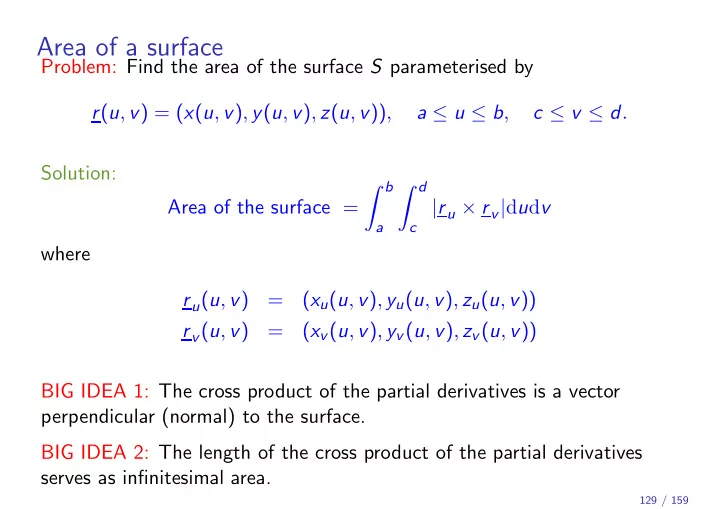

Area of a surface Problem: Find the area of the surface S parameterised by r ( u , v ) = ( x ( u , v ) , y ( u , v ) , z ( u , v )) , a ≤ u ≤ b , c ≤ v ≤ d . Solution: � b � d Area of the surface = | r u × r v | d u d v a c where r u ( u , v ) = ( x u ( u , v ) , y u ( u , v ) , z u ( u , v )) r v ( u , v ) = ( x v ( u , v ) , y v ( u , v ) , z v ( u , v )) BIG IDEA 1: The cross product of the partial derivatives is a vector perpendicular (normal) to the surface. BIG IDEA 2: The length of the cross product of the partial derivatives serves as infinitesimal area. 129 / 159
Area of a surface Example: Find the area of the surface of a sphere of radius R . Solution: Parametrisation (spherical coordinates) r ( u , v ) = ( R cos u sin v , R sin u sin v , R cos v ) , 0 ≤ u < 2 π, 0 ≤ v ≤ π Then r u ( u , v ) = ( − R sin u sin v , R cos u sin v , 0) r v ( u , v ) = ( R cos u cos v , R sin u cos v , − R sin v ) giving r u × r v = ( − R 2 cos u sin 2 v , R 2 sin u sin 2 v , − R 2 sin v cos v ) | r u × r v | = R 2 sin v and thus � 2 π � π � π R 2 sin v d u d v = 2 π sin v d v = 4 π R 2 0 0 0 130 / 159
Surface integral of a scalar function Let f : R 3 → R a scalar function. The integral of f over the surface S parameterised by r ( u , v ) = ( x ( u , v ) , y ( u , v ) , z ( u , v )) , a ≤ u ≤ b , c ≤ v ≤ d . is defined as � b � d �� f d S = f ( r ( u , v )) | r u × r v | d u d v S a c 131 / 159
Surface integral of a scalar function Example: Calculate the surface integral of f ( x , y , z ) = x over the first octant of the surface of the sphere of radius 1. Solution: Parametrisation 0 ≤ u ≤ π 2 , 0 ≤ v ≤ π r ( u , v ) = (cos u sin v , sin u sin v , cos v ) , 2 As before | r u × r v | = sin v and thus π π � � (cos u sin v ) sin v d u d v = ... = π 2 2 4 0 0 132 / 159
Recommend
More recommend