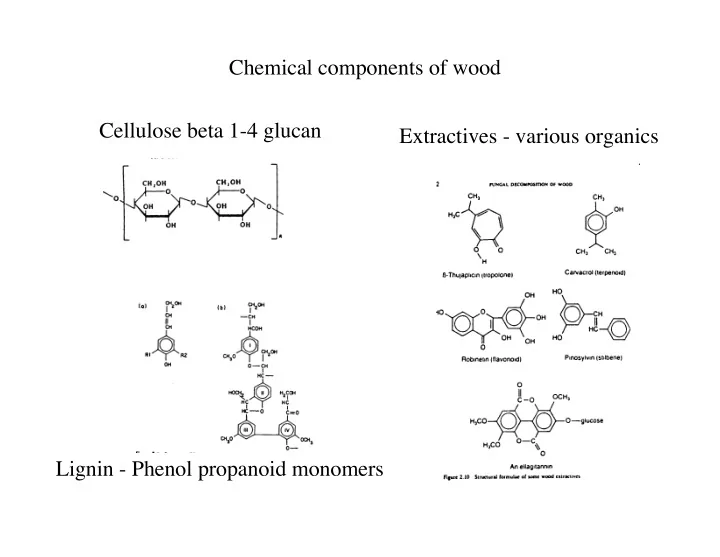

Chemical components of wood Cellulose beta 1-4 glucan Extractives - various organics Lignin - Phenol propanoid monomers
Wood X-section (hardwood) Wood X-section (conifer)
Distribution of water and nitrogen in wood
Brown rots White rots on living trees Oligoporus amarus (incense cedar only) Phellinus pini Oligoporus sequoiae (pines, Douglas-fir, & others) (coastal redwood only) Echinodontium tinctorius O. balsameus (true fir and hemlock) (Cupressus spp.) Ganoderma applanatum (primarily hardwoods, Oak etc.) Laetiporus sulphureus (wide host range, but esp. eucalyptus and oak) Cryptoporus volvatus ( conifers) Sterum hirsutum (hardwoods) Trichaptum abietinum (conifers) Trametes versicolor (hardwoods) ? Fomitopsis pinicola conifers Armillaria mellea gr. Phaeolus schweinitzii Heterobasidion annosum resinous conifers Phellinus weirii Dead trees Dead trees
Hypoxylon an Ascomycete that decays wood and colonizes endophytically
Diagram of Hypoxylon spore germination in response to bark exudates - work by Chapella
Echinodontium tinctorium Indian paint fungus a fungus that enters branch stubs and waits for years to cause heartrot
Brown rots White rots on living trees Oligoporus amarus (incense cedar only) Phellinus pini Oligoporus sequoiae (pines, Douglas-fir, & others) (coastal redwood only) Echinodontium tinctorius O. balsameus (true fir and hemlock) (Cupressus spp.) Ganoderma applanatum (primarily hardwoods, Oak etc.) Laetiporus sulphureus (wide host range, but esp. eucalyptus and oak) Cryptoporus volvatus ( conifers) Sterum hirsutum (hardwoods) Trichaptum abietinum (conifers) Trametes versicolor (hardwoods) ? Fomitopsis pinicola conifers Armillaria mellea gr. Phaeolus schweinitzii Heterobasidion annosum resinous conifers Phellinus weirii Dead trees Dead trees
The genus Phellinus (& Inonotus) has setae, and a brown hymenium
Phellinus pini gr. red ring rot See this on the street side of Tolman Hall
Ganoderma - showing brown spores
Brown rots White rots on living trees Oligoporus amarus (incense cedar only) Phellinus pini Oligoporus sequoiae (pines, Douglas-fir, & others) (coastal redwood only) Echinodontium tinctorius O. balsameus (true fir and hemlock) (Cupressus spp.) Ganoderma applanatum (primarily hardwoods, Oak etc.) Laetiporus sulphureus (wide host range, but esp. eucalyptus and oak) Cryptoporus volvatus ( conifers) Sterum hirsutum (hardwoods) Trichaptum abietinum (conifers) Trametes versicolor (hardwoods) ? Fomitopsis pinicola conifers Armillaria mellea gr. Phaeolus schweinitzii Heterobasidion annosum resinous conifers Phellinus weirii Dead trees Dead trees
Zone lines in wood cause by vegetative interactions between different genotypes of decay fungi
Trichaptum
Phellinus chrysoloma (P. pini gr.)
