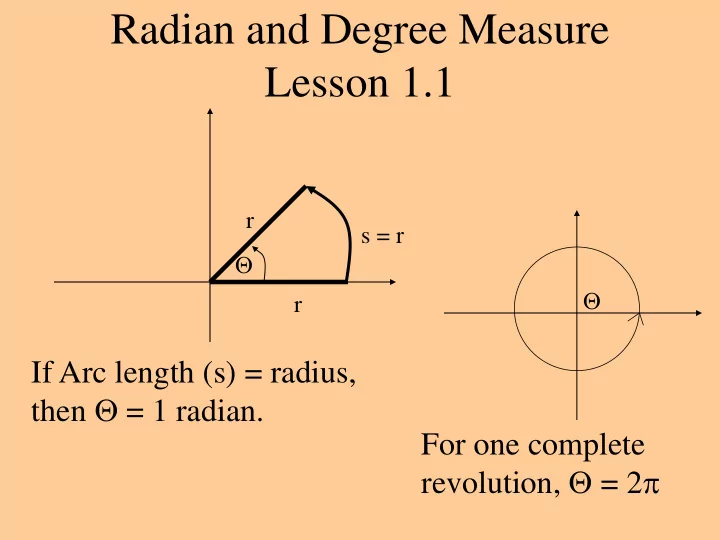

Radian and Degree Measure Lesson 1.1 r s = r r If Arc length (s) = radius, then = 1 radian. For one complete revolution, = 2
/2 1.57 rad Quadrant II Quadrant I 2 1 3 0, 2 6.35 rad 3.14 rad 6 Quadrant III 4 Quadrant IV 5 3 /2 4.72 rad For positive angles
- 3 /2 - 4.72 rad Quadrant II Quadrant I - 5 - 4 - 6 - 0, - 2 - - 3.14 rad -6.35 rad - 3 - 1 Quadrant III Quadrant IV - 2 - /2 - 1.57 rad For negative angles
Ex 1: Estimate the angle to the nearest 1/2 radian. A. C. 2.5 rad - 1 rad B. 3.5 rad
Ex 2: Determine the quadrant in which each angle lies. A. /5 B. 7 /5 0 Quad I Quad III C. - /12 D. - 3.5 Quad II Quad IV
Acute Angles - angles that have a measure 0 < < /2 radians Obtuse Angles - angles that have a measure /2 < < radians
Ex 3: Sketch each angle in standard position. A. 2 /3 B. 5 /4 C. - 7 /4 D. 3
Coterminal - two angles that share the same terminal side. One positive angle Two positive angles + One negative angle
Ex 4: Determine two co-terminal angles (one positive and one negative) for each angle. 2 6 A. 12 + 2 /6 6 6 13 6 12 2 6 6 6 11 6
Ex 4 (cont’d): Determine two co -terminal angles (one positive and one negative) for each angle. B. 5 /6 5 5 2 2 Negative: Positive: 6 6 5 12 5 12 6 6 6 6 7 17 6 6
C. - 2 /3 2 2 6 4 2 Positive: 3 3 3 3 2 6 8 2 Negative: 2 3 3 3 3 25 24 D. /12 2 Positive: 12 12 12 12 24 23 2 Negative: 12 12 12 12
Complementary angles - two angles whose sum is /2 radians Supplementary angles - two angles whose sum is radians Ex 5: Find, if possible, the complement and supplement of each angle A. /3 3 2 x x Compl.: 6 3 2 2 3 6 6 2 Suppl.: 3 3 x x 3 3 3 3
Ex 5 (cont’d): Find, if possible, the complement and supplement of each angle B. 3 /4 3 Complementary angle does not exist. Compl.: 4 2 Suppl.: 3 3 4 3 x 4 x 4 4 4 4
Ex 5 (cont’d): Find, if possible, the complement and supplement of each angle C. 1 D. 2 Compl.: Compl.: Does not x 1 x 1 2 2 2 2 exist . Suppl.: 1 x Suppl.: 2 x x 1 x 2 Homework: p.138 #2-24 even
Recommend
More recommend