Skin Cancer, S Sunscreen, a and T Tips for Su Success i in M - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Skin Cancer, S Sunscreen, a and T Tips for Su Success i in M Managing Com ommon Ra Rashes i in Y our Clinic Brittney Schultz, M D Assistant Professor of Dermatology University of M innesota August 18, 2019 Objec ectives es
Skin Cancer, S Sunscreen, a and T Tips for Su Success i in M Managing Com ommon Ra Rashes i in Y our Clinic Brittney Schultz, M D Assistant Professor of Dermatology University of M innesota August 18, 2019
Objec ectives es • Identify common skin cancers and choose appropriate biopsy techniques for diagnosis • Discuss proper use of sunscreen and evaluate recent sunscreen controversies in the media • Diagnose common rashes in clinic and determine appropriate treatment
Discl closures • No financial disclosures • No off-label use of medications
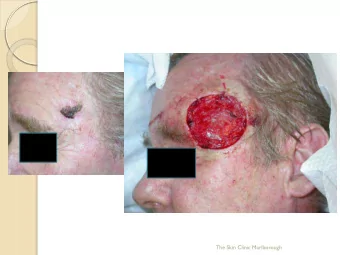
Skin C Cancer: r: It’s a a problem! Basal cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma M elanoma Image source: VisualDx.com
Skin C Cancer r in M Minnesota Source: M innesota Department of Health
Skin C Cancer r in M Minnesota Source: M innesota Department of Health
Clues t to Skin C Cancer S ymptoms Size M atter!
Clues t to Skin C Cancer: r: B Basal cell c carcinoma • Painful • Growing • Bleeding • Shiny • Ulcerated • Prominent vessels • Scaly red patches • Scar-like • Can have pigment! Image source: VisualDx.com
Clues es to Skin Cancer er: S Squamous c cel ell carcinoma • Painful • Growing • Bleeding • Pink bumps • Red patches • Scaly • Can develop quickly Image source: VisualDx.com
Clues t to Skin C Cancer: r: M Melanoma • Painful • Growing • Bleeding • Changing • “ Ugly ducking” • ABCDEs • Can be amelanotic Image source: VisualDx.com
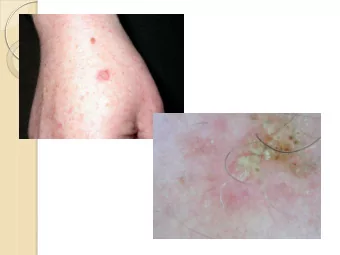
Mimick ckers o s of S Ski kin Cance ancer Seborrheic keratosis Dermal nevus Eczema Image source: VisualDx.com
He Heigh ghten en S Suspicion on • Transplant patient • Immunosuppressed • Azathioprine • Voriconazole • HIV patient • Tanning bed use • Family history of melanoma • History of radiation/ burns/chronic inflammation https:/ /commons.wikimedia.org/ w/ index.php?curid=34547559
Diagnosis of Skin Cancer Biopsy!
When t to Punch, When t to Shave…
Ho How you ou wou ould biop opsy t this l lesion on? Image source: VisualDx.com
Ho How you ou wou ould biop opsy t this l lesion on? Image source: VisualDx.com
Ho How you ou wou ould biop opsy t this l lesion on? Image source: VisualDx.com
Biopsy: B Basal and Squamous Cell C Carcinoma • Shave most commonly • Punch from center of lesion may employed also have advantages • Quicker • M ay better define the growth pattern • Less expensive • E.g. micronodular, morpheaform, or • No suture closure infiltrative features may only be • Can result in surrounding present in deeper portions erythema that creates an • Could change treatment indistinct border and may result in larger than necessary excision/ treatment • Portion is adequate but ensure adequate depth J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Jan;74(1):1-16; quiz 17-8.
Biopsy: M Melanoma • Complete excision recommended • Can be performed via saucerization for macular lesions using 0.5-2 mm margins • Partial biopsy associated with inaccurate diagnosis and staging • Concern for tumor colonization of a deep punch biopsy but no evidence this worsens prognosis J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Jan;74(1):1-16; quiz 17-8.
Biopsy: Le Lenti tigo Malig ligna • Size of lesion may preclude complete excision • Broad thin shave biopsy or multiple small shave biopsies recommended Image source: VisualDx.com J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Jan;74(1):1-16; quiz 17-8.
