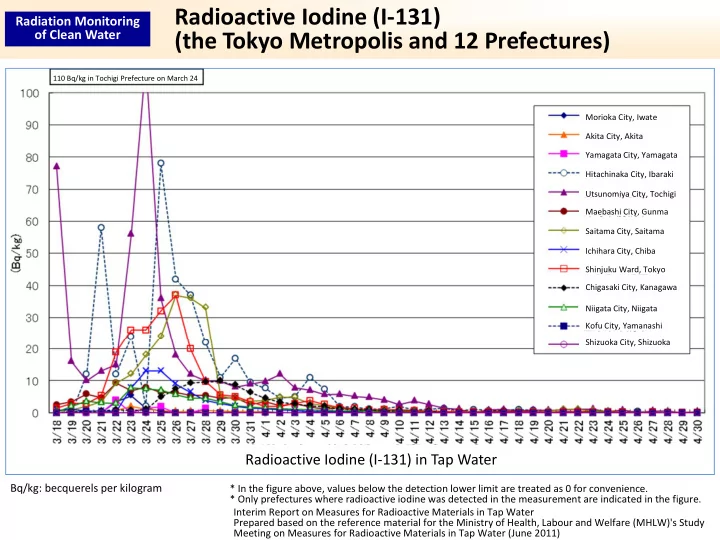

Radioactive Iodine (I‐131) Radiation Monitoring of Clean Water (the Tokyo Metropolis and 12 Prefectures) 110 Bq/kg in Tochigi Prefecture on March 24 Morioka City, Iwate Akita City, Akita Yamagata City, Yamagata Hitachinaka City, Ibaraki Utsunomiya City, Tochigi Maebashi City, Gunma Saitama City, Saitama Ichihara City, Chiba Shinjuku Ward, Tokyo Chigasaki City, Kanagawa Niigata City, Niigata Kofu City, Yamanashi Shizuoka City, Shizuoka ⽔道⽔中の放射性ヨウ素( I-131 ) Radioactive Iodine (I‐131) in Tap Water Bq/kg: becquerels per kilogram * In the figure above, values below the detection lower limit are treated as 0 for convenience. * Only prefectures where radioactive iodine was detected in the measurement are indicated in the figure. Interim Report on Measures for Radioactive Materials in Tap Water Prepared based on the reference material for the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW)'s Study Meeting on Measures for Radioactive Materials in Tap Water (June 2011)
Radioactive Cesium (Cs‐134 + Cs‐137) Radiation Monitoring of Clean Water (the Tokyo Metropolis and 7 Prefectures) 18 Bq/kg in Ibaraki Prefecture on March 21 Morioka City, Iwate Yamagata City, Yamagata Hitachinaka City, Ibaraki Utsunomiya City, Tochigi Maebashi City, Gunma Saitama City, Saitama Ichihara City, Chiba Shinjuku Ward, Tokyo ⽔道⽔中の放射性セシウム( Cs-134 +Cs-137 ) Radioactive Cesium (Cs‐134 + Cs‐137) in Tap Water * In the figure above, values below the detection lower limit are treated as 0 for convenience. Bq/kg:becquerels per kilogram * Only prefectures where radioactive cesium was detected in the measurement are indicated in the figure. * ● is marked on dates when the readings were ND (not detected; below the detection lower limit). Interim Report on Measures for Radioactive Materials in Tap Water Prepared based on the reference material for the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW)'s Study Meeting on Measures for Radioactive Materials in Tap Water (June 2011)
Results of Long‐term Radiation Monitoring of Radiation Monitoring of Tap Water Clean Water 110 100 岩⼿県盛岡市 秋⽥県秋⽥市 Morioka City, Iwate Akita City, Akita 90 ⼭形県⼭形市 茨城県ひたちなか市 Yamagata City, Yamagata Hitachinaka City, Ibaraki 80 栃⽊県宇都宮市 群⾺県前橋市 Utsunomiya City, Tochigi Maebashi City, Gunma 70 (Bq/kg) 埼⽟県さいたま市 千葉県市原市 60 Saitama City, Saitama Ichihara City, Chiba 東京都新宿区 神奈川県茅ヶ崎市 50 Shinjuku Ward, Tokyo Chigasaki City, Kanagawa 40 新潟県新潟市 ⼭梨県甲府市 Niigata City, Niigata Kofu City, Yamanashi 30 静岡県静岡市 Shizuoka City, Shizuoka 20 10 0 3/18 3/25 4/1 4/8 4/15 4/22 4/29 5/6 5/13 5/20 5/27 6/3 6/10 6/17 6/24 7/1 7/8 7/15 7/22 7/29 8/5 8/12 8/19 8/26 9/2 9/9 9/16 9/23 9/30 10/7 10/14 10/21 10/28 11/4 11/11 11/18 11/25 12/2 12/9 12/16 12/23 12/30 1/6 1/13 Radioactive Iodine (I‐131) in Tap Water 20 18 16 岩⼿県盛岡市 ⼭形県⼭形市 Morioka City, Iwate Yamagata City, Yamagata 14 茨城県ひたちなか市 栃⽊県宇都宮市 (Bq/kg) Hitachinaka City, Ibaraki Utsunomiya City, Tochigi 12 群⾺県前橋市 埼⽟県さいたま市 Maebashi City, Gunma Saitama City, Saitama 10 千葉県市原市 東京都新宿区 Shinjuku Ward, Tokyo Ichihara City, Chiba 8 6 4 2 0 3/18 3/25 4/1 4/8 4/15 4/22 4/29 5/6 5/13 5/20 5/27 6/3 6/10 6/17 6/24 7/1 7/8 7/15 7/22 7/29 8/5 8/12 8/19 8/26 9/2 9/9 9/16 9/23 9/30 10/7 10/14 10/21 10/28 11/4 11/11 11/18 11/25 12/2 12/9 12/16 12/23 12/30 1/6 1/13 Radioactive Cesium (Cs‐134 + Cs‐137) in Tap Water Committee on Living Environment and Water Supply in March 2012
