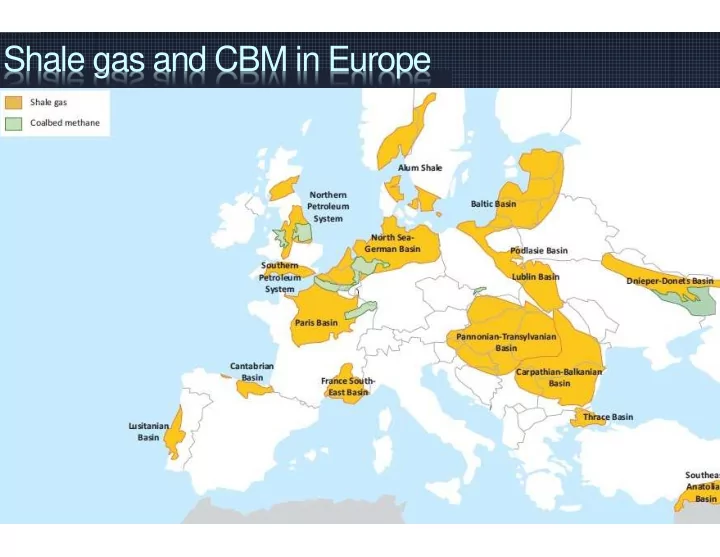
Shale gas and CBM in Europe Shale-shocked Europe and shale gas The - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Shale gas and CBM in Europe Shale-shocked Europe and shale gas The Economist, Feb 2nd 2013 Renewable capacity additions Renewables Gain Share United States Europe Asia Pacific Percent of TWh Percent of TWh Percent of TWh 45 45 45
Shale gas and CBM in Europe
Shale-shocked
Europe and shale gas The Economist, Feb 2nd 2013
Renewable capacity additions
Renewables Gain Share United States Europe Asia Pacific Percent of TWh Percent of TWh Percent of TWh 45 45 45 Solar 40 40 40 Geothermal Biomass/Other 35 35 35 Wind Hydro 30 30 30 25 25 25 20 20 20 15 15 15 10 10 10 5 5 5 0 0 0 '10 '20 '30 '40 '10 '20 '30 '40 '10 '20 '30 '40 *Biomass includes Municipal Solid Waste ExxonMobil 2013 Outlook for Energy
The Solar Wild Card
Nuclear part of the mix
Spot natural gas prices across global markets Spot natural gas prices vary significantly acr global markets since 2008, with many marke � Global spot natural gas, crude oil, and LNG prices � U.S. dollars per million British thermal unit far below oil-related benchmarks 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 U.S. - Henry Hub Japan - LNG France - PEG Canada - AECO Germany - BEB Hub � Source: Derived from Bloomberg, L.P. Netherlands - TTF Belgium - Zeebrugge Brent crude oil UK - NBP
The Growing Importance of Atlantic Energy � From the end of the Cold War to the rise of China and the BRICS: the “forgotten” Atlan � Shifting pattern of US oil import dependenc � Traditional: Middle East, Persian Gulf, Saudi Ara � New rivals to Saudi Arabia and the Arab World ( top 10 national suppliers from the Atlantic Basin � Proliferation of suppliers large enough to negati impact security of US oil supply � Increasing specific mass of the Atlantic Ba in the broad global energy system – geopolitical implications: the return of a ne Atlantic?
Geography of Top 10 Oil Sources � Atlantic Basin • Broader Middle East � Canada (1) � Mexico (2) • Saudi Arabia (3) � Nigeria (4) • Iraq (6) � Venezuela (5) • Algeria (7) � Colombia (8) � Angola (9) � Brazil (10) Atlantic sources will grow in the future, while others could slide. Ecuador is 11 th , Congo (Bzza) 14 th , Cameroon 15th
Key results from the 2013 Annual Energy Outlook � Growth in U.S. energy production outstrips consumption growth � Oil production, particularly from tight oil plays, rises sharply over th next decade � Motor gasoline consumption declines, reflecting the introduction of more stringent fuel economy standards, while diesel fuel consumption is moderated by increased natural gas use in heavy- duty vehicles � The United States. is a net exporter of coal and becomes a net exporter of natural gas over the next decade -- for oil, the United States remains a net importer in the Reference case, but sharply reduces or eliminates import dependence by the mid-2030s in “high resource” sensitivity cases. � U.S. energy-related carbon dioxide emissions remain more than five percent below their 2005 level through 2040, reflecting increased efficiency and the shift to a less carbon-intensive fuel mi
U.S. energy use: slow growth - improving energy efficiency and a slow and extended economic recovery 120 U.S. primary energy consumption Shares of total U.S. energy quadrillion Btu History Projections 100 2000 2011 Natural gas 80 28% 24% Renewables (excluding liquid biofuels) 26% Nuclear 60 11% 6% 8% 8% Liquid biofuels 9% 8% 2% 1% Coal 23% 40 19% 20% 20 39% 36% 32% Oil and other liquids 0 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 2030 2035 2040
Multiple factors have US Crude Oil Estimates UP contributed to U.S. crud resource estimate incr U.S. crude oil and lease condensate resources in non-prohibited areas over the years, with tig billion barrels contributing recently 250 Unproved Alaska (1) 222.6 Unproved L48 Offshore (2) Unproved Tight Oil (3) 23.8 200 Unproved Tight Oil (reclassified from onshore) Unproved Other L48 Onshore 48.6 Proved Reserves 150 41.6 100 16.5 67.0 50 25.2 0 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 Year of Annual Energy Outlook (1) The USGS reduced NPR-A resource estimates, which is responsible for the lower AEO2013 Alaska resources. (2) Prior to AEO2009, resources in Pacific, Atlantic, and Eastern GOM OCS were under moratoria and not included. (3) Includes shale oil. Prior to AEO2011, tight oil is included in unproved other lower-48 onshore category. � Source: EIA, Annual Energy Outlook 2013 Early Release
Energy Supply � There are significant resources in the ground � The world is not running out of energy any time soon � A rise in unconventional sources of energy is expected � Geographically more ‘level’ playing field � Towards an Atlantic Energy Basin?
