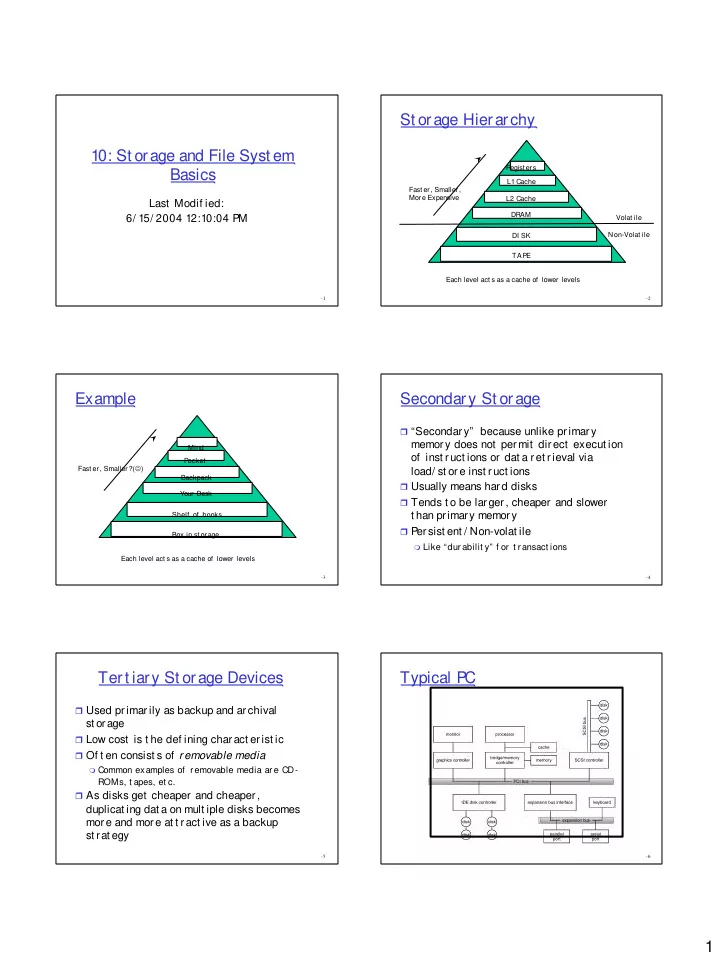

St orage Hierarchy 10: St orage and File Syst em Regist ers Basics L1 Cache Fast er, Smaller, More Expensive L2 Cache Last Modif ied: DRAM 6/ 15/ 2004 12:10:04 PM Volat ile Non-Volat ile DI SK TAPE Each level act s as a cache of lower levels -1 -2 Example Secondary St orage � “Secondary” because unlike primary memory does not permit direct execut ion Mind of inst ruct ions or dat a ret rieval via Pocket Fast er, Smaller?( ☺ ) load/ st ore inst ruct ions Backpack � Usually means hard disks Your Desk � Tends t o be larger, cheaper and slower t han primary memory Shelf of books � Persist ent / Non-volat ile Box in st or age � Like “dur abilit y” f or t r ansact ions Each level act s as a cache of lower levels -3 -4 Tert iary St orage Devices Typical P C � Used pr imar ily as backup and ar chival st orage � Low cost is t he def ining charact erist ic � Of t en consist s of r emovable media � Common examples of r emovable media ar e CD- ROMs, t apes, et c. � As disks get cheaper and cheaper, duplicat ing dat a on mult iple disks becomes more and more at t ract ive as a backup st rat egy -5 -6 1
Disk Basics Terms � Track = one r ing ar ound t he sur f ace of one � Disk drives cont ain met allic plat t ers of t he plat t ers spinning around a cent ral spindle � Sect or = one piece of a t r ack (usually 512 � Read/ writ e head assembly is mount ed on an byt es); More sect ors in out er t racks arm t hat moves across t he surf ace of t he � Cylinder = all t racks at t he same dist ance plat t ers f rom t he cent er of t he plat t ers (I .e. all Tr ack t racks readable wit hout moving t he disk arm) -7 -8 Disk Addressing Disk Format t ing � Ear ly disks wer e addr essed wit h cylinder # , sur f ace # and sect or # � Low-level f or mat t ing involves dividing t he � Today disks hide inf or mat ion about t heir geomet r y magnet ic media int o sect or s � Disks export a logical array of blocks � Each sect or act ually consist s of a header, dat a and a � Disk it self maps f rom logical block address (LBA) t o t railer cylinder/ surf ace/ sect or � Header and t railer cont ain inf ormat ion like sect or � Allows disk t o remap bad sect ors (when f ormat t ed disk number and error correct ing codes (ECC) reserves some sect ors t o use as replacement s) � ECC is addit ional redundant bit s t hat can of t en correct � Allows disk t o hide t he non- unif ormit y of t he st orage f or bit errors in t he st ored value • Mor e dat a on out er t r acks, et c. � OS also f ormat s drive � Disks also have int er nal caches so t hat not all � 1 st divides int o part it ions – each part it ion can be t reat ed r equest s go t o t he media as a logically separat e drive � On reads t ake advant age of mult iple accesses t o t he same t rack � 2cd f ile syst em f ormat t ing of part it ions (more on t hat lat er) � On writ es, say writ e is “done” when it is memory inside t he disk -9 -10 Disk I nt erf aces RAI D � I nt er f ace t o t he disk � Expose an array of sect ors but � Request specif ied wit h LBA and lengt h implement ed as mult iple physical disks � Request placed on bus, lat er reply placed on bus � Arrangement and relat ionship of disks � Device dr iver hide t hese det ails � P rovide abst ract ion of synchronous disk read � RAI D levels � OS use t he disk t o pr ovide ser vices � Virt ual memory � OS expor t s higher level abst r act ions � File syst ems � Some applicat ions use t he device dr iver int er f ace t o build abst r act ions of t heir own (get t heir own par t it ion) � Dat abase syst ems -11 -12 2
