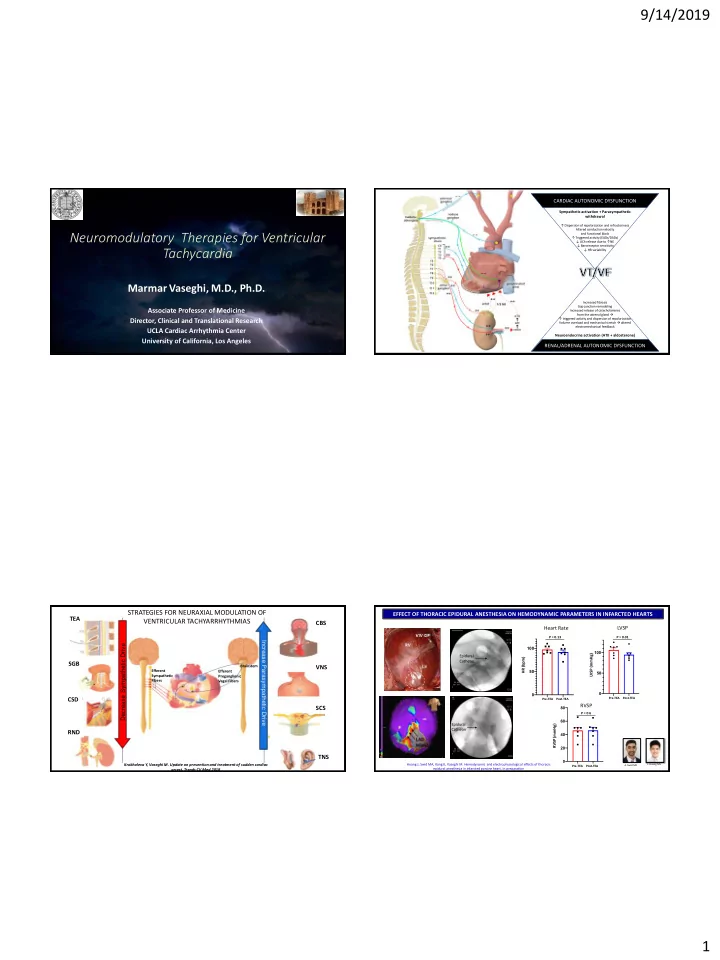

9/14/2019 S CARDIAC AUTONOMIC DYSFUNCTION BERKELEY • DAVIS • IRVINE • LOS ANGELES • RIVERSIDE • SAN DIEGO • SAN FRANCISCO SANTA BARBARA • SANTA CRUZ Sympathetic activation + Parasympathetic withdrawal ↑ Dispersion of repolarization and refractoriness Altered conduction velocity Neuromodulatory Therapies for Ventricular and functional block ↑ Triggered activity (EADs/DADs) ↓ ACh release due to ↑ NE ↓ Baroreceptor sensitivity Tachycardia ↓ HR variability Marmar Vaseghi, M.D., Ph.D. Increased fibrosis Gap junction remodeling Associate Professor of Medicine Increased release of catecholamines from the adrenal gland à ↑ triggered activity and dispersion of repolarization Director, Clinical and Translational Research Volume overload and mechanical stretch à altered electromechanical feedback UCLA Cardiac Arrhythmia Center Neuroendocrine activation (ATII + aldosterone) University of California, Los Angeles RENAL/ADRENAL AUTONOMIC DYSFUNCTION RENAL/SUPRARENAL AUTONOMIC DYSREGULATION STRATEGIES FOR NEURAXIAL MODULATION OF EFFECT OF THORACIC EPIDURAL ANESTHESIA ON HEMODYNAMIC PARAMETERS IN INFARCTED HEARTS TEA VENTRICULAR TACHYARRHYTHMIAS CBS CBS LVSP Heart Rate P = 0.13 P = 0.01 Increase Parasympathetic Drive Decrease Sympathetic Drive 100 100 LVSP (mmHg) Epidural HR (bpm) Catheter SGB Brainstem VNS Efferent 50 Efferent 50 Sympathetic Preganglionic Fibers Vagal Fibers 0 0 CSD Pre-TEA Post-TEA Pre-TEA Post-TEA RVSP SCS 80 P = 0.6 60 Epidural RVSP (mmHg) Catheter RND 40 20 TNS 0 Krokhaleva Y, Vaseghi M. Update on prevention and treatment of sudden cardiac Hoang J, Swid MA, Kang K, Vaseghi M. Hemodynamic and electrophysiological effects of thoracic A. Swid MD J. Hoang MS Pre-TEA Post-TEA arrest. Trends CV Med 2018 epidural anesthesia in infarcted porcine heart. In preparation 1
9/14/2019 EFFECT OF THORACIC EPIDURAL ANESTHESIA ON BARORECEPTOR SENSITIVITY EFFECT OF THORACIC EPIDURAL ANESTHESIA ON ELECTROPYSIOLOGICAL PARAMTERS IN INFARCTED HEARTS AH Interval HV Interval Ba Baror orece ceptor or Sensit nsitiv ivit ity Incr crease ses 55 200 P = 0.49 P = 0.001 Post-TE TEA With h Phenyelp lphe herin ine 50 150 AH (msec) HV (msec) Epidural Epidural 45 P = 0.015 Catheter Catheter 100 40 50 35 BRS (ms/mmHg) 0 30 Pre-TEA Post-TEA Pre-TEA Post-TEA AERP VERP P = 0.006 P = 0.001 300 280 260 Epidural Epidural AERP (msec) VERP (msec) 225 Catheter Catheter 240 150 220 Pre-TEA Post-TEA 200 75 J. Hoang MS A. Swid MD Pre-TEA Post-TEA Pre-TEA Post-TEA Hoang J, Swid MA, Kang K, Vaseghi M. Hemodynamic and electrophysiological effects on thoracic Hoang J, Swid MA, Kang K, Vaseghi M. Hemodynamic and electrophysiological effects of thoracic epidural anesthesia in infarcted porcine heart. In @drive CL 450 msec epidural anesthesia in infarcted porcine heart. In preparation preparation ACUTE MANGEMENT OF VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA STORM-THORACIC EPIDURAL ANESTHESIA EFFICACY OF STELLATE GANGLION BLOCKADE IN MANAGING ELECTRICAL STORM Impact of stellate ganglion block on ventricular arrhythmia episodes and defibrillator shocks. Approaches� to� anesthetic�use� for� stellate�ganglion�block.