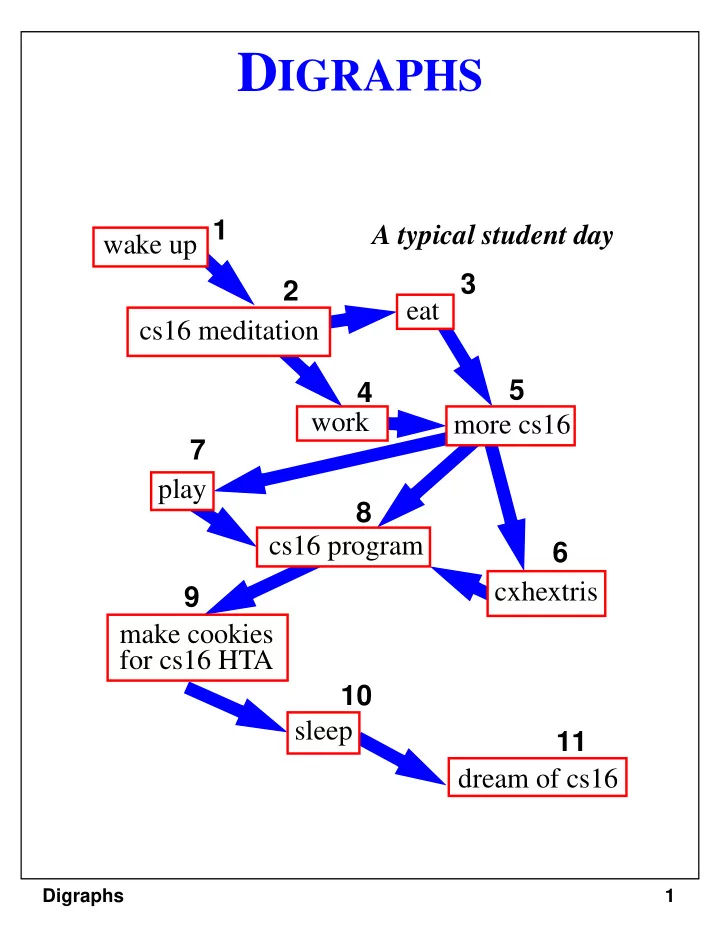

D IGRAPHS 1 A typical student day wake up 3 2 eat cs16 meditation 5 4 work more cs16 7 play 8 cs16 program 6 cxhextris 9 make cookies for cs16 HTA 10 sleep 11 dream of cs16 Digraphs 1
What’s a Digraph? a) A small burrowing animal with long sharp teeth and a unquenchable lust for the blood of computer science majors b) A distressed graph c) A directed graph Each edge goes in one direction Edge (a,b) goes from a to b , but not b to a a b You’re saying, “Yo, how about an example of how we might be enlightened by the use of digraphs!!” − Well, if you insist. . . Digraphs 2
Applications Maps: digraphs handle one-way streets (especially helpful in Providence) Tunnel O’ Doom D’Angelo’s! Bookstore Thayer Store 24 Waterman Angell SciLi Thomas J. Watson Jr. Center for Information 143 Technology Brook ME! Digraphs 3
Another Application Scheduling: edge (a,b) means task a must be completed before b can be started cs15 cs16 cs22 cs126 cs127 cs141 cs32 cs167 cs31 Old programmers never die - they just fall into black holes Digraphs 4
DAG’s dag: (noun) dÂ-g 1. D i- A cyl- G lycerol − My favorite snack! 2.“man’s best friend” person’s 3. directed acyclic graph Say What?! directed graph with no directed cycles a b a b c c e d e d DAG not a DAG Digraphs 5
Depth-First Search Same algorithm as for undirected graphs On a connected digraph, may yield unconnected DFS trees (i.e., a DFS forest) a b c f e d a e b d f c Digraphs 6
Reachability DFS tree rooted at v : vertices reachable from v via directed paths a b c f e d e c f b a c a b d d Digraphs 7
Strongly Connected Digraphs Each vertex can reach all other vertices a g c d e f b Digraphs 8
Strongly Connected Components a g c d e f b { a , c , g } { f , d , e , b } Digraphs 9
Transitive Closure Digraph G * is obtained from G using the rule: If there is a directed path in G from a to b , then add the edge (a,b) to G * G * G Digraphs 10
Computing the Transitive Closure We can perform DFS starting at each vertex Time: O ( n ( n + m )) Alternatively ... Floyd-Warshall Algorithm: If there’s a way to get from a to b , and from b to c , then there’s a way to get from a to c Digraphs 11
Example v 7 BOS v 4 ORD JFK v 2 v 6 SFO DFW LAX v 3 v 1 MIA v 5 v 7 BOS v 4 ORD JFK v 2 v 6 SFO DFW LAX v 3 v 1 MIA v 5 Digraphs 12
Floyd-Warshall Algorithm • this algorithms assumes that methods areAdjacent and insertDirectedEdge take O(1) time (e.g., adjacency matrix structure) Algorithm FloydWarshall( G ) let v 1 ... v n be an arbitrary ordering of the vertices G 0 = G for k = 1 to n do // consider all possible routing vertices v k G k = G k-1 for each (i, j = 1, ..., n) (i ! = j) (i, j ! = k) do // for each pair of vertices v i and v j if G k-1 .areAdjacent (v i ,v k ) and G k-1 .areAdjacent (v k ,v j ) then G k .insertDirectedEdge (v i ,v j ,null) return G 0 • digraph G k is the subdigraph of the transitive closure of G induced by paths with intermediate vertices in the set { v 1 , ..., v k } • running time: O(n 3 ) Digraphs 13
Example • digraph G v 7 BOS v 4 ORD JFK v 2 v 6 SFO DFW LAX v 3 v 1 MIA v 5 Digraphs 14
Example • digraph G* v 7 BOS v 4 ORD JFK v 2 v 6 SFO DFW LAX v 3 v 1 MIA v 5 Digraphs 15
Topological Sorting For each edge ( u,v ), vertex u is visited before vertex v 1 A typical student day wake up 3 2 eat cs16 meditation 5 4 work more cs16 7 play 8 cs16 program 6 cxhextris 9 make cookies for cs16 HTA 10 sleep 11 dream of cs16 Digraphs 16
Topological Sorting Topological sorting may not be unique A A B C D or B C A C B D D − You make the call! Digraphs 17
Topological Sorting Labels are increasing along a directed path A digraph has a topological sorting if and only if it is acyclic (i.e., a dag) 1 A 2 3 B C 5 4 E D Digraphs 18
Algorithm for Topological Sorting method TopologicalSort if there are more vertices let v be a source; // a vertex w/o incoming edges label and remove v ; TopologicalSort ; A B C E D Digraphs 19
Algorithm (continued) Simulate deletion of sources using indegree counters TopSort(Vertex v); label v; foreach edge(v,w) indeg(w) = indeg(w) − 1; if indeg(w) = 0 TopSort(w); 1. Compute indeg( v ) for all vertices 2. Foreach vertex v do if v not labeled and indeg( v ) = 0 then TopSort( v ) Digraphs 20
Example ? 0 ? 0 A B ? 1 C D ? 3 ? 2 E F ? 1 G ? 2 H ? 1 I ? 3 Digraphs 21
Reverse Topological Sorting RevTopSort(Vertex v) mark v; foreach edge(v,w) if v not marked RevTopSort(w); label v; A B C E D Digraphs 22
Recommend
More recommend