Avoiding Seek and Rot at ional Disk P erf ormance Delay � Divide t he t ime f or an access int o st ages � To t ake advant age of higher t r ansf er r at e, OS must t r ansf er lar ger and lar ger chunks of dat a at � Seek t ime – t ime t o move t he disk arm t o t he correct cylinder a t ime and avoid seek and r ot at ional delay • How f ast can mechanical arm move? I mproves some wit h � Size and placement of virt ual memory pages? smaller disks but not much � Size and placement of FS blocks? � Rot at ional delay – t ime wait ing f or t he correct sect or t o � OS t r ies t o avoid seek and r ot at ional delay by rot at e under t he read/ writ e head placing t hings on disk t oget her t hat will be • How f ast can spindle t ur n? RP Ms go up but slowly accessed t oget her � Transf er t ime – once head is over t he right spot how long t o t ransf er all t he dat a � Can also avoid seek and r ot at ional delay by queuing • Larger f or larger t ransf ers up mult iple disk r equest s and ser vicing t hem in an • Rat e det ermined by RP Ms and by densit y of t he bit s on t he order t hat minimizes head movement (disk disk (densit y going up ver y quickly!) scheduling) � Get t ing good per f or mance f r om a dr ive (seeing � Like wit h CP U scheduling, t here are many disk scheduling impact of a “f ast er ” dr ive” means avoiding seek algorit hms and r ot at ional delay) -13 -14 First Come First Serve Short est Seek Time First (FCFS) (SSTJ ) � Select s t he request wit h t he minimum seek I llust rat ion shows t ot al head movement of 640 cylinders t ime f rom t he current head posit ion. � SSTF scheduling is a f or m of SJ F scheduling; may cause st arvat ion of some request s. -15 -16 SSTF SCAN I llust rat ion shows t ot al head movement of 236 cylinders � The disk arm st art s at one end of t he disk, and moves t oward t he ot her end, servicing request s unt il it get s t o t he ot her end of t he disk, where t he head movement is reversed and servicing cont inues. � Somet imes called t he elevat or scheduling -17 -18 3
SCAN (Cont .) C-SCAN I llust rat ion shows t ot al head movement of 208 cylinders � P rovides a more unif orm wait t ime t han SCAN (wit h scan t hose in middle wait less) � The head moves f rom one end of t he disk t o t he ot her. servicing request s as it goes. When it reaches t he ot her end, however, it immediat ely ret urns t o t he beginning of t he disk, wit hout servicing any request s on t he ret urn t rip. � Treat s t he cylinders as a circular list t hat wraps around f rom t he last cylinder t o t he f irst one. -19 -20 C-SCAN (Cont .) C-LOOK I llust rat ion shows t ot al head movement of 382 cylinders � Version of C-SCAN � Arm only goes as f ar as t he last request in each direct ion, t hen reverses direct ion immediat ely, wit hout f irst going all t he way t o t he end of t he disk. Misleading because seek t ime not a linear f unct ion of number of cylinder s -21 -22 Select ing a Disk-Scheduling C-LOOK (Cont .) Algorit hm I llust rat ion shows t ot al head movement of 322 cylinders � SSTF is common and has a nat ur al appeal � St arvat ion not observed t o be a problem in pract ice � SCAN and C -SCAN perf orm bet t er f or syst ems t hat place a heavy load on t he disk. � Per f or mance depends on t he number and t ypes of request s. � Request s f or disk ser vice can be inf luenced by t he f ile-allocat ion met hod. � Eit her SSTF or C -LOOK is a r easonable choice f or t he def ault algorit hm. -23 -24 4
Tracking Technology Trends Drive Specs (6/ 2004) � Exact comparison bet ween t echnologies changes all t he t ime � How much slower is disk t han main memor y? � Var iat ion even in disks and var ious memor y t echnologies � Tracking t hese t hings t akes a f air amount of wor k -25 -26 Memory Types and P rices More det ails! (6/ 2004) -27 -28 Pr ice per Megabyt e of DRAM, Two random point s (2002) From 1981 t o 2000 � Memor y: 128 MB, PC 133, SDRAM, $ 45 � $0.35/ MB � ~8 nanosecond access t ime � Disk: 20 GB, Ult r a ATA/ 100, $ 109 � $0.005/ MB (1/ 2 penny per MB!!) � 9.5 ms average seek (what is average? Seek t ime increases wit h number of t racks moved but not linearly) � 4.16 ms average lat ency (1/ 2 rot at ion at 7200 RPM?) � 100 MB/ sec burst t ransf er (25- 41 MB/ sec sust ained t ransf er) � Disk/ Memor y Rat ios � P rice: 1/ 70 � Size: 160/ 1 � Speed (Access t ime): 13 ms/ 8ns = 1625000/ 1 � Speed (Transf er rat e): 40 MB/ s / 1.1 GB/ s = 1/ 30 -29 -30 5
Recommend
More recommend