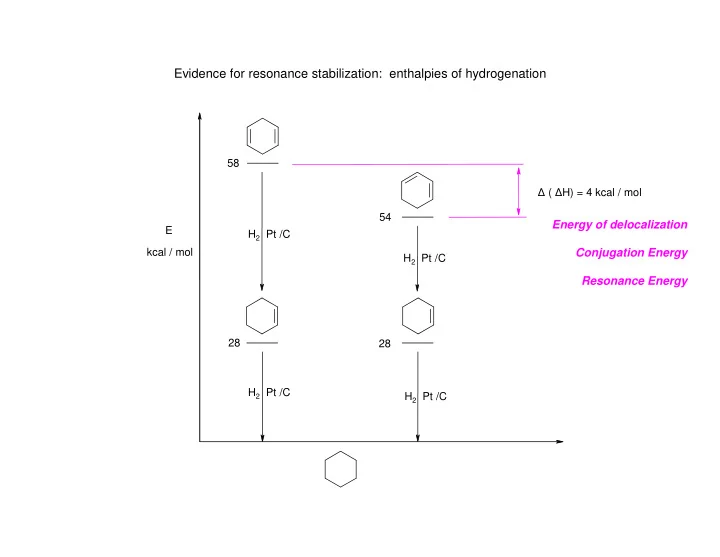

Evidence for resonance stabilization: enthalpies of hydrogenation 58 � ( � H) = 4 kcal / mol 54 Energy of delocalization E H 2 Pt /C Conjugation Energy kcal / mol H 2 Pt /C Resonance Energy 28 28 H 2 Pt /C H 2 Pt /C
Evidence for resonance stabilization: bond lengths C sp 2 - C sp 2 bond length: 1.34 H H C C H H C sp 2 - C sp 2 H H bond length: C C 1.34 H H C C C sp 2 - C sp 2 bond length: 1.46 H H H H H C C H H H C sp 3 - C sp 3 bond length: 1.54
Consider ( E )-1,3-pentadiene:
Evidence for resonance stabilization: conformational preferences Just as there is a barrier to rotation about the C 2 =C 3 of cis and trans -2-butene, there is a barrier to rotation about the C 2 - C 3 in 1,3-butadiene: H H H H H H H H H H H H s - trans s - cis conformation conformation E 3.9 kcal / mol 2.8 0 90 180 C 1 = C 2 --C 3 = C 4 torsion, degrees
Synthesis of conjugated dienes: • Just like alkene synthesis, only twice – conjugated dienes prefer to form as major products because they are the most thermodynamically stable products • Dehydrohalogenation of allylic halides Br CH 3 CH 2 O - Na + CH 3 CH 2 OH, � 90 % • Isolated dienes form only when it is impossible to form the conjugated isomer
What would the E1 outcome of dehydrobromination of 4-bromo-2,3,3-trimethylhexene be? Br ? CH 3 CH 2 OH, �
Reactions of conjugated dienes: • Additions of HX Br HBr + Br dark, -80 � C 81 % 19 %
Reactions of conjugated dienes: • Additions of HX Br HBr + Br dark, -80 � C 81 % 19 % 1,2-addition 1,4-addition Markovnikov addition product conjugate addition product
What’s the mechanism? + Br- + Br- + + H Br + Br Br
Looking at the carbocation intermediate more closely: what possible addition products can form? + + H H H H H H 3 3 + 4 4 C C 3 C C 4 C C H H C CH 3 C CH 3 H C CH 3 2 2 1 1 2 1 + . + + . + + + Br- Br- Br- 1,4-addition 1,3-addition 1,2-addition Br . . Br Br less stable isomer never observed more stable isomer
Reactions of conjugated dienes: • Additions of HX Br HBr + Br dark, -80 � C 81 % 19 % 1,2-addition 1,4-addition major minor Br HBr + Br dark, 45 � C 19 % 81 % 1,2-addition 1,4-addition minor major
Energy vs reaction coordinate diagram: + + Br- Br + HBr Br
Energy vs reaction coordinate diagram: + + Br- Br + HBr Br
Energy vs reaction coordinate diagram: + + Br- Br + HBr Br
Energy vs reaction coordinate diagram: For the second step, E act < E act so the rate of 1,2-addtion > the rate of 1,4-addition + + Br- Br 1,2-addition + HBr Br 1,4-addition When the major product that forms is the fastest forming product, a reaction is said to be under rate or kinetic control.
Energy vs reaction coordinate diagram: For the second step, if the temperature of the reaction is � E act reverse then the 1,2- addition product can equilibrate to the the more stable 1,4-addition product + + Br- Br 1,2-addition + HBr Br 1,4-addition When the major product that forms is the most stable product, a reaction is said to be under equilibrium , thermodynamic or stability control.
The Alder Rule diastereoselection is such that endo products predominate: O O OCH 3 OCH 3 O exo OCH 3 + or O OCH 3 O OCH 3 endo
exo transition state: C=O carbon hoovers over CH 2 of 1,3-cyclopentadiene more stable endo transition state: C=O carbon hoovers endo adduct over forming C2–C3 C=C of the cyclopentadiene
Ultraviolet - Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy Consider the ground state electronic configuration of ethene: � * C-C � � � � * C-H � � � E � * C-C � � � (lumo) C-C � � � � (homo) C-H � � � � C-C � � � � H H C C H H
The smallest � E that will promote a bonding electron to an antibonding orbital is: � * C-C � � � � * C-H � � � E � * C-C � � � (lumo) � E = UV-Vis (with λ = 162 nm here) C-C � � � � (homo) C-H � � � � C-C � � � � H H C C H H
λ max = 175 λ max = 245 λ max = 275 λ max = 215 Absorbance wavelength, nm
O = 280 nm A: � � � *
O = 204 nm O A: � � � * B: n � � * = 254 nm
C=O π electron transitions LUMO π * 254 nm 204 nm HOMO n HOMO-1 π
Lawsone in pH 7.2 phosphate buffer O OH O λ max A 215 1.52 265 2.16 290 (sh) 1.07 330 0.22 452 0.27
Recommend
More recommend