� Anesthetic�Agent Number�of� patients Dose� Volume (Concentration,�%) (ml) Bupivacaine 16 0.25-0.5 9� ± 5.6 Ropivacaine 11 0.2 6� ± 5.7 Lidocaine 9 1-4 8� ± 3.8 Patient factors for which TEA could be considered Mepivacaine 2 2 4� ± 0.0 Incessant VT despite 2+ antiarrhythmic agents Continued VT storm despite initial ablation attempt Type� of� administration�of� anesthetics Number�of� patients LV EF and type of cardiomyopathy does not Decrease in VT burden to deep sedation Bolus� injections 28 influence efficacy Hypotension limiting deep sedation Continuous�infusion 9 Long wait time anticipated before definitive therapy Both� bolus�injections�and� continuous� 1 Absolute Contraindications infusion Active infection Dual antiplatelet therapy Requirement for uninterrupted therapeutic anticoagulation Utility�of� imaging� guidance Number�of� patients Landmark� only�without�imaging 13 Relative Contraindications Ultrasound 21 Acute myocardial infarction Fluoroscopy 4 Active major non-cardiac medical or surgical process Do DH, Bradfield J, Ajijola O, Vaseghi M, Le J, Rahman S, Mahajan A, Nogami A, Boyle NG, Shivkumar K. Thoracic Epidural Anesthesia can be Effective for the Acute Management of Ventricular Tachycardia Storm. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2017 10.1161/JAHA.117.007080 Meng L, Tseng CH, Shivkumar K, Ajijola OA. Efficacy of Stellate Ganglion Blockade in Managing Electrical Storm JACC Electrophys 2017 Duc Do MD 2
9/14/2019 International Cardiac Sympathetic Denervation Collaborative Study ICSDC-International Cardiac Sympathetic Denervation Collaborative Group BILATERAL CARDIAC SYMPATHECTOMY IS EFFECTIVE FOR VT CONTROL 75% had VT Storm, Mean EF 30%, 92% were on A PatientCharacteristics N = 121 MCG & Stellate Complex N=121 BB+1AAD, 59% on >2 AADs 1.0 n = 121 patient Age (y) 55 ± 13 -Free� � Transplant-Free� Female 26% Transplant� 0.8 NYHA Class 2.4 ± 0.8 LVEF 30 ± 12% Survival� ICM 27% 0.6 Shock-Free� Shock-Free� #ICD shocks (median, IQR) 10 (5,18) Polymorphic VT 38% 0.4 25 P < 0.01 >1 VT Morphology 63% VT/ICD� VT/ICD� VT Storm 75% Number of ICD Shocks 0.2 20 Hypertension 56% Hyperlipidemia 44% 15 0.0 0 � � � � � � 2 � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 6� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 8� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 12� � � � � � Afib 25% Follow� Up� (months)� CKD 27% 10 No.� at� � Risk� � � 121 � � � � � 79� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 67� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 57� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 55� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 49� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 44� DMII 19% 58% ICD Shock Free, Transplant Free 5 Beta-blockers 92% Survival at One year >1 AAD 49% 0 Left Only 19% Pre-CSD Post-CSD Vaseghi M, Barwad P , Malavassi F, Tandri H, Mathria N, Sáenz L, Lokhandwala Y, Shivkumar K. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017 Vaseghi M, Barwad P, Malavassi F, Tandri H, Mathria N, Sáenz L, Lokhandwala Y, Shivkumar K. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017 Procedural Complications of Cardiac Sympathetic Denervation: ICSDC Study 50 yo female with non-ischemic cardiomyopathy, EF 40% and three different monomorphic ventricular tachycardias, s/p endocardial ablation at an outside hospital, s/p epicardial and endocardial ablation Procedural Complications Total (N=121) 3 months ago, has recurrence of ICD shock for monomorphic VT. Do Hemothorax 3 (2.4%) you…. Pneumothorax 6 (5%) Ptosis – mild 5 (4%)- resolved in 4 (A) Refer for repeat epi/endo ablation patient by 6 months Vasopressor support – ≥24 16 (13%) (B) Refer for cardiac sympathetic denervation hours post-procedure (C) Refer for heart transplantation Incisional Cellulitis 2 (1.6%) Nausea/vomiting 1(0.8%) (D) Refer for renal denervation UTI 1 (0.8%) Multi-focal pneumonia 1 (0.8%) Vaseghi M, Barwad P, Malavassi F, Tandri H, Mathria N, Sáenz L, Lokhandwala Y, Shivkumar K. Outcomes after cardiac sympathetic denervation for refractory ventricular arrhythmias: an international collaborative study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2017 3
Recommend
More recommend