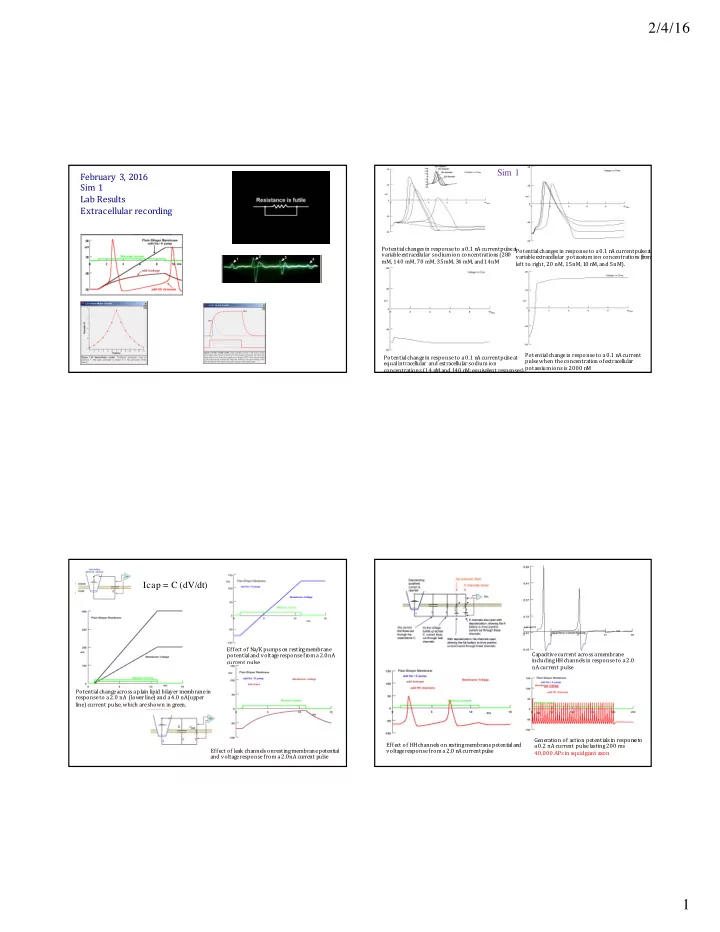

2/4/16 Sim 1 February ¡ 3, ¡2016 Sim 1 Lab ¡Results Extracellular ¡recording Potential ¡changes ¡in ¡response ¡to ¡a ¡0.1 ¡n A ¡current ¡pu lse ¡a t ¡ Potential ¡changes ¡in ¡response ¡to ¡a ¡0.1 ¡n A ¡current ¡pu lse ¡a t ¡ variable ¡extracellular ¡ sodium ¡ion ¡concentration s ¡(28 0 ¡ variable ¡extracellular ¡ potassium ¡ion ¡concentration s ¡( fr om ¡ mM, ¡140 ¡mM, ¡70 ¡mM, ¡35 ¡mM, ¡3 4 ¡mM, ¡and ¡14 ¡nM left ¡to ¡right, ¡20 ¡nM, ¡15 ¡nM, ¡1 0 ¡n M, ¡and ¡5 ¡nM). Potential ¡change ¡in ¡response ¡to ¡a ¡0.1 ¡n A ¡current ¡ Potential ¡change ¡in ¡response ¡to ¡a ¡0.1 ¡n A ¡current ¡pu lse ¡at ¡ pulse ¡when ¡the ¡concentration ¡of ¡extracellular ¡ equal ¡intracellular ¡ and ¡extracellular ¡sodium ¡ion ¡ potassium ¡ions ¡is ¡2000 ¡n M concentrations ¡(14 ¡n M ¡and ¡1 40 ¡n M; ¡equivalent ¡responses) . Icap = C (dV/dt) Effect ¡of ¡Na/K ¡pumps ¡on ¡restin g ¡membrane ¡ potential ¡and ¡voltage ¡response ¡fr om ¡a ¡2.0 ¡nA ¡ Capacitive ¡current ¡across ¡a ¡membrane ¡ including ¡HH ¡channels ¡in ¡response ¡to ¡a ¡2.0 ¡ current ¡pulse nA ¡current ¡pulse Potential ¡change ¡across ¡a ¡plain ¡lipid ¡bilayer ¡membrane ¡in ¡ response ¡to ¡a ¡2.0 ¡nA ¡ ¡(low er ¡line) ¡and ¡a ¡4.0 ¡nA ¡(up per ¡ line) ¡current ¡pulse, ¡which ¡are ¡shown ¡in ¡green. Generation ¡of ¡action ¡potentials ¡in ¡respon s e ¡to ¡ Effect ¡of ¡HH ¡channels ¡on ¡r esting ¡membrane ¡potential ¡an d ¡ a ¡0.2 ¡nA current ¡pulse ¡lasting ¡200 ¡ms Effect ¡of ¡leak ¡channels ¡on ¡resting ¡membrane ¡potential ¡ voltage ¡response ¡from ¡a ¡2.0 ¡n A ¡current ¡pu lse 40,000 ¡APs ¡in ¡squid ¡giant ¡axon and ¡voltage ¡response ¡from ¡a ¡2.0 ¡nA ¡cu rrent ¡p ulse 1
2/4/16 Lab 1 Summary Sim 1 Hodgkin and Huxley Voltage divider Membrane Model What’s different in signal shape? Space constant Changes in R input reflect changes in R m Neurons: Calculation of R input experimentally 0.01- 1mm from a neuron?? V= IR in R in = V/I 2
2/4/16 Time constant Material basis of thinking RC circuit Synaptic Integration Cm = 1 µF/cm 2 Neurons: 1 - 20 ms 200 ms in very large cells Extracellular recording example: Lobster stomach motor pattern Extracellular Recording Extracellular recording example: Lobster chemoreceptor response 3
2/4/16 Traveling action potential Extracellular Field Potentials AP current field Attenuation of signal Making “sense” of extracellular Extracellular AP shapes- monophasic AP shapes Extracellular AP shapes- biphasic 4
2/4/16 Extracellular AP shapes- complex Extracellular AP shapes- complex Picture credit: Joannalyn Data from Gigi and Marek Summary: Recording geometry too complicated Many resistive pathways for current to flow to give mechanistic information Different recording geometries produce different extracellular AP shapes Complex extracellular AP shapes due to multiple current pathways in saline 5
2/4/16 Membrane AP to amplifier output Increase signal strength: Incr ease voltage difference between le ads How do we apply Ohm’s law? resting potential Axon Hook electrode V = IR Extracellular fluid Suction electrode Also patch clamp Pin electrodes insulated with vasoline Amplifier 6
Recommend
More recommend