Stellar Evolution: Low Mass Stars Mass 2-3 M sun But what about - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Stellar Evolution: Low Mass Stars Mass 2-3 M sun But what about High Mass Stars and all of those other elements??? GRAVITY When core T=10 8 K, He fuses into C (& O) What happens when the Helium runs out?? PRESSURE Answer
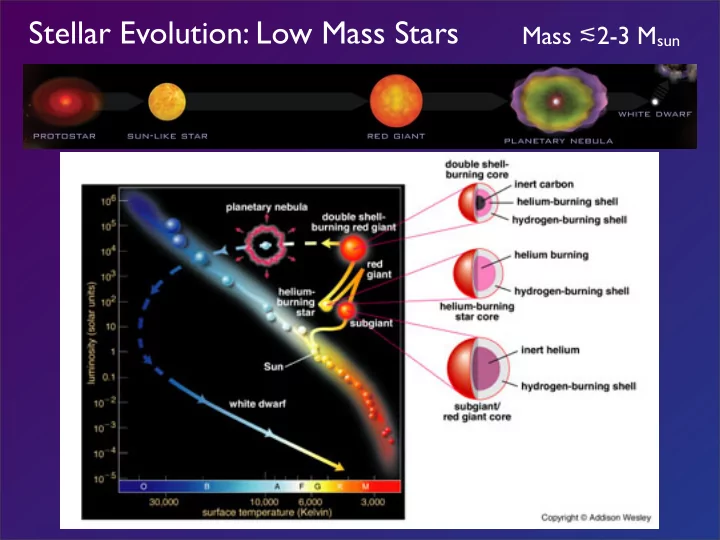
Stellar Evolution: Low Mass Stars Mass ≲ 2-3 M sun
• But what about High Mass Stars and all of those other elements???
GRAVITY • When core T=10 8 K, He fuses into C (& O) • What happens when the Helium runs out?? PRESSURE Answer Depends on MASS!
GRAVITY • When core T=10 8 K, He fuses into C (& O) • Sun: 100 million yrs • Intermediate/High Mass: 100,000 yrs! PRESSURE
GRAVITY • Int/High Mass Stars: Battle continues... • T ~600 mil. K, C --> O/Ne/Mg • 1,000 yrs PRESSURE
GRAVITY • High Mass Stars: Battle continues... • T ~1.5 Billion K! Ne fusion • a few yrs! PRESSURE
GRAVITY • High Mass Stars: Battle continues... • O (1 year!) • Si (1 day!!!) PRESSURE
Iron - The Nuclear Turnip • Requires energy to fuse heavier than Iron
Iron - The Nuclear Turnip • Gravity takes over, outer layers collapse into iron core and....
Iron - The Nuclear Turnip BOOM!! • Supernova explosion creates more elements and sends them into space!
• But what about High Mass Stars and all of those other elements???
Supernovae - Fun Facts How frequent? 3/100 years in MW How long? t collapse < 1 second! SN Energy in seconds = Solar output over 1 Billion years!
Will the Sun ever become a Supernova? ?? BOOM?
Stellar Evolution: Low Mass vs. High Mass Stars Mass ≲ 2-3 M sun THE ENTIRE EVOLUTION OF A STAR IS DETERMINED BY ITS MASS Mass > 3 M sun
Stellar Evolution: Low Mass vs. High Mass Stars Where do elements heavier than Fe come from?
All elements heavier than IRON were created in in Supernova Explosions!
Galactic Recycling SN provide raw materials for new generations of stars!!
SOUPernovae (mmmm) Early Universe: 75% H, 25% He Local Universe: 70% H, 28% He, 2% Heavy Elements Supernovae enrich the interstellar medium... ISM: 70%H, 28% He, 2% heavy
How Does SF Happen? Recall: SF happens in Giant Molecular Clouds ...collapse GMCs... to form stars
How Does SF Happen? What causes the clouds to start collapsing? ??
Triggered Star Formation #1 - Supernova Shocks
Triggered Star Formation - Supernova Shocks Density Enhancements
Triggered Star Formation #2 - Winds from Massive Stars NGC 1999 W5
Triggered Star Formation - Winds from Massive Stars Lagoon Nebula Cavity Excavation
Other Possibilities Plain Old Gravity (example: Bok Globule ) Galaxy Collisions (MICE!) Starbursts @ Galactic Center
Formation of Stars: Sets the Stage for Planets! Protostar + Disk Cloud Protostar Star! (T Tauri Star)
Formation of Stars! 0. Cold Cloud of Gas & Dust T~30K 1. SN/wind triggers collapse (rotation) density increases, T increases 2. Protostar forms (more rotation) density increases , T ~3000K Protostar emits in infrared
Formation of Stars! 0. Cold Cloud of Gas & Dust T~30K 1. SN triggers collapse (rotation) T increases 2. Protostar forms (more rotation) T ~3000K 3/4. Protostellar Disk forms T ~3000-1 Million K density increases star accretes material from disk T Tauri Stars Star + Disk emits in infrared
T Tauri Stars - Accretion Disks Protostar accretes material from disk
T Tauri Stars - Protostars with Disks
T Tauri Stars - Disks, Jets & Winds Star Formation is Active! (jets move 100-1000 km/s)
T Tauri Stars: Protostars w/Disks, Jets, Winds WHY? Allow rotational energy to escape! (conserve angular momentum)
Current Model of Star Formation 0. Cold Cloud of Gas & Dust 1. SN triggers collapse (rotation) 2. Protostar forms (more rotation) 3. Protostellar Disk forms - TTauri Star 4. T reaches 10 Million K - STAR!!
Current Model of Star Formation 5. T reaches 10 Million K - STAR!! (e.g. Vega) What happens to the disk?? Stellar Leftovers - DEBRIS DISK Seeds for Planet Formation!!
How Do Planets Form Out of Debris Disks?? ACCRETION! Disks contain DUST Dust ACCRETES
How Do Planets Form Out of Debris Disks?? ACCRETION! Slow moving particles collide and stick together
Forming Planets Out of Debris Disks Dust Begins to Accrete forms PLANETESIMALS Planetesimals Collide Small Bodies Break up...
Forming Planets Out of Debris Disks Planetesimals grow to form protoplanets... Protoplanets collide to form Planets! Leftovers are Asteroids, Comets, Meteoroids, & Dwarf Planets... ...fossil records of SS Formation!
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.