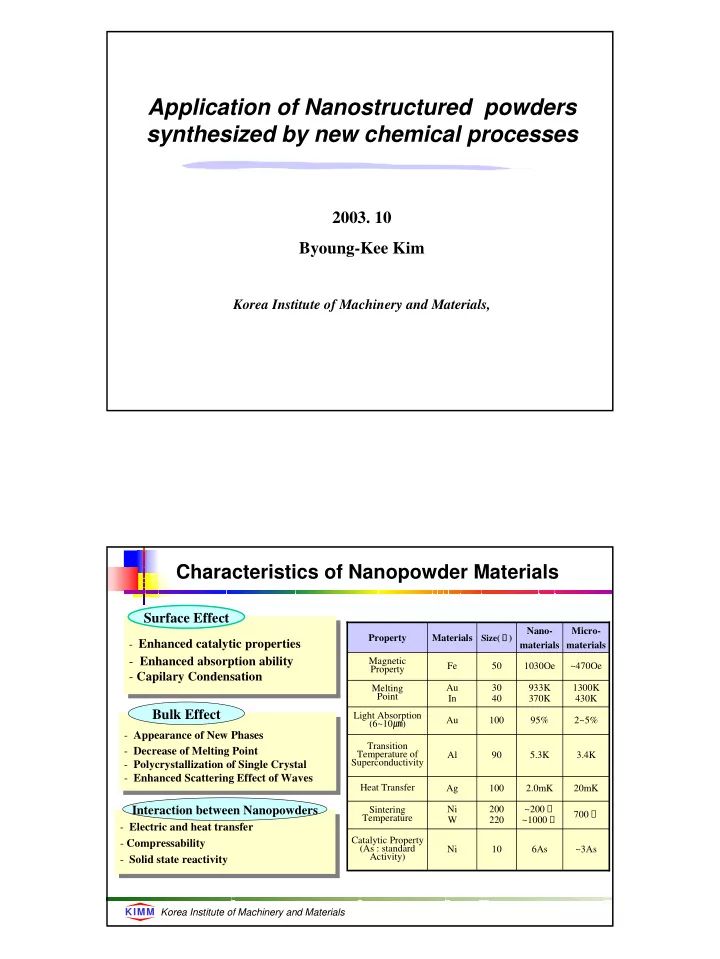

Application of Nanostructured powders synthesized by new chemical processes 2003. 10 Byoung-Kee Kim Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials, Characteristics of Nanopowder Materials Surface Effect Nano- Micro- Size( Å ) Property Materials - Enhanced catalytic properties materials materials - Enhanced catalytic properties - Enhanced absorption ability Magnetic - Enhanced absorption ability Fe 50 1030Oe ~470Oe Property - Capilary Condensation - Capilary Condensation Melting Au 30 933K 1300K Point In 40 370K 430K Bulk Effect Light Absorption (6~10 ㎛ ) Au 100 95% 2~5% - Appearance of New Phases - Appearance of New Phases Transition - Decrease of Melting Point - Decrease of Melting Point Temperature of Al 90 5.3K 3.4K Superconductivity - Polycrystallization of Single Crystal - Polycrystallization of Single Crystal - Enhanced Scattering Effect of Waves - Enhanced Scattering Effect of Waves Heat Transfer Ag 100 2.0mK 20mK ~200 ℃ Interaction between Nanopowders Sintering Ni 200 700 ℃ ~1000 ℃ Temperature W 220 - Electric and heat transfer - Electric and heat transfer Catalytic Property - Compressability - Compressability (As : standard Ni 10 6As ~3As Activity) - Solid state reactivity - Solid state reactivity KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
Application Field of Nanopowder Materials Electronic Electronic Magnetic Magnetic Optical Optical ◆ Advanced tones ◆ Optoelectronic devices ◆ Passive electronic ◆ Diagnostic contrast agents devices ◆ Ferrofluids ◆ IC substrate ◆ Magnetic Recording ◆ Thermistor and varistor ◆ Piezoelectric actuators ◆ Magnetic Refrigerator ◆ CMP ◆ Cutting tool ◆ Catalysts ◆ Die ◆ Chemical sensors ◆ Coating ◆ Energy storage devices ◆ Pigments ◆ Abrasive components ◆ Membranes Structural Others Structural Others KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials Research of Nanopowders in KIMM Area Materials Abrasives, Cutting tools, CMP, Wear-resistant components Tool Materials WC-Co hard materials Ferrofluid, Magnetic refrigerator, Recording media, Magnetic Materials Hard/Soft Magnets, Fe/Co magnetic materials, Nd-Fe-B hard magnet Thermistor, Varistor, Piezoelectric actuator Electric/Electrode Materials Cu-Al 2 O 3 electrode, W-Cu heat sink Chemical/Catalytic Chemical Sensor, Membranes, Filter, TiO 2 photocatalysts Materials KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