T ECHNOLOGY
Energy Technologies: Examples Primary Energy Sources: Primary Energy Sources: Primary Energy Sources: Primary Energy Sources: End Use Technologies: End Use Technologies: End Use Technologies: End Use Technologies: Extraction & Conversion Technologies: Extraction & Conversion Technologies: Extraction & Conversion Technologies: Extraction & Conversion Technologies: • Light Crude • ICEs • Exploration • Heavy Oil • Adv. Batteries • Deeper water • Tar Sands • Hybridisation • Arctic • Wet gas • Fuel cells • LNG • CBM • Hydrogen storage • Refining • Tight gas • Gas turbines • Differentiated fuels • Nuclear • Building efficiency • Advantaged chemicals • Coal • Urban infrastructure • Gasification • Solar • Systems design • Syngas conversion • Wind • Other efficiency technologies • Power generation • Biomass • Appliances • Photovoltaics • Hydro • Retail technologies • Bio-enzyimatics • Geothermal • H 2 production & distribution • Wave/Tidal • CO 2 capture & storage There are no “silver bullets” There are no “silver bullets” There are no “silver bullets” There are no “silver bullets” But some have a larger calibre than others ! But some have a larger calibre than others ! But some have a larger calibre than others ! But some have a larger calibre than others ! • We have about 30-40 years to deal with these problems so we have to find those technologies which will have the bigges impact at the lowest cost
Necessary Steps for the Technology � We need technically informed, coherent, and stable government policies � educated decision makers and an educated public � For short/mid term technologies, we should avoid winners/losers � a level playing field for all applicable technologies � emissions trading � For long term technologies, we need support for pre-competitive research like fission, PV, biofuels, etc… � Business needs reasonable expectation of carbon price � Universities/labs must recognize and act on importance of energy research (technology and policy) � Need business to get involved in this research in the next several decades since business like it or not is the way to get things done
Summing up � Diversification is happening � Energy mix: Oil, coal and gas likely to remain the most important fuels over the next 20 years; their market shares are likely to roughly equalize, at 25% to 30% each. This would be the first time in histor that the world has not been dominated by one single fuel � Geographical mix: for the first time, a more equitable global spread of energy sources � Incentives and regulations for low-carbon energy � EU key player � US National Renewable Energy Laboratory, part of the US Department of Energy, predicts that 80% o US electricity could be renewable by 2050 � China’s 12th Five Year plan calls for reductions in greenhouse gas (GHG) and other air emissions and increase in the share of non-fossil fuel primary energy consumption � Energy efficiency is starting happening � globally one-third of primary energy demand – roughly 160 quadrillion BTUs – is lost in energy production, transformation, transmission and distribution: great strides being made NOT through socia engineering (self-sacrifice) but through technological innovation (in building, manufacturing, transportation and other sectors – urbanization offers great promise here. � Global energy intensity today is at a 100-year low and the differences across countries ar the smallest since the beginning of the industrial revolution � Over the past 30 years, the world’s proved reserves of oil and natural gas increased 130% (2.5 trillion barrels of oil equivalent) � Nurture positive black swans
N ATIONAL S ECURITY AND E NERGY S ECURITY A D UTCH E XAMPLE – F OR B ETTER AND FOR W ORSE
Towards a balanced capability portfolio…
From the trees… …to the forest
Recommend
More recommend
Explore More Topics
Stay informed with curated content and fresh updates.