Sunscreen
Sunscreen B Basics • Sun gives off UVA and UVB (and UVC) • UVA � aging, passes through windows • UVB � sunburn, does not pass through windows • SPF = Sun Protection Factor 5 min No sunscreen SPF = M inimal erythema dose (protected) M inimal erythema dose (unprotected) SPF 5 min x SPF 30 = 150 min 30
Sunscreen B Basics • Chemical blockers (organic) • Physical blockers (inorganic) • Oxybenzone • Titanium dioxide • Avobenzone • Zinc oxide Not all • Octisalate protect • Ensulizole against both UVA/ UVB UVA/ UVB • Octocrylene UVA/ UVB • Octinoxate Absorb UVA + UVB � Scatter/ deflect UVA/ UVB photochemical reaction to render ineffective
Daylight = sunlight! Sunscreen B Basics • Use broad-spectrum (UVA and • Better yet… UVB) • Sun protective clothing • Avoid peak hours of sun (10 am to • SPF 30 or higher 2 pm) • Waterproof • Caution with water, snow, sand • Apply 15 minutes before going outside • Re-apply every 2 hours or after sweating/swimming • M ost adults need 1 ounce to cover entire body
“Does sunscreen even work rk?”
“Does sunscreen even work rk?” • Reduce UV exposure/sunburn? Y es. • Reduce skin cancer? A little more complicated. • UV exposure definitively associated with skin cancer • Some studies demonstrate reduction of skin cancer with sunscreen use and some do not, but overall quality of evidence has been poor • Bottom line: Probably yes but challenging to definitively prove Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Jul 25;7:CD011161. J AM A Dermatol. 2018 Sep 1;154(9):1001-1009. J Clin Oncol. 2011 Jan 20;29(3):257-63.
“I n need to get a a base t tan”
“I n need to get a a base t tan” • Not true – every UV exposure is damaging your skin • “ Base tan” provides SPF 3 • Reduces sun protection measures on vacation 5 min No sunscreen 5 min x 3= 15 min • Bottom line: No you don’t J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005 Dec;53(6):1038-44.
“My vi vitamin D D is already low”
“My vi vitamin D D is already low” • Sources of vitamin D: diet and sun exposure (UVB) • “ Exposure of 5% of uncovered body surface 2x/ week in summer may be equivalent to intake of 430 IU of vitamin D daily; however, for a given surface area, a plateau is reached after 20 minutes” • 8 oz glass of milk: 100 IU • 3.5 oz salmon: 360 IU • Vitamin D supplements do not carry risk of skin cancer and photoaging • Bottom line: Supplement J J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005 M ay;52(5):868-76.
“Su “Sunsc screens s are d e damagin ing c cor oral r l ree eefs”
“Su “Sunsc screens s are d e damagin ing c cor oral r l ree eefs” • Organic (chemical) UV filters have been identified in water worldwide • Oxybenzone #1 • Highest percutaneous absorption and identified in human urine, serum, and breast milk • Others: octocrylene, octinoxate, 4-methylbenzylidene camphor (4-M BC) • Also found in cosmetics, shampoos, fragrances, flavors • Difficult to remove from water supply • Hormonal effects have been reported, including antiandrogen and both proestrogen and antiestrogen effects, but significance in humans unclear J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jan;80(1):266-271.
“Su “Sunsc screens s are d e damagin ing c cor oral r l ree eefs” • In vitro, a species of green algae was exposed to varying levels of oxybenzone • Lowest levels ~similar to environment (0.01-0.1 parts per billion) • Highest up to 5000 parts per billion • Higher concentrations of oxybenzone � decrease chlorophyll content and growth • High concentrations of oxybenzone in fish species � decreased egg production and fewer hatchings • High concentrations of zinc oxide nanoparticles in vitro � bleaching (not seen with titanium dioxide) Sci Total Environ. 2018 Oct 1;637-638:1279-1285. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2019 Jan;80(1):266-271.
Oxybenzone Octinoxate
“Su “Sunsc screens s are d e damagin ing c cor oral r l ree eefs” Bottom line: • There is concerning data regarding chemical sunscreens and nanoparticles , however, these were in vitro studies with much higher concentrations that currently found in the water supply • Additional studies are needed • In meantime – safest thing to do is use physical sunscreens without nanoparticles and continue using sun-protective clothing, seeking shade, etc.
“Sunscreen een gets in you our blood oodstrea eam”
“Sunscreen een gets in you our blood oodstrea eam” J AM A. 2019 M ay 6. Epub ahead of print.
“Sunscreen een gets in you our blood oodstrea eam” • 24 participants • Randomized to 1 of 4 sunscreens: spray 1, spray 2, lotion, and cream • 2 mg of sunscreen per 1 cm 2 was applied to 75% BSA 4 times daily for 4 days • 30 blood samples collected over 7 days • Not exposed to direct sunlight during this time period • Primary outcome = maximum plasma concentration of avobenzone • Secondary outcomes = maximum plasma concentrations of oxybenzone, octocrylene, and ecamsule • Particularly interested in 0.5 ng/ mL threshold (established by FDA for potentially waiving nonclinical toxicology studies for sunscreens) J AM A. 2019 M ay 6. Epub ahead of print.
J AM A. 2019 M ay 6. Epub ahead of print.
J AM A. 2019 M ay 6. Epub ahead of print.
“Sunscreen een gets in you our blood oodstrea eam” • Y es but… • What does it mean? • What are the health effects of this? • Were this realistic conditions? J AM A. 2019 M ay 6. Epub ahead of print.
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.