Radiation Inspections by Water Suppliers Monitoring of Clean Water Changes in Number of Specimens for Radioactive Cesium Inspection Detection of Radioactive Cesium (Purified Water) (specimens) (Bq/kg) (Note) Number of cases where radioactive cesium Purified Raw 浄⽔ 原⽔ 180 detection was reported water water (specimens) 165 ⽚⽅が >1 、合計が ≦ 10 の検出検体数 Number of specimens with either showing a 8000 value over 1 and the total being 10 or less 160 合計が >10 の検出検体数 Number of specimens with the total being 7176 over 10 6812 6680 6441 6670 6666 6573 6753 7000 最⾼濃度 134Cs+137Cs ( Bq/kg ) 最⾼濃度 Cs-134+Cs-137 ( Bq/kg ) 140 140.5 Maximum concentration (Cs‐134+Cs‐137) 6418 6101 6000 120 5000 100 130 83 4000 80 68.8 3000 60 2603 67 2000 40 29 19 1000 20 35 6.1 3.1 13 3 212 186 168 173 148 165 158 158 119 133 127 16 1.5 0.5 1 1 1 0.4 0 6 6 0 0 Bq/kg: becquerels per kilogram 12th Health Sciences Council's Committee on Living Environment and Water Supply in March 2012
Radiation Clean Water Behavior of Radioactive Cesium Monitoring of Conceptual Diagram of Behavior of Radioactive Cesium Environmental Water Tap water Air water purification (mainly river water) Cs I May cesium iodide, gaseous cesium, etc. Cs Cs be contained? Cs Removal Cs Mote (coagulating Mote sedimentation, filtering) + + Cs Cs Particulate cesium Partial removal (adsorption, coagulating Cesium ion sedimentation, filtering) Cesium may exist in such forms as particulate cesium or Cs+ (cation) in environmental water. Generally, cations are easily adsorbed by + I Iodine Cs Cesium ion adsorptive suspensoids with exchange capacity. Prepared based on the reference material for the 12th Health Sciences Council's Committee on Living Environment and Water Supply in March 2012
Radiation Clean Water Control of Radioactive Cesium Monitoring of Most of the radioactive cesium that reaches sources of tap water is adsorbed into suspensoids such as soil and flows out. Therefore, radioactive cesium can be controlled through strict turbidity management. 浄⽔場における放射性セシウム ( 134 Cs 、 137 Cs) の挙動例 Example of Behavior of Radioactive Cesium (Cs‐134 and Cs‐137) at Water Purification Plant 国立保健医療科学院(投稿中データ) National Institute of Public Health (Kosaka, et al., Journal of Japan Water Works Association, 2014) Radioactive cesium (Bq/L) Cs-137 Cs-134 <0.83 <0.59 <0.76 <0.67 <0.58 <0.47 <0.50 <1.0 <0.58 <0.57 Water after Biological activated Raw water Rapid filtered water sedimentation carbon treated water Zeolite, ion exchangers, nanofiltrationmembranes and reverse osmosis membranes are professionally used for removing radioactive materials, but these cannot be used for ordinary water purification due to high cost, required facilities and inefficiency (in particular, the use of nanofiltrationmembranes and reverse osmosis membranes is power consuming). Bq/L: becquerels per liter 12th Health Sciences Council's Committee on Living Environment and Water Supply in March 2012
Radiation Clean Water Waterworks System Monitoring of Changes in Radioactive Cesium Concentrations at Water 1 Intake tower (raw water) Purification Plants in Fukushima Prefecture as of April 28, 2011 National Institute of Public Health Sampling Sedimentation pond (water after 8 sedimentation) points Distributing reservoir (rapid 12 filtered water) Below quantitation General purification system (rapid filtration) limit Cs-137 <0.58 Approx. 12 Bq/L Cs-134 <0.57 (Cs‐134 + Cs‐137) 5 6 9 7 10 13 4 8 3 11 12 2 1 Below quantitation limit Cs-137 <0.59 Cs-134 <1.0 ① Intake tower ② Sand basin ③ Intake pump ④ Receiving well ⑤ Flocculant injection facility ⑥ Chemical mixing basin ⑦ Floc forming basin ⑧ Sedimentation pond ⑨、⑪ Chlorine injection facility ⑩ Filter basin ⑫ Distributing reservoir ⑬ Water pump Bq/L: becquerels per liter Prepared based on the reference material for the 12th Health Sciences Council's Committee on Living Environment and Water Supply in March 2012
Recommend
More recommend