convert solar energy into a form of energy that is useable to all organisms • Solar energy is stored in the chemical bonds of glucose (chemical energy)
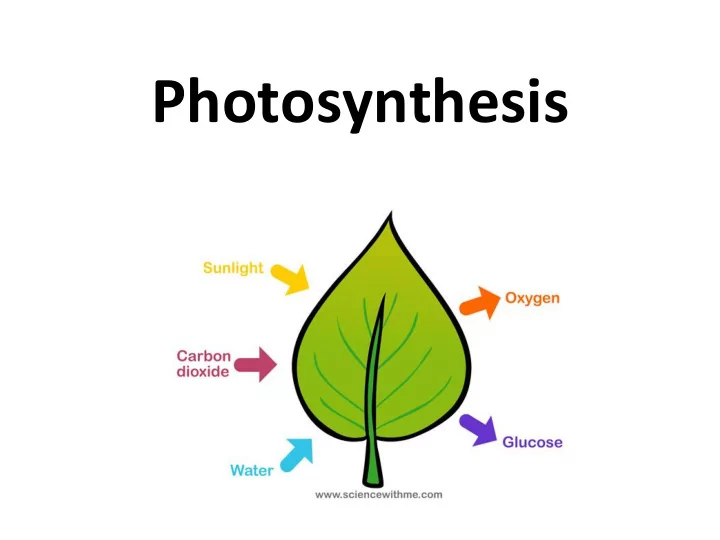
Photosynthesis Reaction “putting together with light”
Photosynthetic Organisms • Green plants • Algae • Cyanobacteria
Simple Story of Photosynthesis and Food
Reactants and Products for Photosynthesis • Identify the reactants: • Identify the products:
Photosynthetic Organelle • Photosynthetic reactions occur within the chloroplast • Contains the green pigment chlorophyll
Summary of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Summary • The reactions of photosynthesis use solar energy to convert carbon dioxide and water into high energy sugars (glucose) and oxygen gas
Photosynthesis Reaction 1. Light absorption by chlorophyll molecules 2. Light dependent reactions 3. Calvin Cycle
Chloroplast
Light Absorption by the Chlorophyll Molecules • Clusters of chlorophyll pigments called photosystems absorb light energy • Light energy “excites” or energizes the electrons of the chlorophyll pigments • Shorter wavelengths of light have more energy and are therefore more effective at “exciting” electrons
Photosystems are embedded within the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts
Light Dependent Reactions • Occur within the thylakoid membranes of the chloroplasts • “energy building” reactions • Require light in order to occur
Light Dependent Reactions
Light Dependent Reactions Summary • Light energy splits water molecules into hydrogen ions (H + ) and oxygen gas ( photolysis) • Two high energy compounds, ATP and NADPH , are also produced • ATP and NADPH transfer energy (“excited” electrons) to the Calvin cycle
Light Dependent Reactions
Light Dependent Reactions Products • Oxygen gas – released into the atmosphere (waste product) • ATP and NADPH – to the Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle • Occur in the stroma of the chloroplasts • “sugar building” reactions
Calvin Cycle
Calvin Cycle • Inorganic carbon (from CO 2 ) is incorporated into organic carbon (carbon fixation) • CO 2 combines with a five-carbon sugar called RuBP (forms an intermediate 6-carbon compound) • Energy stored in ATP and NADPH is used to convert the temporary 6-C intermediate compound into carbohydrates
Recommend
More recommend