Cryptoporus volvatus The golf-ball fungus
Brown rots White rots on living trees Oligoporus amarus (incense cedar only) Phellinus pini Oligoporus sequoiae (pines, Douglas-fir, & others) (coastal redwood only) Echinodontium tinctorius O. balsameus (true fir and hemlock) (Cupressus spp.) Ganoderma applanatum (primarily hardwoods, Oak etc.) Laetiporus sulphureus (wide host range, but esp. eucalyptus and oak) Cryptoporus volvatus ( conifers) Sterum hirsutum (hardwoods) Trichaptum abietinum (conifers) Trametes versicolor (hardwoods) ? Fomitopsis pinicola conifers Armillaria mellea gr. Phaeolus schweinitzii Heterobasidion annosum resinous conifers Phellinus weirii Dead trees Dead trees
edge of root disease center note progressively thinner crowns and shorter heights
Lion’s tailing A crown symptom caused by lack of expansion of shoot and lower needle retention
Tree failure, a symptom of root decay Heterobasidion annosum P-strain in action at Yosemite village
Heterobasidion annosum P strain button conks under bark conks inside stumps stringy decay of roots
Heterobasidion center in Yosemite Valley image from Rizzo
Heterobasidion site Yosemite valley image from Rizzo
image from Rizzo
Heterobasidum parviporum (S-strain) behavior in fir ( Abies )
Heterobasidion parviporum S strain on fir ( Abies ) stump
Armillaria Complex of "biological species" mating Species Pathogenicity / Virulence distr. group NABS I A. ostoyae major major pathogen pathogen on conifers, also NA, Eur. attacks hardwoods, large clones NABS NABS VI VI A. mellea major major pathogen pathogen on hardwoods NA, Eur particularly ornamentals, also attacks conifers NABS NABS VII VII A. gallica weak pathogen, but may act as a NA, Eur. ( bulbosa) secondary invader of stressed trees, common in suppressed over mature hardwoods, very large clones A. borealis moderate pathogen, common butt rot Eur of conifers in northern Europe A. cepistipes similar to A . gallica in morphology NA, Eur and behavior, associated with butt rot of conifers in Finland NABS II A. gemina apparently weak pathogen NA NABS III A. calvenscens Observed as a hardwood pathogen in NA the NE NABS V A. sinapina Weak pathogen acts like A . gallica , NA haploids may be more virulent NABS NABS IX IX A. nabsnona Weak pathogen acts like A . gallica , NA haploids may be more virulent NABS X unnamed NA NABS XI unnamed NA bold species are known from California
Armillaria mycelial fan under bark Aerial view of A ostoyea centers Armillaria rhizomorphs
Armillaria mushrooms
Phellinus weirii aerial view
Phellinus weirii causing a butt rot in Douglas-fir note resinosus
Phellinus weirii furry looking setae Phellinus weirii laminar rot pattern and resupinate fruit body
Phaeolus schweinitzii brown cubic butt-rot
Inonotus triqueter upper surface X-section of fruitbody Lower surface (tubes)
Blackstain ( Leptographium wageneri var ponderosae ) in ponderosa pine
L. wageneri var. wageneri L. wageneri var. ponderosae Mesa Verde L. wageneri var. pseudotsugae Blodgett Forest meadow boarder on Mt. Tam
Blackstain: cross-section of Douglas fir On smaller root
Leptographium Mitotic spore state distribution
Bluestain fungi Ophiostoma, Ceratocystis and others
Bluestain fungi Ceratocystis Ophiostoma Perithecia Black Black or white Anamorphs Chalara Phialographium , Leptographium , (asexual states) Trichosporium , & other non-phialidic anamorphs Cell Walls Cellulose -. Rhamnose - Cellulose +. Rhamnose + Sensitivity to + - Cyclo-hexamide
Increment cores showing Little Leaf disease on short leaf pine reduced growth (right) Phytophthora- like zoosporangium
Recommend
More recommend