Mechanical Properties of WC/Co Mechanical Properties of WC/Co � Chemical compositions(contents of Co) � Chemical compositions(contents of Co) � Particle size of h ard phase(WC) � Particle size of h ard phase(WC) � Homogeneity of WC/Co (mean free path) � Homogeneity of WC/Co (mean free path) � Hardness � Hardness � Compressive Strength � Reduction of WC size � Compressive Strength � Reduction of WC size � TRS Strength � Decrease of mean free path � TRS Strength � Decrease of mean free path � Wear Resistance � Wear Resistance Key for high mechanical properties Key for high mechanical properties � Fabrication of very fine WC � Fabrication of very fine WC � Higher homogeneity of WC and Co phases � Higher homogeneity of WC and Co phases KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials Manufacturing of WC/Co Alloys Manufacturing of WC/Co Alloys Solid Phase Process Liquid Phase Process Gas Phase Process A P T p o w d e r W, C o c h l o r i d e s W, C o me t a l o r g a n i c s C a l c i n a t i o n s E v a p o r a t i o n / S p r a y d r y i n g C a r b u r i z a t i o n Milling(+C) Removal of Chlorides WC , WC - C o Reduction Milling(+C) Reduction/ Milling(+Co) Carburization Reduction/ G.S. < 30nm Carburization Carburization G.S. > 100nm G.S. > 300nm KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
n - WC p o w d e r n - WC p o w d e r WC 1400 He H 2 /CH 4 H 2 /He Temperature( ℃ ) H 2 /CH 4 1200 W 2 C H i g h C H 2 /He 1000 W 2 (C,O) WC L o w C He WC+W 2 C 800 W W 2 C + W WC +W 2 C+ W Total : 600sccm 400 1200 800 sccm 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 Temperature( ℃ ) Concentration of Methane 10nm • l o w p r e s s u r e • l o w p r e s s u r e ( 1 0 a t m) ( 1 0 - 3 a t m) - 3 • s i z e : 5 n m 20nm • s i z e : 5 n m KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials C o a t i n g o f n -WC , C o p o w d e r Oxide coating Co, Fe powder Carbon coating WC powder C o 4nm F e F e o x i d e C o o x i d e 5 n m • C o r e ( me t a l ) / S h e l l ( O x i d e ) • C o r e ( me t a l ) / S h e l l ( O x i d e ) • WC p o w d e r : 4 n m • WC p o w d e r : 4 n m • O x i d e s h e l l: 3 n m) • O x i d e s h e l l: 3 n m) WC(C:10.5%)/CVC Weight Change(%) WC(C:5.78%)/CVC 116 WC-10Co/TCP Taegutech 112 108 104 Co oxidation 100 0 200 400 600 800 1000 o C) Temperature( KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
C o m p a c t a b i l i t y o f n - WC p o w d e r C o m p a c t a b i l i t y o f n - WC p o w d e r 700 600 500 Load(kgf) 400 300 200 10nm-1.0% 10nm-2.0% 100 100nm-1.0% 100nm-2.0% 0 Rearrange 10 9 8 7 6 5 Displacement(mm) of particles Power BET A.D. type size (m 2 /g) (g/cm 3 ) A 20nm 18.4 0.77 C o m p a c t d e s i t y 4 7 % (NRL) 100nm B 2.02 1.85 (granule) C 100nm 3.09 2.2 KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials S i n t e r b i l i t y o f n - WC / C o p o w d e r Solid sintering temp. 890 o C 890 o C 1070 o C 1070 o C 835 o C 835 o C 1010 o C 1010 o C • WC ( 2 0 n m) + C o ( 2 0 n m) : 8 3 5 o C • WC ( 2 0 n m) + C o ( 2 0 n m) : 8 3 5 o C • WC ( 2 0 n m) + C o ( 1 0 0 n m) : 8 9 0 C • WC ( 2 0 n m) + C o ( 1 0 0 n m) : 8 9 0 o C o • WC / C o ( 1 0 0 n m) : 1 0 1 0 C • WC / C o ( 1 0 0 n m) : 1 0 1 0 o C o • WC / C o ( 2 0 0 n m) : 1 0 7 0 o C • WC / C o ( 2 0 0 n m) : 1 0 7 0 o C WC / C o ( 2 0 n m) WC ( 2 0 n m) / C o ( 1 0 0 n m) WC / C o ( 2 0 0 n m ) WC / C o ( 1 0 0 n m ) 20nm → 2 ㎛ 100nm → 1 ㎛ ( x 100) ( x 10) • s i n t e r i n g t e m p : WC s i z e ( 1 0 7 0 →8 3 5 C ) o C o s i z e ( 8 9 0 →8 3 5 C ) G r a i n g r o w t h i n h i b i t o r s o • a b n o r m a l g r a i n g r o w t h ( 1 0 0t i m e s , ) KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
P l a s m a s i n t e r i n g / g r a i n g r o w t h i n h i b i t o r P l a s m a s i n t e r i n g / g r a i n g r o w t h i n h i b i t o r P l a s m a s i n t e r i n g Conventional WC-10Co • H i g h D i s l o c a t i o n D e n s i t y • S t a c k i n g F a u l t s WC - 1 0 C o WC - 1 0 C o f a c e t t e d s h a p e 1 ㎛ ( x 5 0 ) f a c e t t e d s h a p e 1 ㎛ ( x 5 0 ) Nano. WC-10Co WC - 1 0 C o - 0 . 6 V C WC - 1 0 C o - 0 . 6 V C • D i s l o c a t i o n f r e e WC g r a i n s r o u n d , 7 0 n m ( x 4 ) r o u n d , 7 0 n m ( x 4 ) • T w i n s i n WC g r a i n s KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials Properties of Nanostructured WC-Co Alloy 2000 TCP 1800 MCP S u b m i c r o n 1.2E-8 1600 350 2050 1900 1400 Hardness(Hv) >1.0 ㎛ 1650 200 1200 1000 2.1E-9 Nanophase 800 <0.1 ㎛ Submicron(0.6 µ m) 600 Submicron(1.9 µ m) 400 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Sintered Hv TRS Wear rate ( ㎛ ) (kgf/mm 2 ) (kgf/mm 2 ) (mm 3 /m) Temperature( o C) KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
Nano sized Fe and Co Magnetic Materials � Magnetic Fluid : Magnetite(Fe 3 O 4 ) � Saturation Magnetization of Fe = 2 times of that of Fe 3 O 4 Coercivity ; proportional to inverse of particle size (Hc = a+b/D) � Synthesis of nano-sized Fe ⇒ High performance magnetic fluid materials ( Saturation Magnetization : 1500emu/cm 3 , Coercivity : 3000Oe) Development of Fe based nanopowder for magnetic fluids Development of Fe based nanopowder for magnetic fluids by Chemical Vapor Condensation by Chemical Vapor Condensation KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials Microstructures of Fe Nanoparticles Intensity (arb. unit) Co nanoparticles (fcc-type) Fe nanoparticles KIMM (bcc-type) 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 2 θ 5 nm Core Core Crystalline Fe Crystalline Fe Shell Shell Crystalline Fe Crystalline Fe oxides oxides Fe Co KIMM Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials
Recommend
More recommend